
IPSec Types & Properties
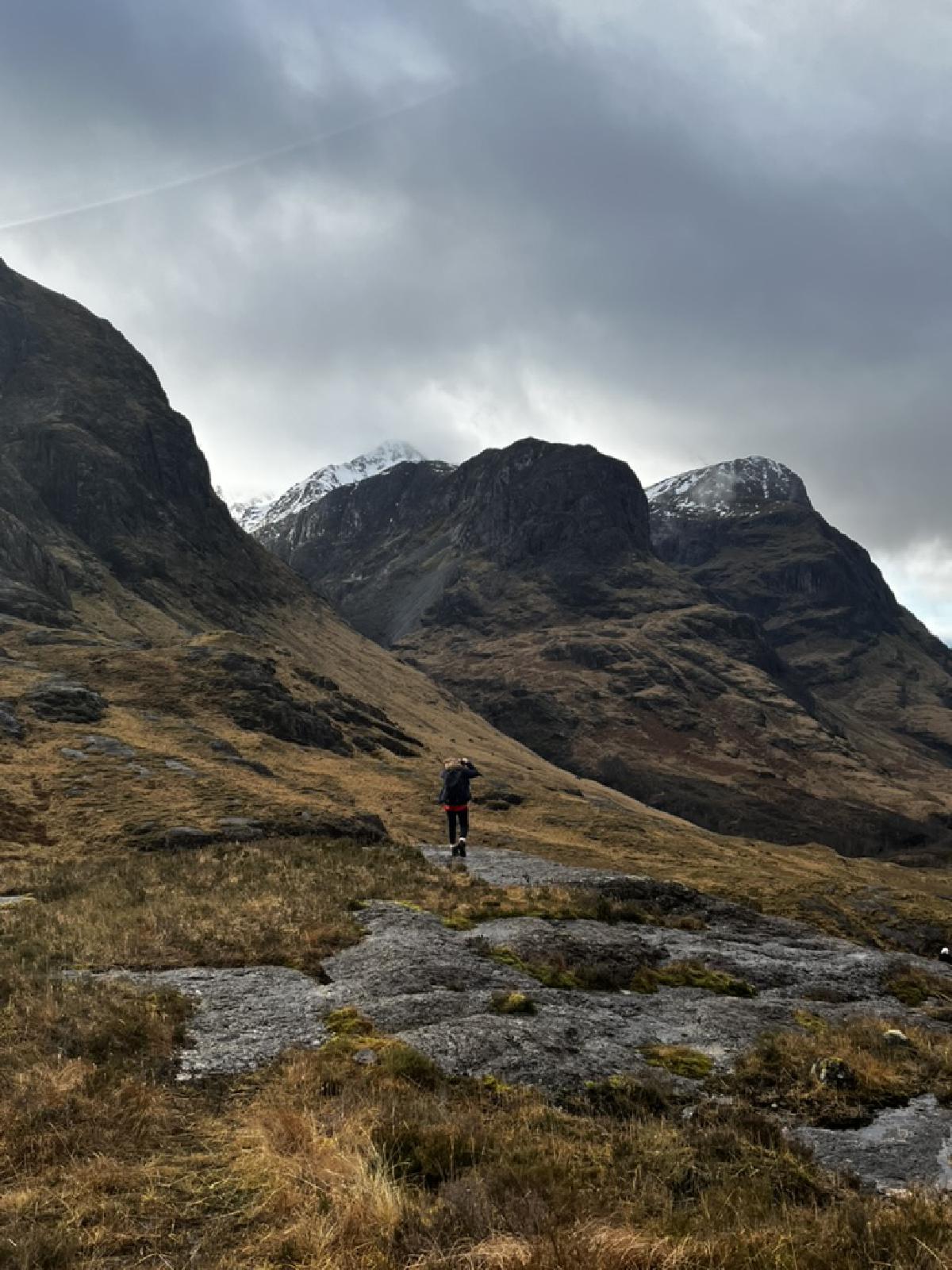
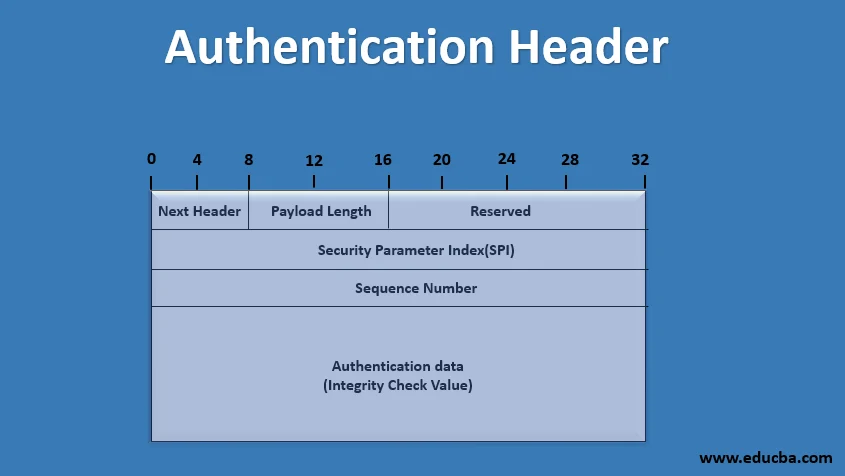
2 Protocols → Authentication Header (AH)
Original packet:
|IP header | Payload | TCP header |
|seq# | from_to-idx |
|auth_data |
Authentication Header (AH)
| IPSec Services | AH | ESP | ESP w/auth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access control | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Integrity | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Data origin auth | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Replay protection | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Confidentiality | ✓ | ✓ |
→ Provides data integrity (with MAC) and auth. of IP pkts. → Parties share secret key created by IKE → prevents modification, spoofing, replay attacks.
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
|SPI |
|Seq # |
|Init. val |
|Payload data |
|TRL PAD |
|CV |
→ Provides msg confidentiality (but not traffic flow confidentiality), can provide auth. services (opt.) → Supports AES, 3DES, CBC is most common.
2 Modes → Transport Mode
→ Provides security for upper-layer protocols (Network, Transport, Application)
|IP header | IPSec header | TCP header | Payload |
encrypted
→ TCP or UDP headers, ICMP pkt are protected for potential eavesdropping → Used for VPNs?
→ Tunnel Mode
|New IP header | IPSec header | IP header | TCP header | Payload |
encrypted
→ Provides security for entire IP packet (entire pkt is payload of new outer IP pkt with new header) → No routers can examine/unpack pkt contents including inner IP pkt
Comparison Table
| Transport Mode | Tunnel Mode | |
|---|---|---|
| Auth. Header (authentication + date integrity) | → Authenticates IP payload (upper layer protocol data), immutable/predictable headers - source address, dest. address, fields, entire packet. → Uses MAC over immutable fields (except auth data) and mutable fields (which are zero’d). → AH is inserted after the og. IP header, before the IP Payload. [IP header|AH |Payload] | → Authenticates entire inner IP pkt (IP header + IP Payload) - covers entire original pkt. → Uses MAC over og pkt, authenticates except auth data and mutable fields in new IP header. → AH is inserted btwn the og IP header and a new outer IP header. [New IP hdr|AH|orig hdr|Payload] |
| Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) (→ encryption → confidentiality) (→ opt. authentication) | → Encrypts IP payload after ESP header - provided directly btwn 2 hosts (end-to-end) traffic. → For host-to-host (end-to-end) traffic [Og. IP header|ESP header|TCP|Data|ESP trail|ESP auth] (encrypted → authenticated) | → Encrypts entire inner IP pkt. → Add new/outer IP header & intermediate outer protection. → Good for VPNs - gateway-to-gateway security - hides int. net. or abnormal, less keys needed - no traffic information (encrypted) [IP hdr|ESP(orig hdr|TCP|Data|ESP trail|ESP auth)] (Authenticates inner IP pkt) |
Authenticates IP payload - but not IP header
Authenticates inner IP pkt
Computer Vision
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
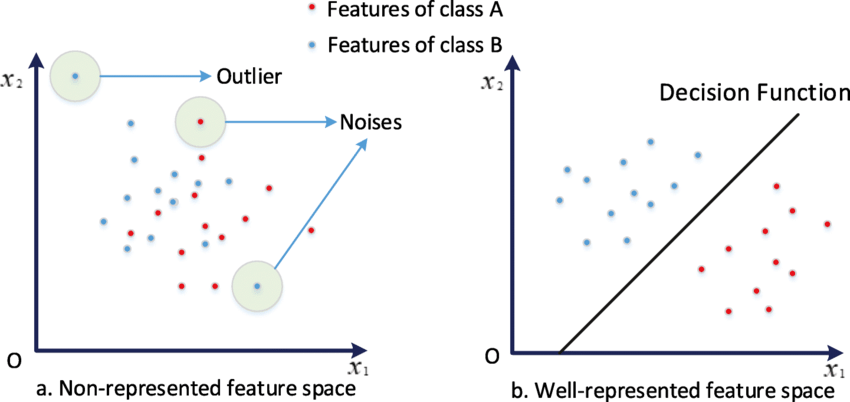
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
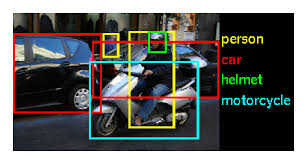
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
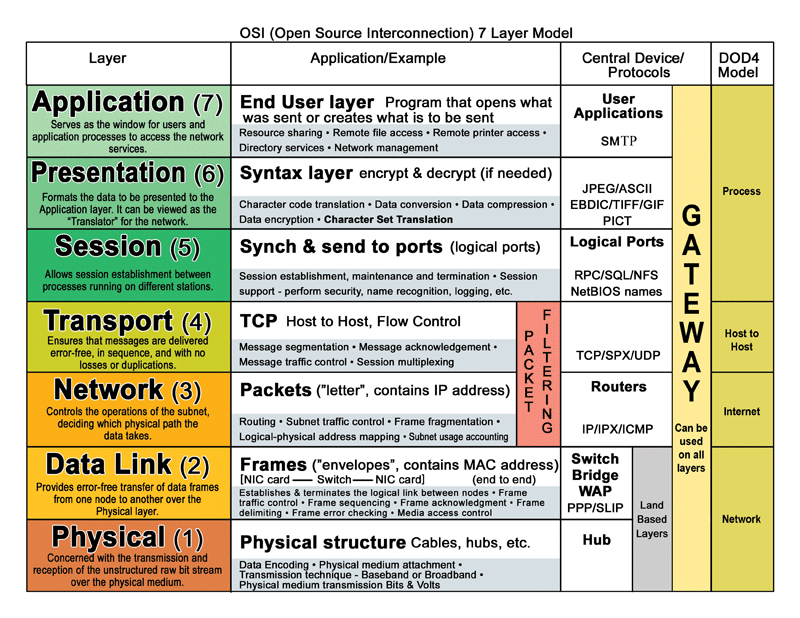
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
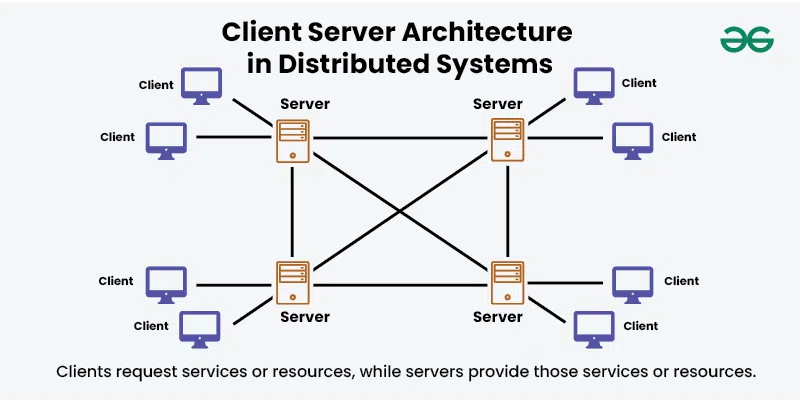
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
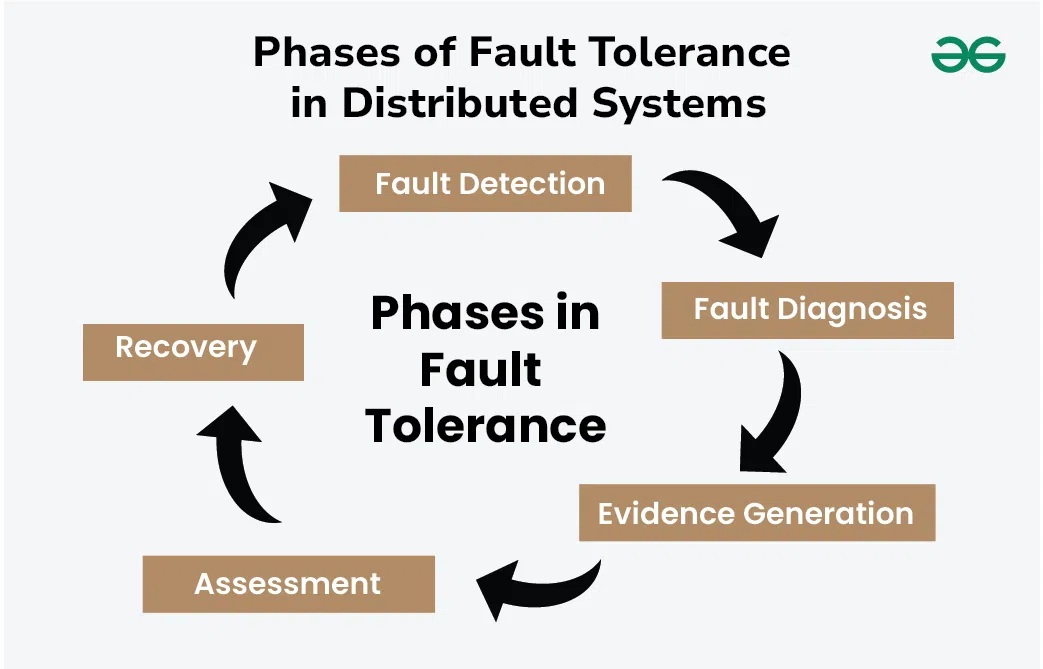
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
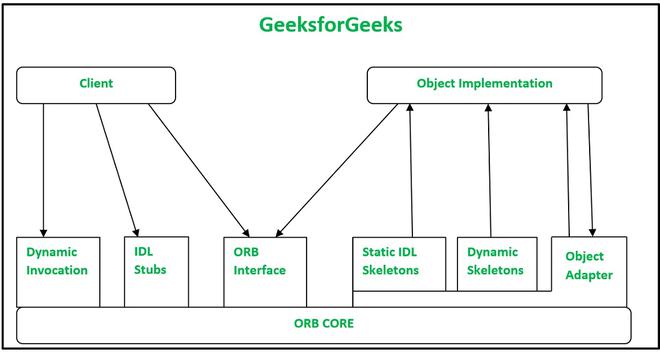
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
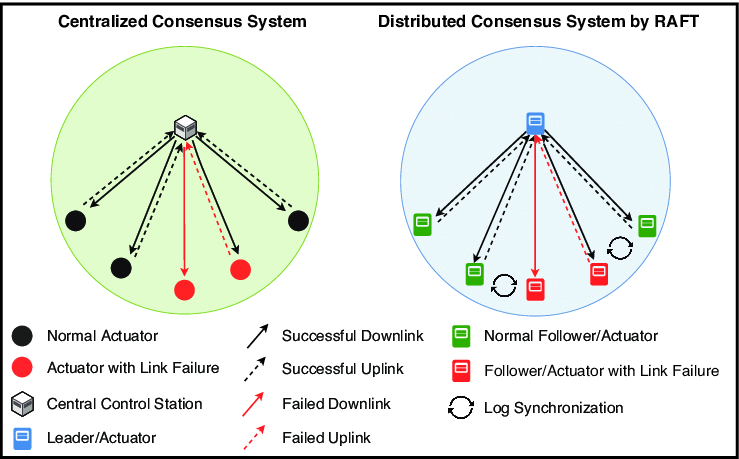
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
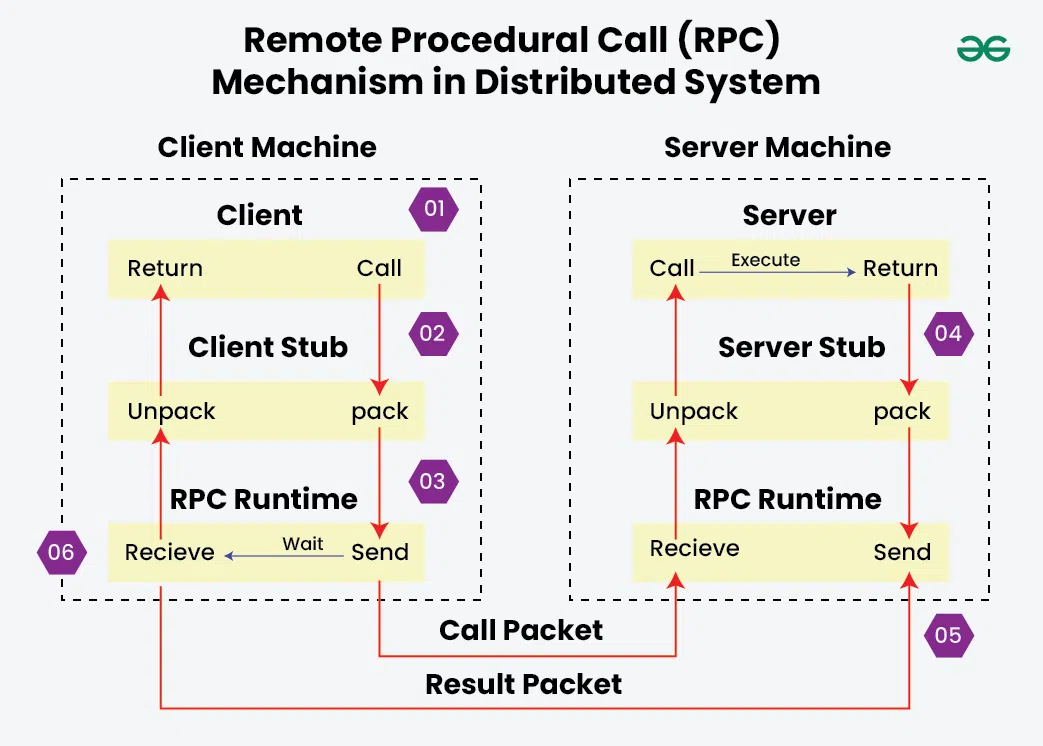
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
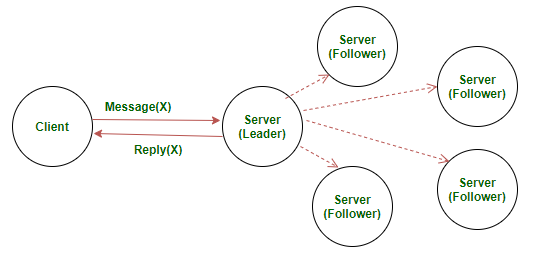
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
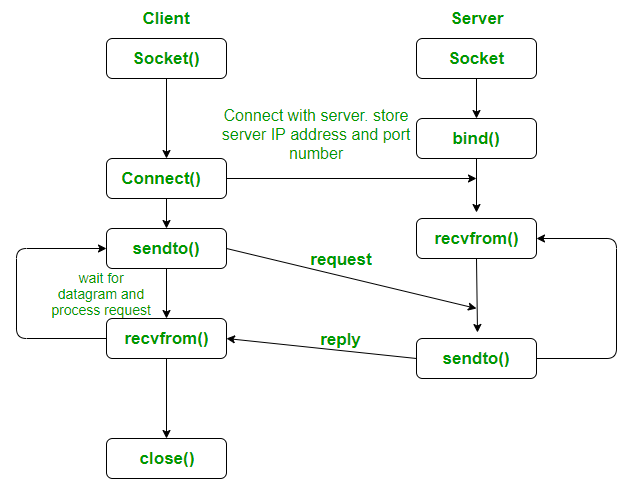
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
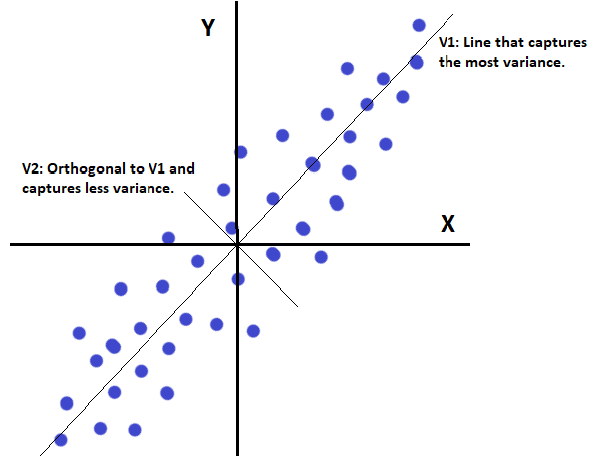
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
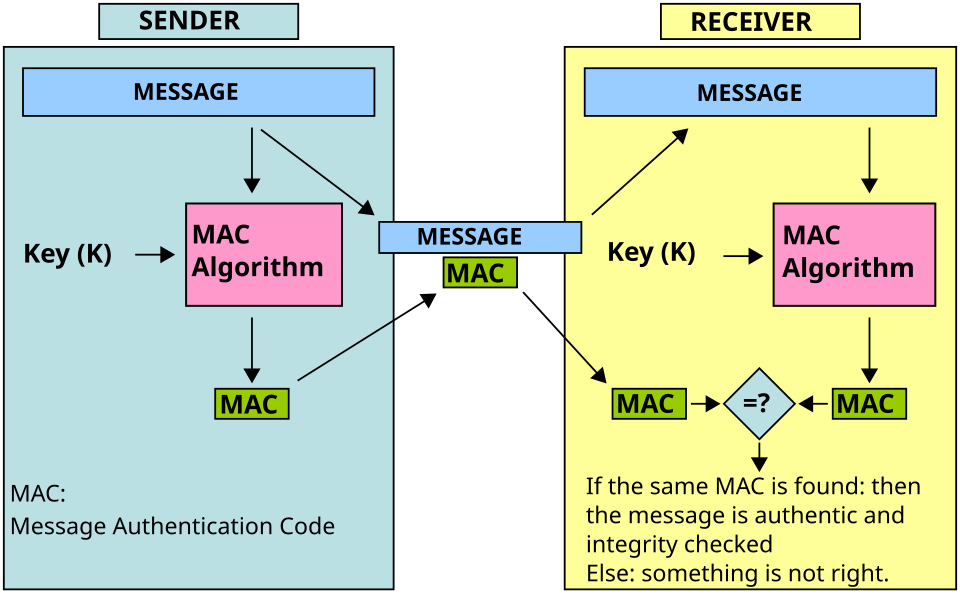
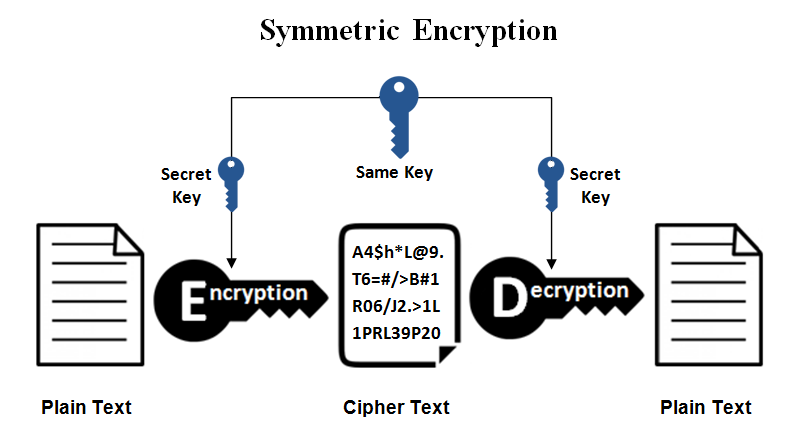
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
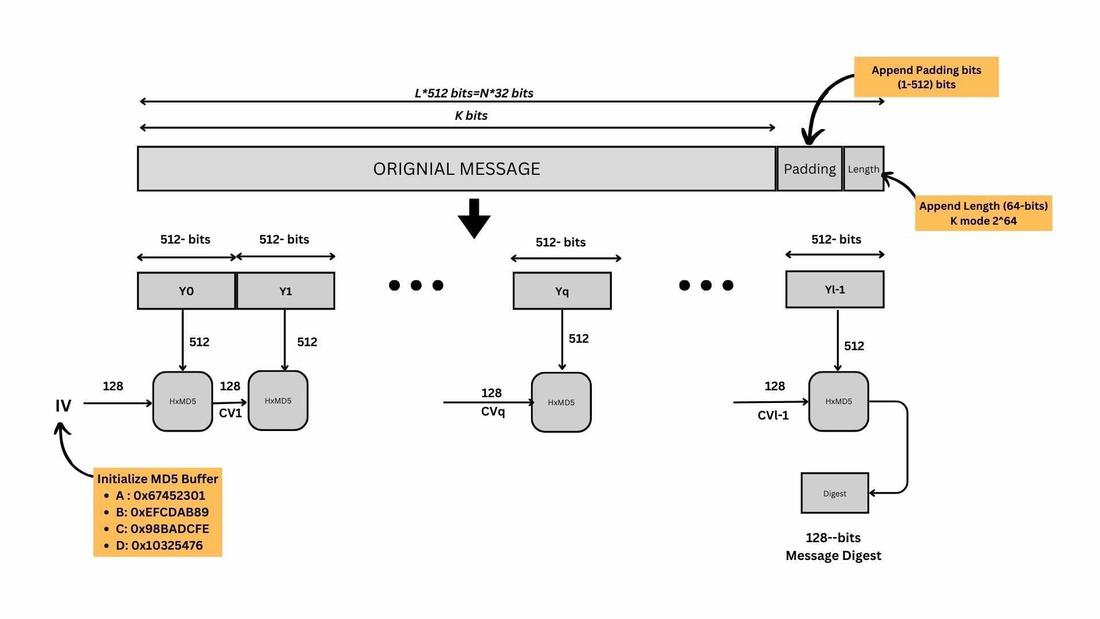
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
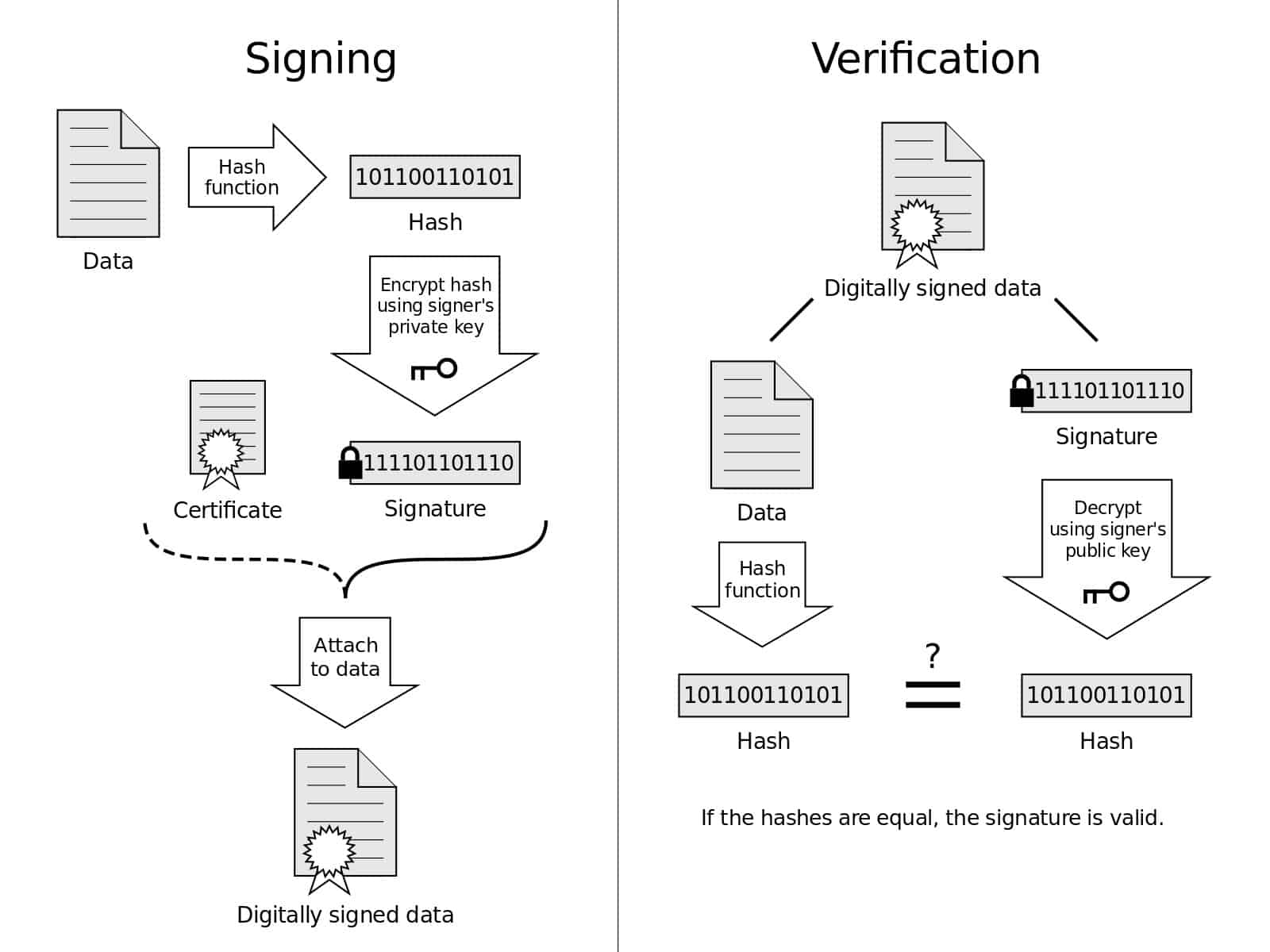
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations

IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes