
Hash Functions
Overview
Hash functions map messages of arbitrary size to fixed-size outputs without using any keys.
Basic Properties:
- Map a msg of arbitrary size → fixed size
- No KEY
- Data integrity - check msg to prevent modification during transmission
Function: Hₖ: M → T
- Uses key (k) to map msg to tag with fnc. Hₖ
- Tag is fixed length
Hash Function Properties
Hash Function: H: M → T
Collision Definition
For a hash function H, a pair of messages, m₀, m₁ ∈ M where:
- H(m₀) = H(m₁) but m₀ ≠ m₁
- Any 2 msgs (m₀,m₁) map to the same hash value.
Collision Resistance
Adv_CR[A,H] = Pr[A outputs collision for H] is ’neg’
- The probability of getting a collision is negligible.
Preimage Problem / Strong Collision Resistance
(Infeasible to compute any collision (m,m’))
Definition: For a hash fn H, find m ∈ M s.t. H(m) = y. → this would be bad.
- Should be hard to get an m that gives y, given y.
Given m it is easy to find:
- ✓ H: M → T
Given y (H(m) = y), hard to find m.
- H₄ m → Y H(m)
Preimage Resistance: It is infeasible to find m ∈ M such that H(m) = y
- Given the hash value y, it is infeasible to find m.
Why? - b/c hash fn isn’t 1:1 mapping, multiple inputs map to y
- y → H(m) won’t give right one!
2nd Preimage Problem / Weak Collision Resistance
(Infeasible to compute collision (m,m’) for any m≠m')
Definition: For a hash fn H, and m, a message m ∈ M, find m’ ∈ M, such that m’ ≠ m and H(m’) = H(m)
Given m, it is hard to find another m’ where m ≠ m’ but they have the same hash.
- H(m’) = H(m)
- i.e.: m ≠ m’, m → y₁, y₁ ≠ y₂, m’ → y₂
Second preimage resistance: It is infeasible to find m’ ∈ M s.t. m’ ≠ m and H(m’) = H(m)
- Given 2 diff msgs m,m, they map to the same hash value (can’t choose!)
Collision Resistance & Hash Functions (Detailed)
H: M→T
Collision For a hash function H, a pair of messages, m₀, m₁ ∈ M H(m₀) = H(m₁) but m₀ ≠ m₁ → Any 2 msgs (m₀,m₁) map to the same hash value.
Collision Resistance Adv_CR[A,H] = Pr[A outputs collision for H] is ’neg' → The probability of getting a collision is negligible.
Preimage For a hash fn H, find m ∈ M s.t. H(m) = y. → this would be bad. → Should be hard to get an m that gives y, given y.
Preimage Resistance It is infeasible to find m ∈ M such that H(m) = y → → given the hash value y, it is infeasible to find m.
Second Preimage For a hash fn H, and m, a message m ∈ M, find m’ ∈ M, such that m’ ≠ m and H(m’) = H(m)
Second preimage resistance It is infeasible to find m’ ∈ M s.t. m’ ≠ m and H(m’) = H(m) → Given 2 diff msgs m,m, they map to the same hash value (can’t choose!)
Relationship Between Properties
★ Strong collision resistance ⟺ Second pre-image resistance & preimage resistance
→ If you can solve preimage problem for a hash function, you can find a collision,
→ Weak collision resistance ⟺ Second preimage resistance
Preimage ← 2nd image ← Collision
★ Strong collision resistance ⟺ Second pre-image resistance & preimage resistance
- If you can solve preimage problem for a hash function, you can find a collision
Weak collision resistance ⟺ Second preimage resistance
So technically collision is strongest - b/c if given collision you can’t find anything else but to find everything - you can use preimage.
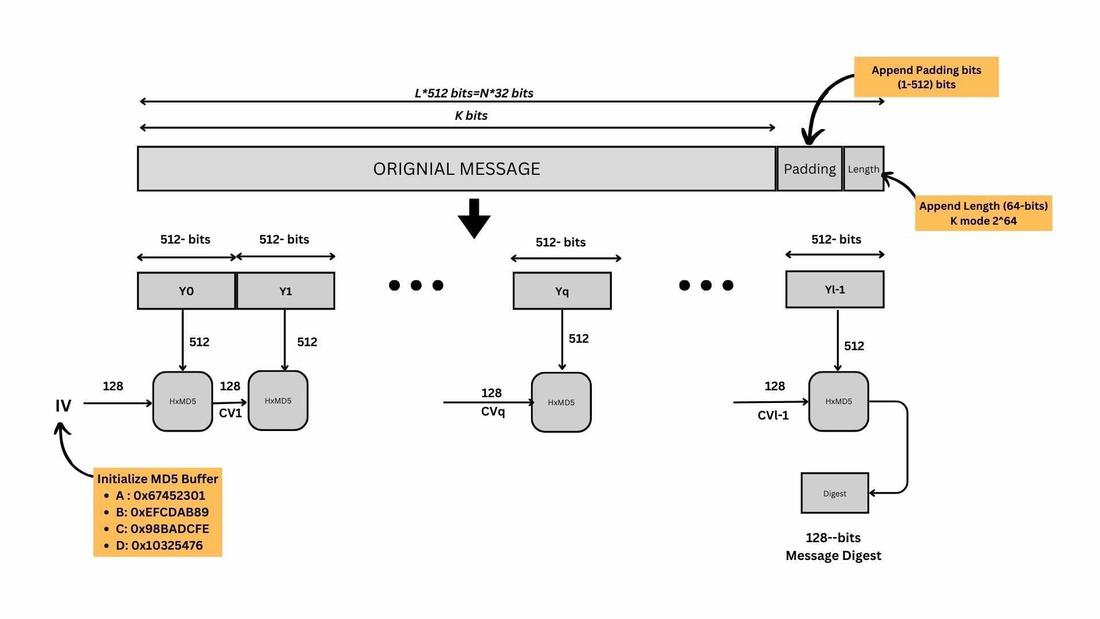
MD5
Status: Found 1st collision - No longer secure
Specifications:
- Block: 512 bit } small!
- Output: 128 bit }
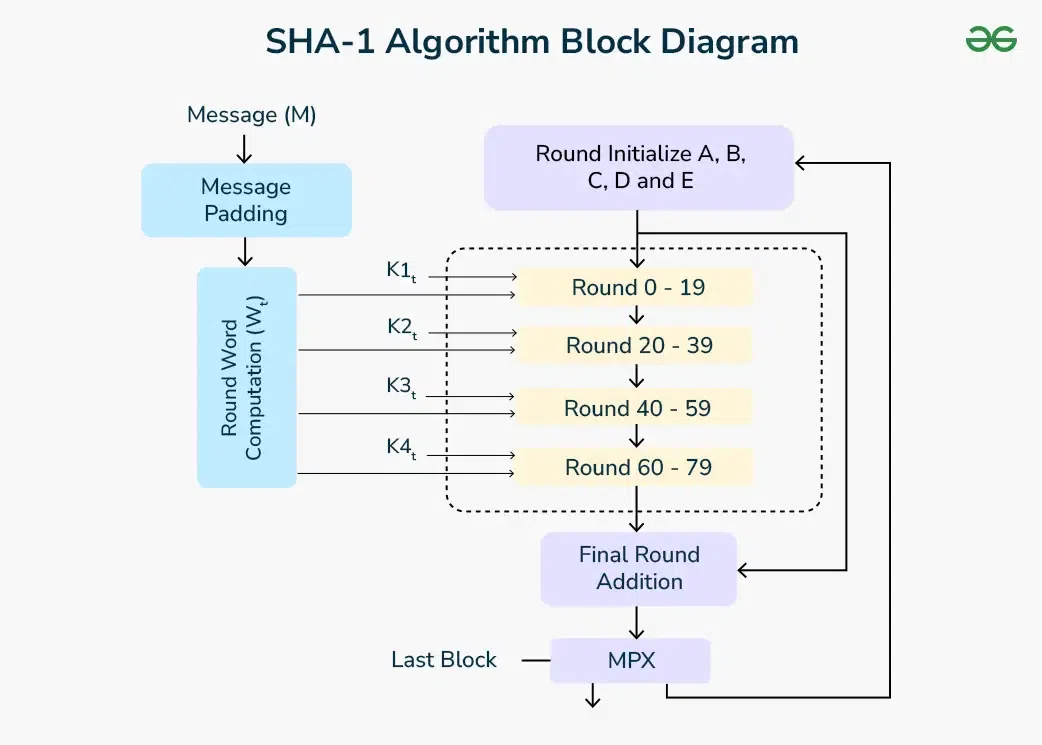
SHA-1
Specifications:
- Input: Divide msg (> 2⁶⁴ bit) into 512-bit bits - pad orig. append bits
- Rounds: 80 round
- Output: 160-bit output
Status: Not secure b/c of 2 msg with some hash ∴ 2nd preimage/break → broke.
SHA-2 / SHA-3
SHA-2:
- 6 diff. output sizes in family
- Longer output - better security
- SHA-256: 32-bit, 512-bit, 64 round
- block word
- Current standard
SHA-3:
- 6 diff. 1024bit 80 round
- block word
Summary of Hash Algorithm Comparisons
| Algorithm | Block Size | Output Size | Rounds | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 512 bit | 128 bit | - | Broken (collision found) |
| SHA-1 | 512 bit | 160 bit | 80 | Broken (preimage attack) |
| SHA-256 | 512 bit | 256 bit | 64 | Current standard ★ |
| SHA-3 | 1024 bit | Variable | 80 | Secure |
Computer Vision
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
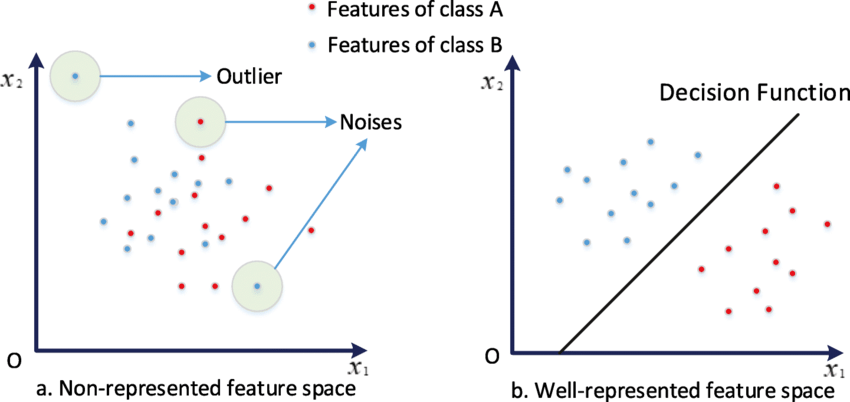
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
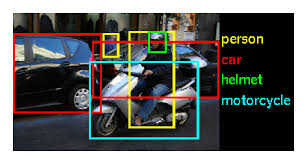
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
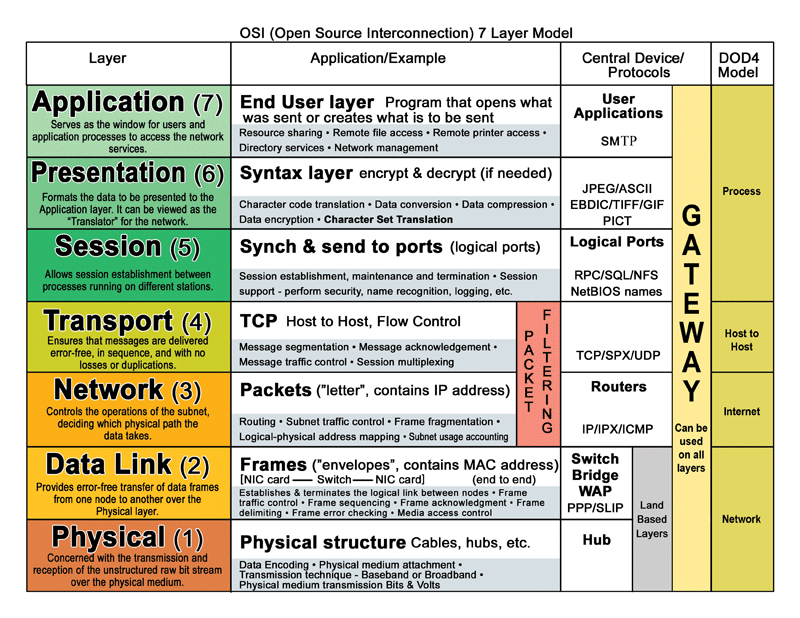
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
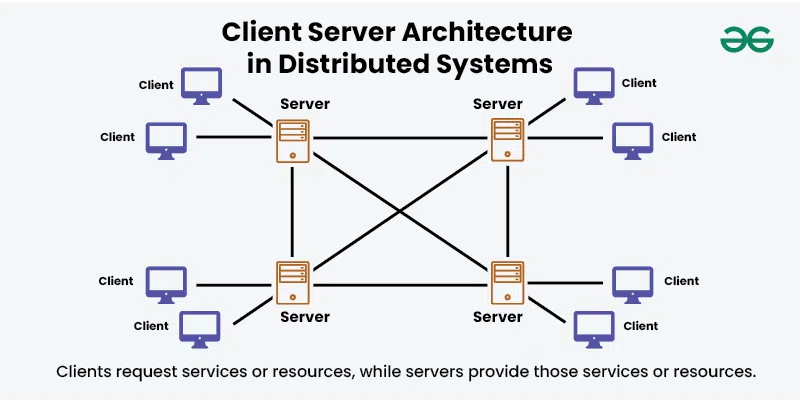
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
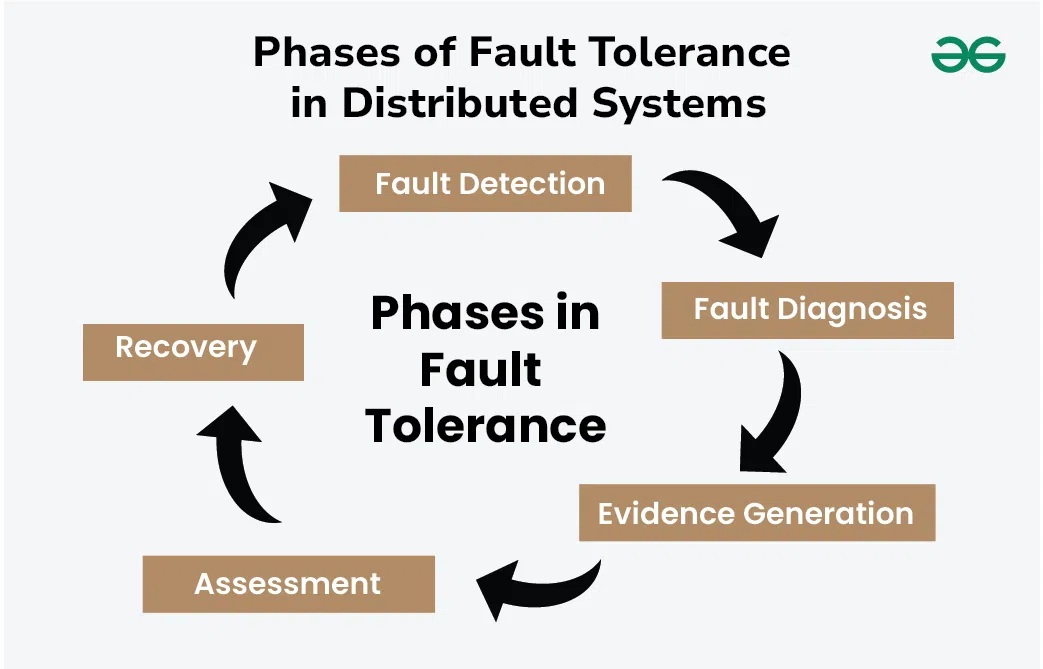
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
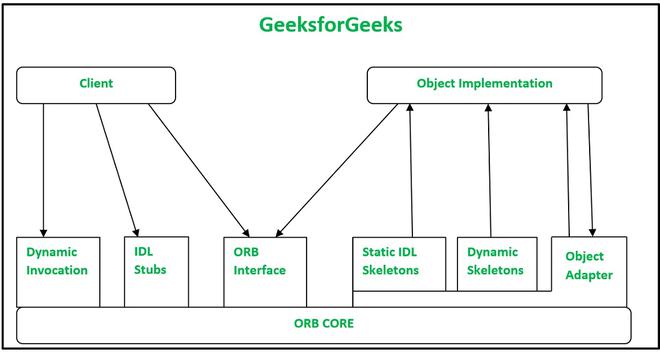
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
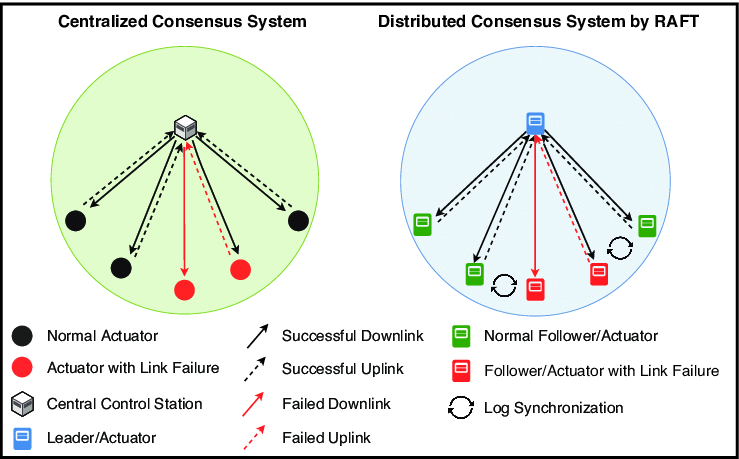
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
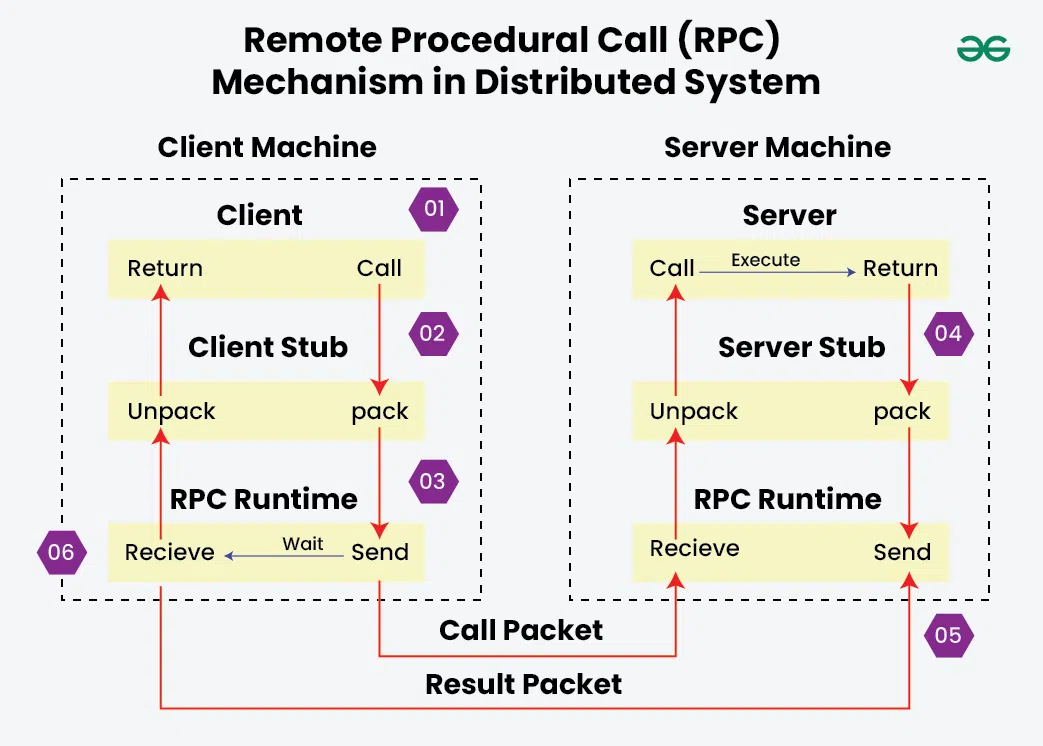
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
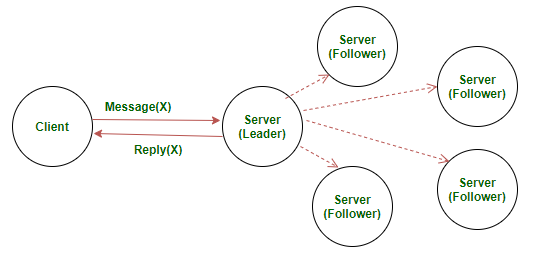
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
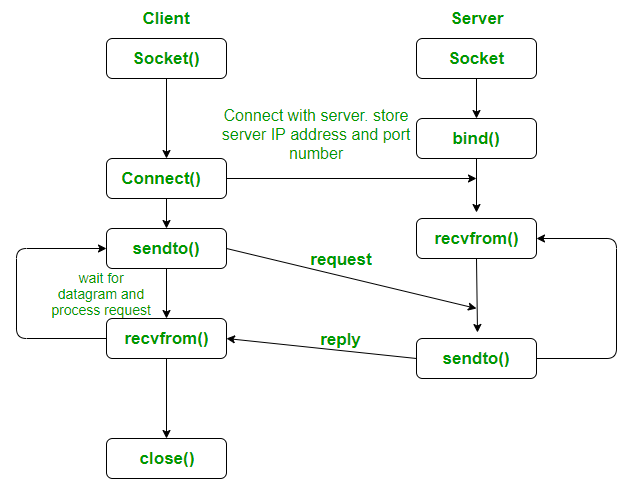
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
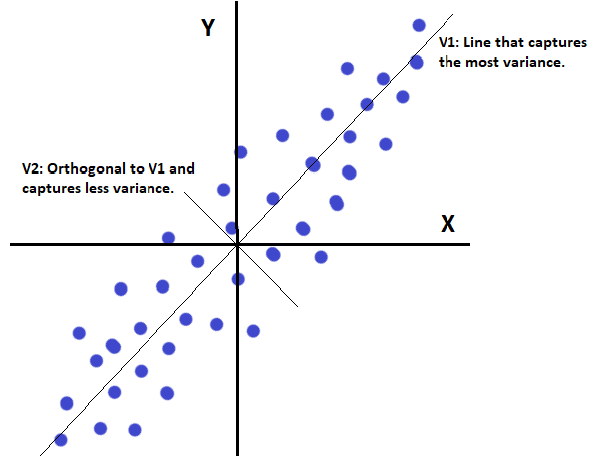
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
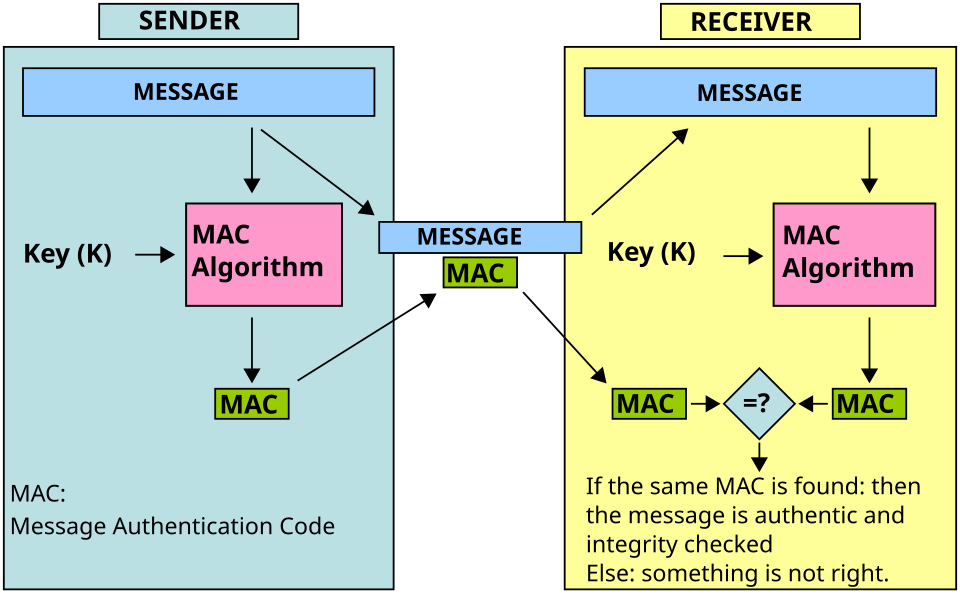
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers

Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
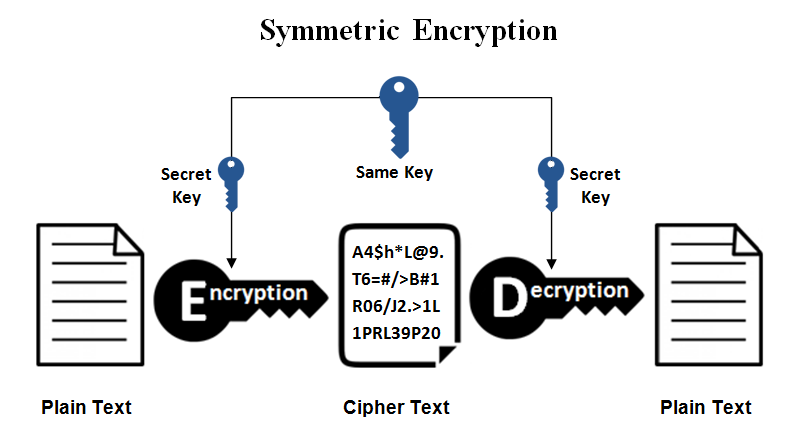
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
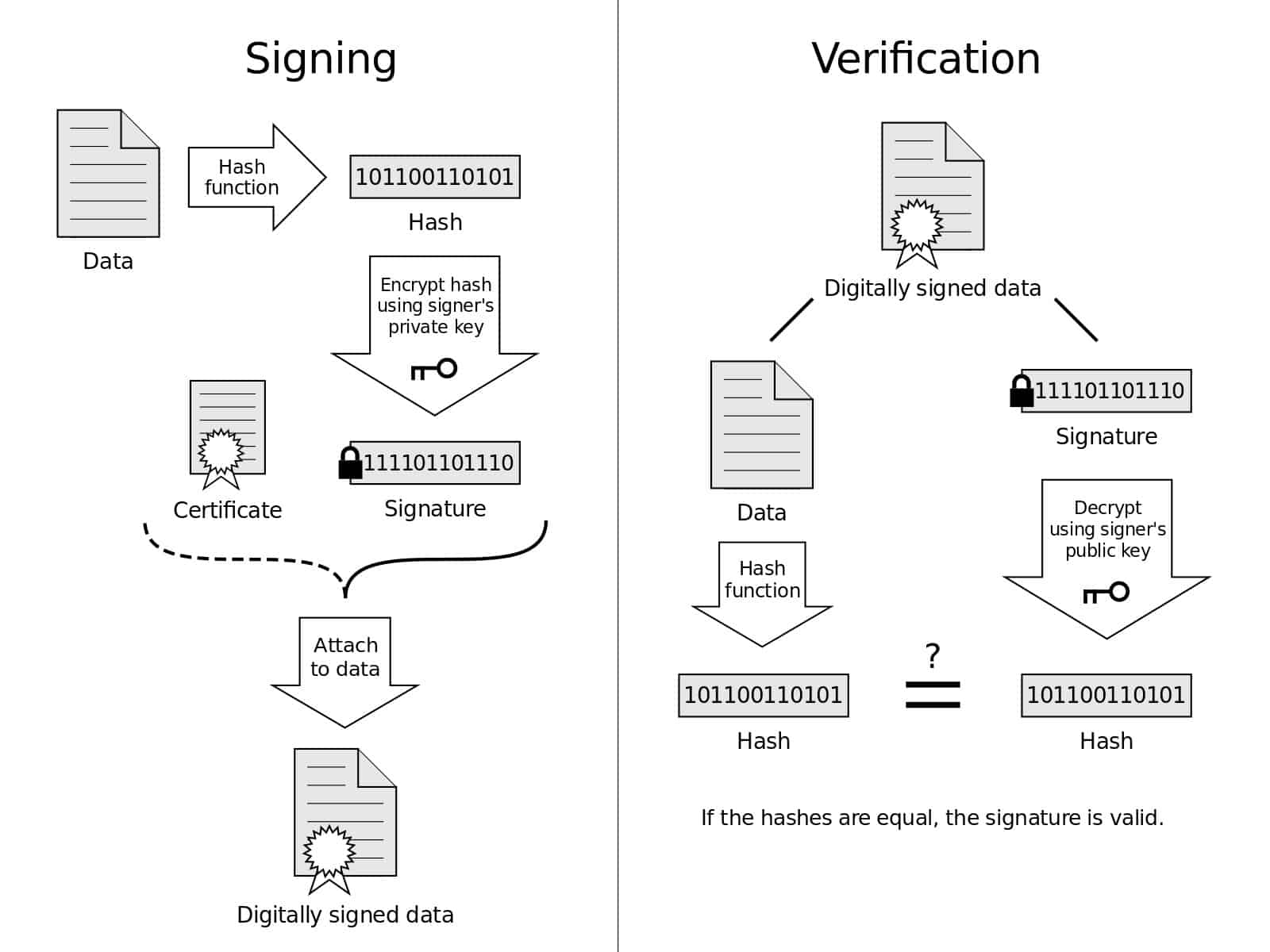
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
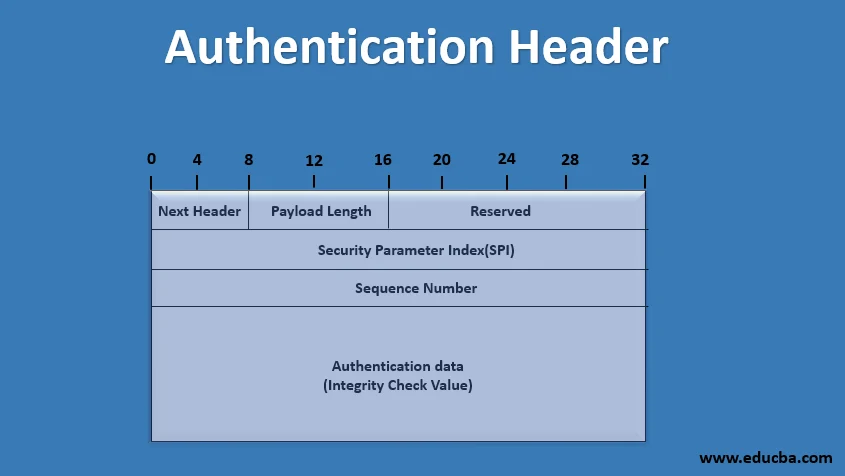
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes