
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Overview
Digital signatures and authentication protocols prove identity and message authenticity using public-key cryptography.
Public-Key Authentication
Asymmetric Authentication (Digital Signature)
Use private key (digital signature)
- Bob convinces Alice he knows the private key without telling anyone (even Alice).
Public Key: Generated with digital signature
- Each person can create signatures
- Only 1 person could create signatures with private key
Public-Key Mutual Authentication
Based on public key certificate → links pub. key to ID.
Authentication Protocol
Alice Bob
(sk_a, pk_a) (sk_b, pk_b)
r₂ = 2018 ←———————r₁———————→ 2018
y₁ = Sign_A(pk_B || r₁ || r₂)
——(r₂, y₁)——→
Use pk_A to verify: (is its encrypted with Alice's ID)
Verify_pk_A(pk_B || r₁ || r₂, y₁) = true?
←——————y₂————— If true: y₂ = Sign_sk_B(pk_A || r₂)
Verify_pk_B(pk_A || r₁, y₂)
Security Analysis
Secure? Yes.
IFF (If and only if):
- Signature is secure
- Random challenges are L bits long
Proof of Security
→ Signatures gen’d by Alice/Bob on different ∴ contain random values chosen by Alice/Bob in each session
→ Eve can’t compute new y₁, y₂ (sign. is secure)
→ Old y₁, y₂ can’t be re-used b/c it’s a diff. random value.
RSA Signatures
Key Generation
Pick e: gcd(e,φ(n)) = 1
Find d:
- ed = 1 mod P(n)
- d = e⁻¹ mod P(n)
Public key → (n,e) Private key → d
Signing & Verification
Signature → σ = H(m)ᵈ mod n
Verify → h = σᵉ mod n
Key Difference from Encryption
- Encrypt with e (public key)
- Sign with d! (private key)
Correctness Proof
Euler’s → aᵖ⁽ⁿ⁾ = 1 mod n
- gcd(a,n) = 1
- σ = H(n)ᵈ mod n
Since pq = n, ed ≡ 1 mod P(n) ← Prove this:
σᵉ ≡ H(m)ᵉᵈ ≡ H(m)¹ᵐᵒᵈᵏ⁽ⁿ⁾⁺¹ ≡ H(m)¹ᵏ⁽ⁿ⁾ᵏ⁺¹ ≡ H(m)ᵏᵖ⁽ⁿ⁾ᵏ · H(m) ≡ H(n) mod n
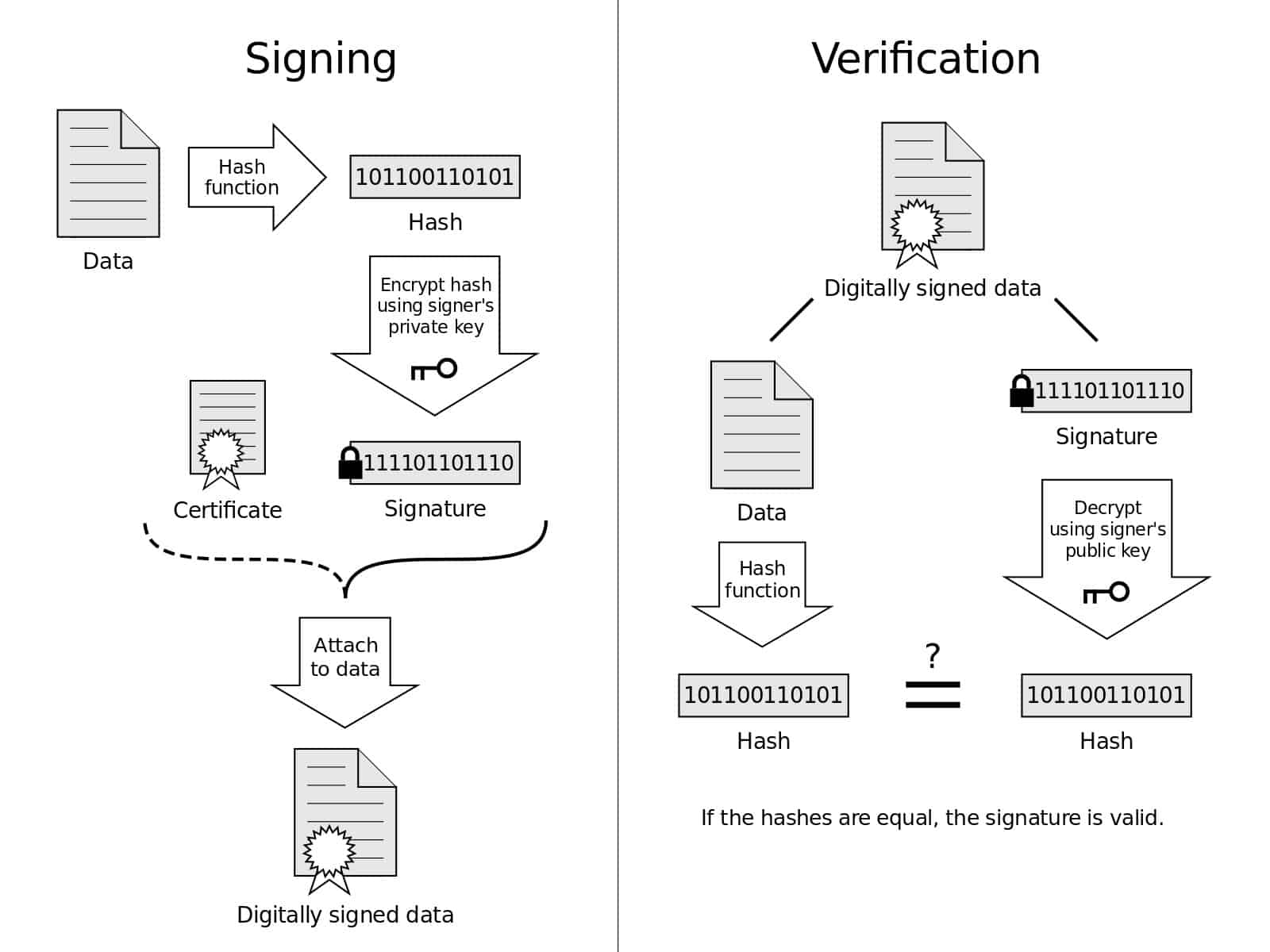
Digital Signature Flow & Properties
Signature Flow
[plaintext] ——signature——→ [verification] ——→ accept or reject
↓ ↑ [plaintext]
[sk] ——→ [signing algo] ——→ [pk] or signer
Signature Characteristics
Signature is unique - need unique private key for unique signature.
Signature is a stream - generated from document + private key - a string of bits attached to a msg.
Validate using document, signature and public key
→ Easy to generate → Easy to verify → Hard to forge
3-Algorithm Syntax
Signature(KeyGen, Sign, Verify)
KeyGen(λ): Randomize key pair (pk,sk) output
Sign(sk, m∈M): Outputs σ
Verify(pk, m, σ): public! pub key, msg, σ
Note: Multiple messages can have same signature - b/c signature is shorter than M (N:1 mapping).
σ - valued signature
DSS & DSA
DSA - 320-bit signature, 160-bit prime
- DSA has smaller signature size + faster computation than RSA.
- Security depends on discrete logarithm difficulty.
Security Properties
Integrity - msg wasn’t modified, b/c of private key
Authenticity - msg is Bob - b/c they’re checking Bob’s public key to make
Non-repudiation - Sender can’t deny their signature.
→ Only owner of private key can generate their signature.
Consistency: For all (pk,sk) by KeyGen: Verify: Verify(pk,m,σ) = accept
Security Goals & Attacks
Goals (from attacker’s perspective)
Total break: Eve determines Alice’s private key - generate valid signature on any msg.
Selective Forgery: Create a valid signature on given m, even m not create msg, signature per for a chosen m.
Existential Forgery: Create a valid signature for at least one msg, create (m,σ) pair where Verify(pk,m,σ) = accept.
Attack Types
Key-Only: Only has public verification key
Known-Message: Attacker has valid signature for variety of messages but didn’t choose which msgs.
Chosen-Message: Attacker can choose msg and learns signature on message at attacker’s choice.
Key Concepts
Authenticity vs Integrity
Authenticity - Is msg mod’d?
Integrity - Was msg sent by right person?
Security Considerations
If key is intercepted - attacker can send msg, and they’ll pass!
Computer Vision
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
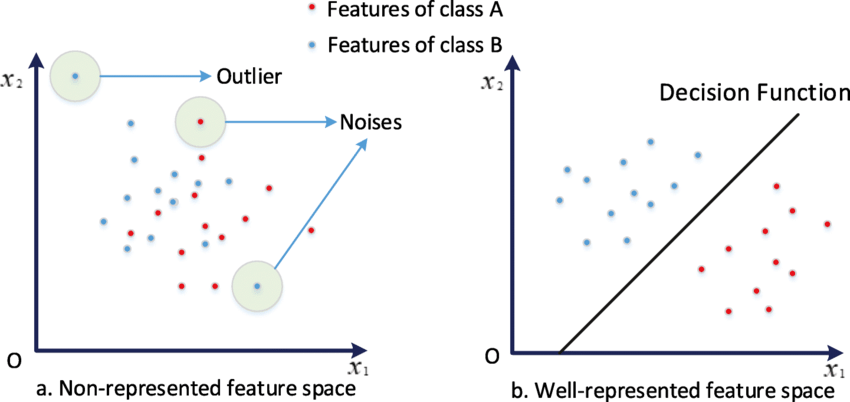
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
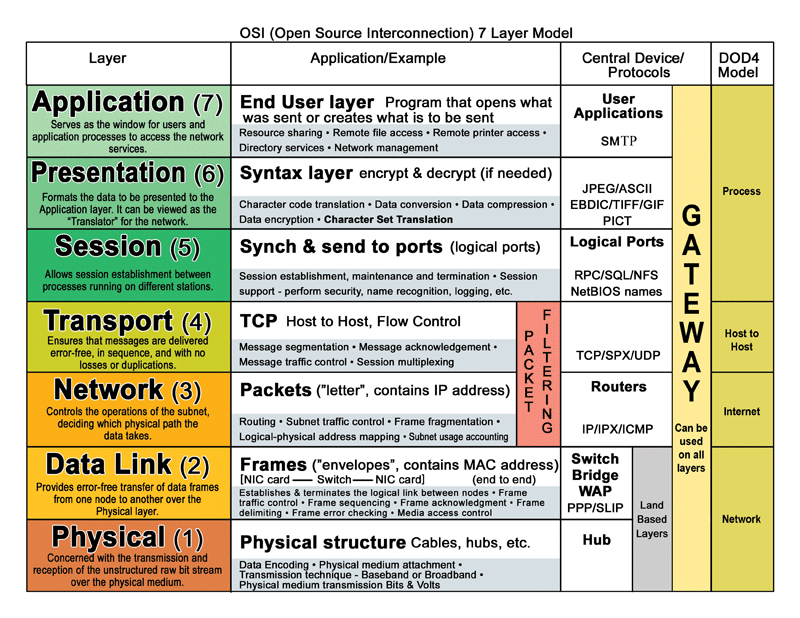
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
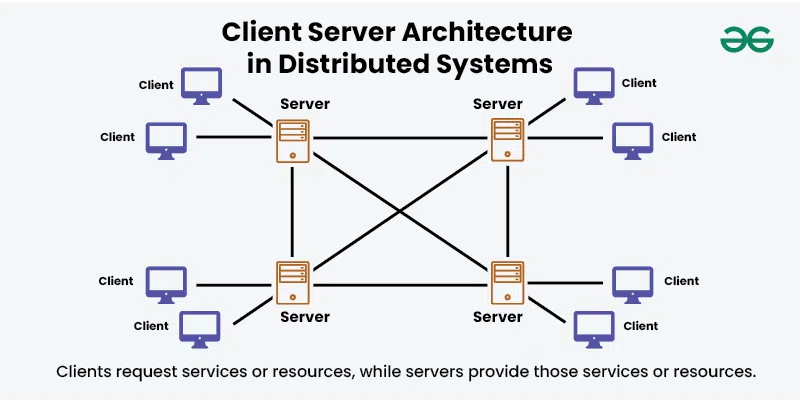
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
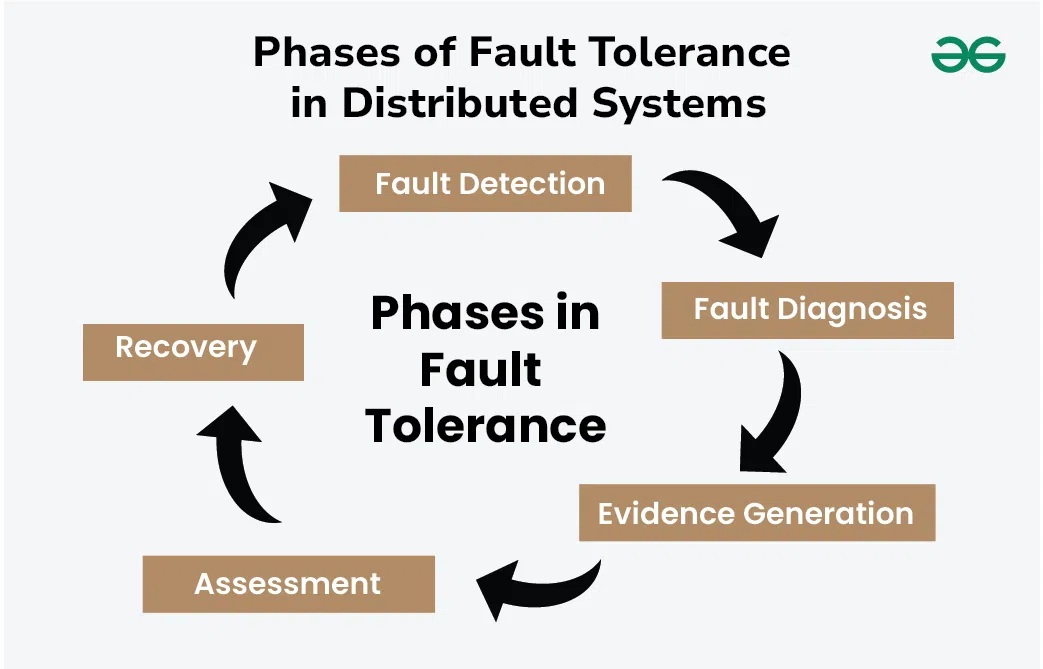
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
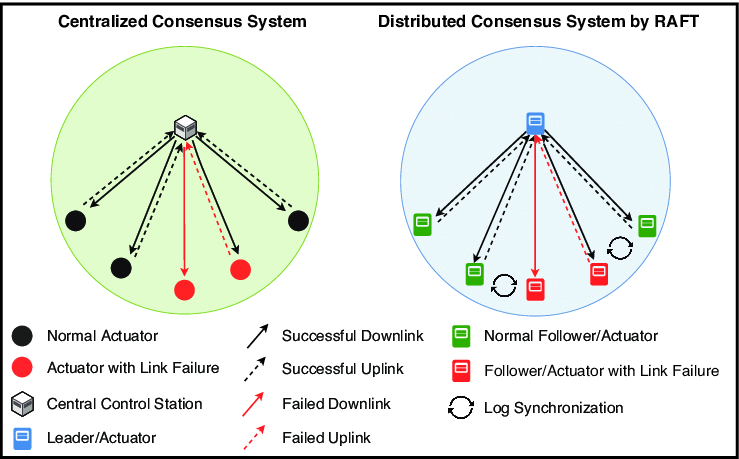
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
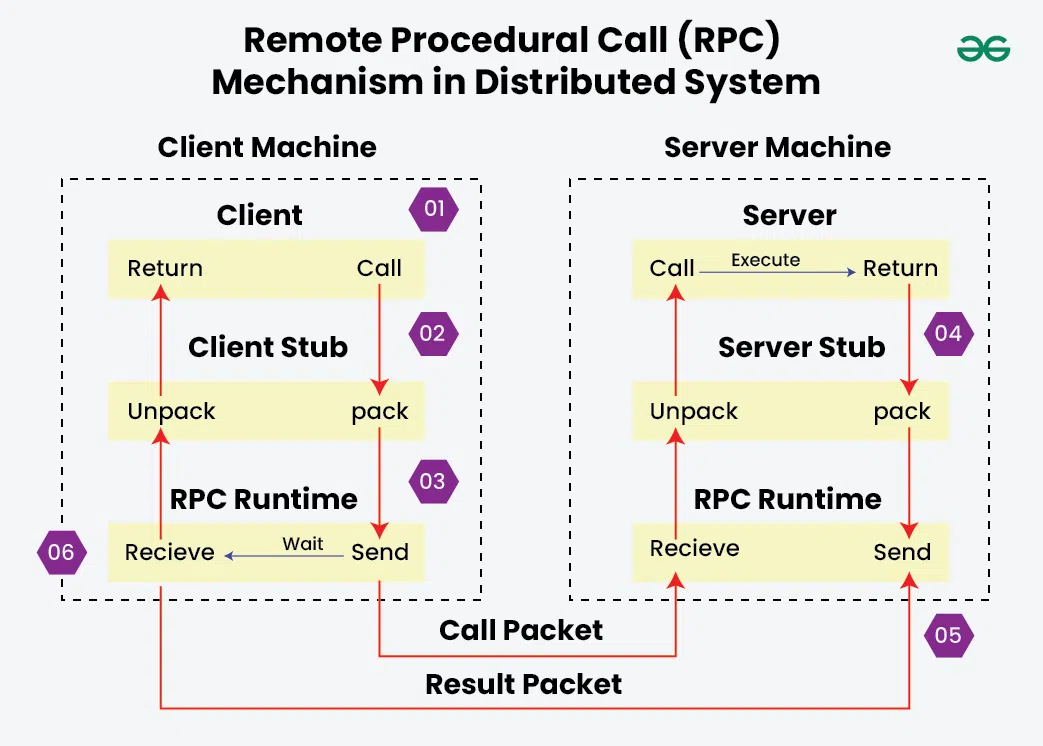
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
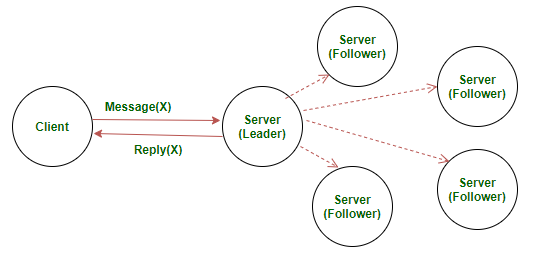
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
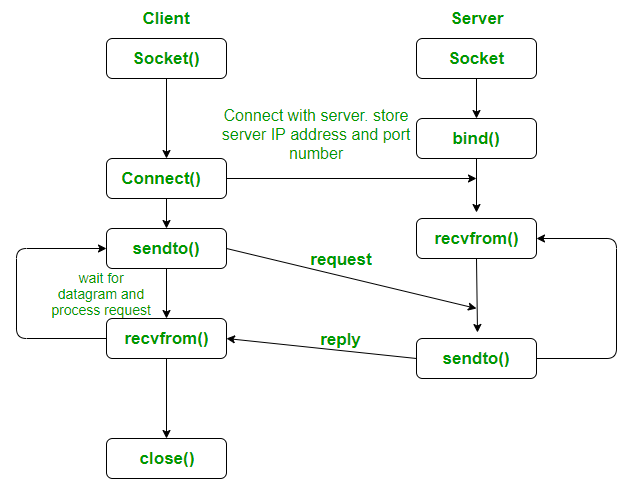
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
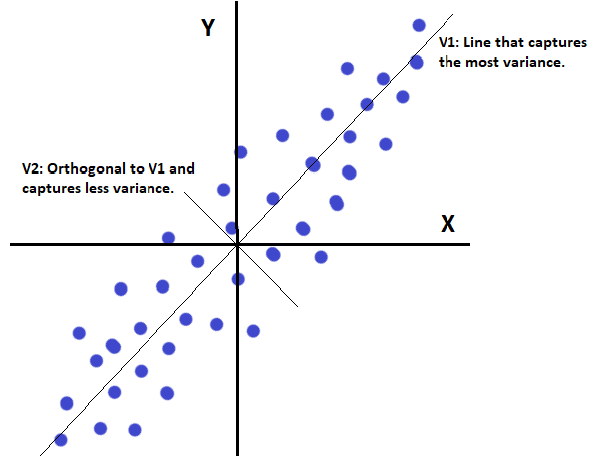
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
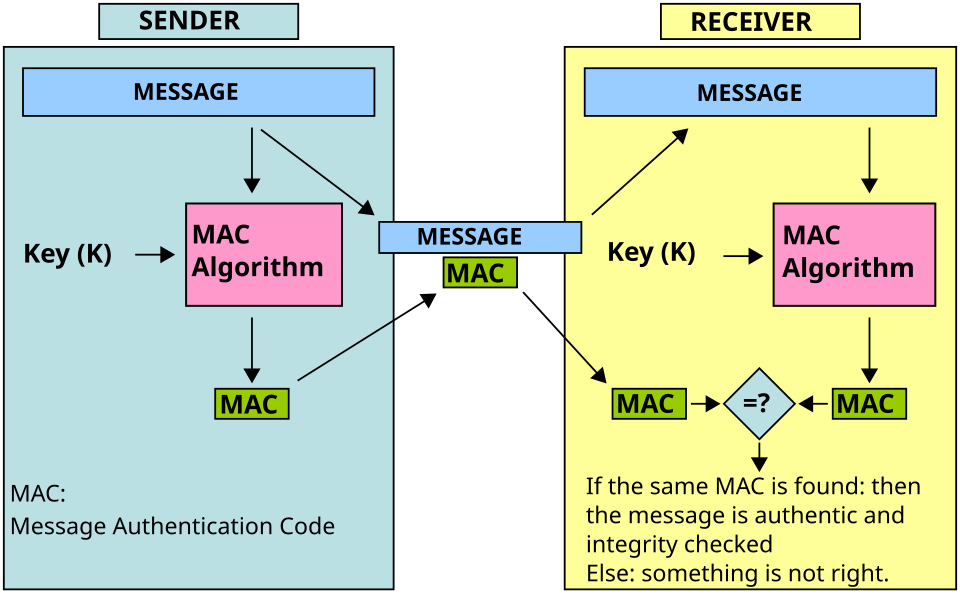
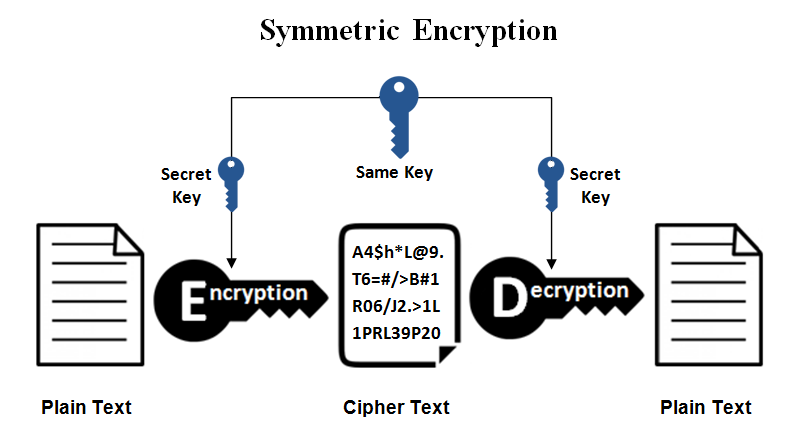
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
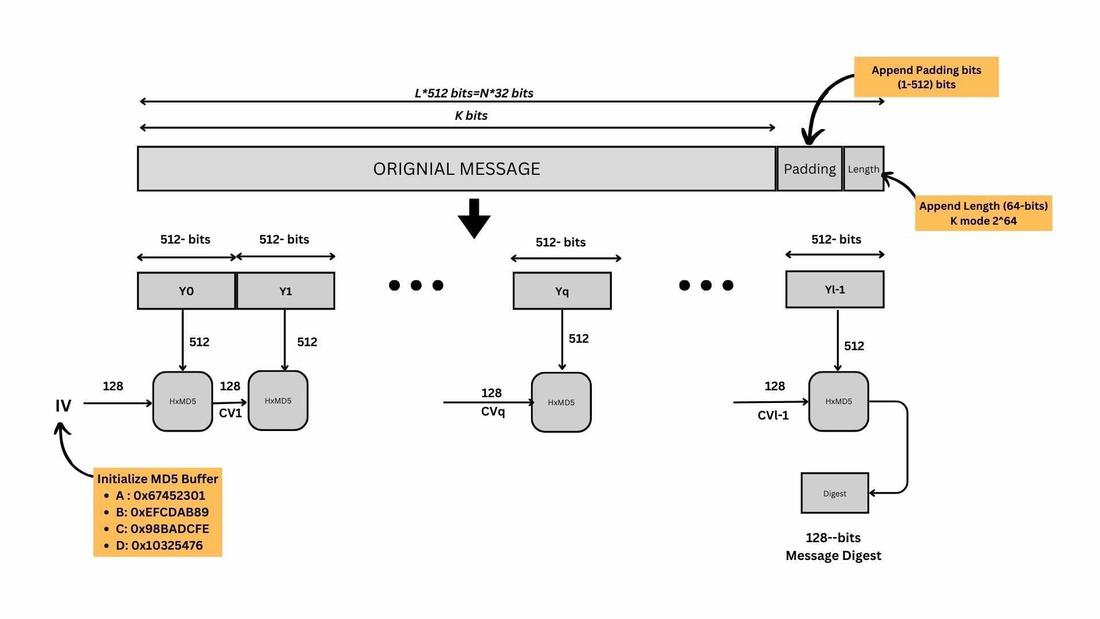
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes

Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
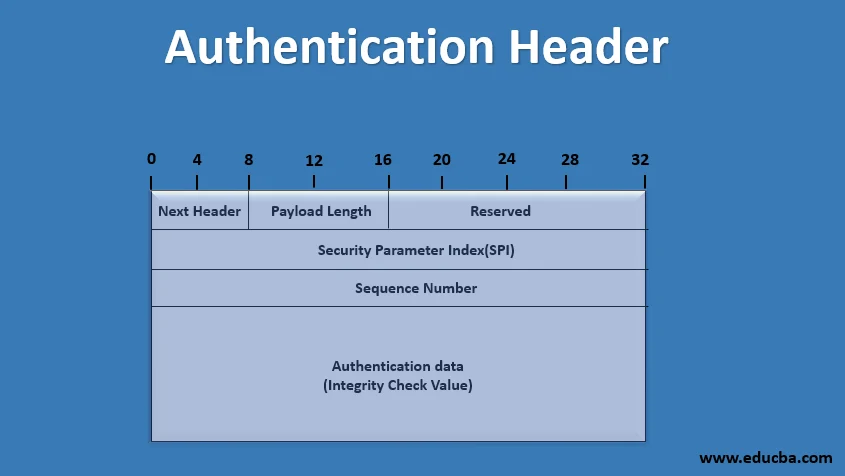
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes