
Number Theory
Euclidean Algorithm
a|b - a divides b (a is divisor)
gcd(a,b) = 1 - coprime
Example: gcd(299, 221) = ?
299 = 221·1 + 78
221 = 78·2 + 65
78 = 65·1 + 13
65 = 13·5 + 0
gcd(299, 221) = 13
Extended euclidean algo: → compute x, y s.t. ax + by = gcd(a,b)
Extended Example: gcd(299, 221) = 13 13 = 78 - 65·1 = 78 - (221 - 78·2) = 3·78 - 221 = 3(299 - 221·1) - 221 = 3·299 - 3·221 - 221 = 3·299 - 4·221 x = 3 y = -4
Number Factorization
Factor a number n as a product ∴ n = a × b × c
Prime factorizations of n - write n as a product of primes. → 91 = 7 × 13
a ≡ b mod n → congruent (any modulus) residue a = b mod n
Modulo Addition
(Zₙ, +) Additive group. Abelian
Identity element = 0 ∃e ∈ G | ∀x ∈ G, e ∘ x = x ∘ e = x
(Zₙ, +) = 3 + 6 + 9 + 0 (Zₙ, +)
(Zₙ, +) - not a group! there’s no O⁻¹.
(Zₙ, ) (no zero) - might not be a group b/c not all a⁻¹ doesn’t exist. (∴ a⁻¹ only exists ⟺ gcd(a,n) = 1 ⟺ ax + yn = 1 ⟺ [a]∘[x] + [n]∘[y] = [1] in Zₙ. ⟺ [a]∘[x] = [1] in Zₙ ny = 0 → [a⁻¹] = [x] in Zₙ.
Modulo Multiplication
*(Zₙ, ) - not a group! (no O⁻¹)
but (Zₙ, ) = ½ a ∈ Zₙ, gcd(a,n) = 1 (so thus a⁻¹)
→ a ∘ b = ab mod n → 1 = identity (e ∘ x = x ∘ e = x) → a⁻¹ - compute with extended Euclidean
Primality Testing
For (p > 2; p ∈ n; p++)
- Extended: gcd(299, 221) = 13
- e = 0
- if (n/p = 0)
- while (n/p ≠ 0)
- e++
- e++ growth n/p
a ≡ b mod n → congruent (any modulus) residue a = b mod n ie: 6 ≡ 25 mod 10 5 = 25 mod 10 25 = 5a + 10
Zₙ: 30, 1, … n-13
(Zₙ, +) → [a ∘ b = (a+b) mod n] ie: Z₁₂ = {1, 5, 7, 123} = 5 + 7 = 35 mod 12 (so thus a⁻¹) 35 = 12 + 2 + 11 35 ≡ 12 + 2 + 11 gcd(5, 12) = 1 ∴ a⁻¹ exist
Residue Class modulo n
[a]ₙ - all integers congruent to a modulo n
a ≡ b mod n 5 ≡ 25 mod 10 10 ≡ 25 mod 10
[a]ₙ = [5], [10], [15]
[a]ₙ = [b]ₙ ⟺ a ≡ b mod n. there are n residue classes mod n
[0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32]
ie: Z₀ = {5 + 5·9 + 4·6 + 2·8·3} [a]ₙ = 42 mod 10 42 = a·q + 10
Find a⁻¹
(Step 1) Prove gcd(a,n) = 1
(Step 2) Find x,y using extended Euclidean
ax + ny = gcd(a,n) = 1 ax = 10 a⁻¹ = x
Computer Vision
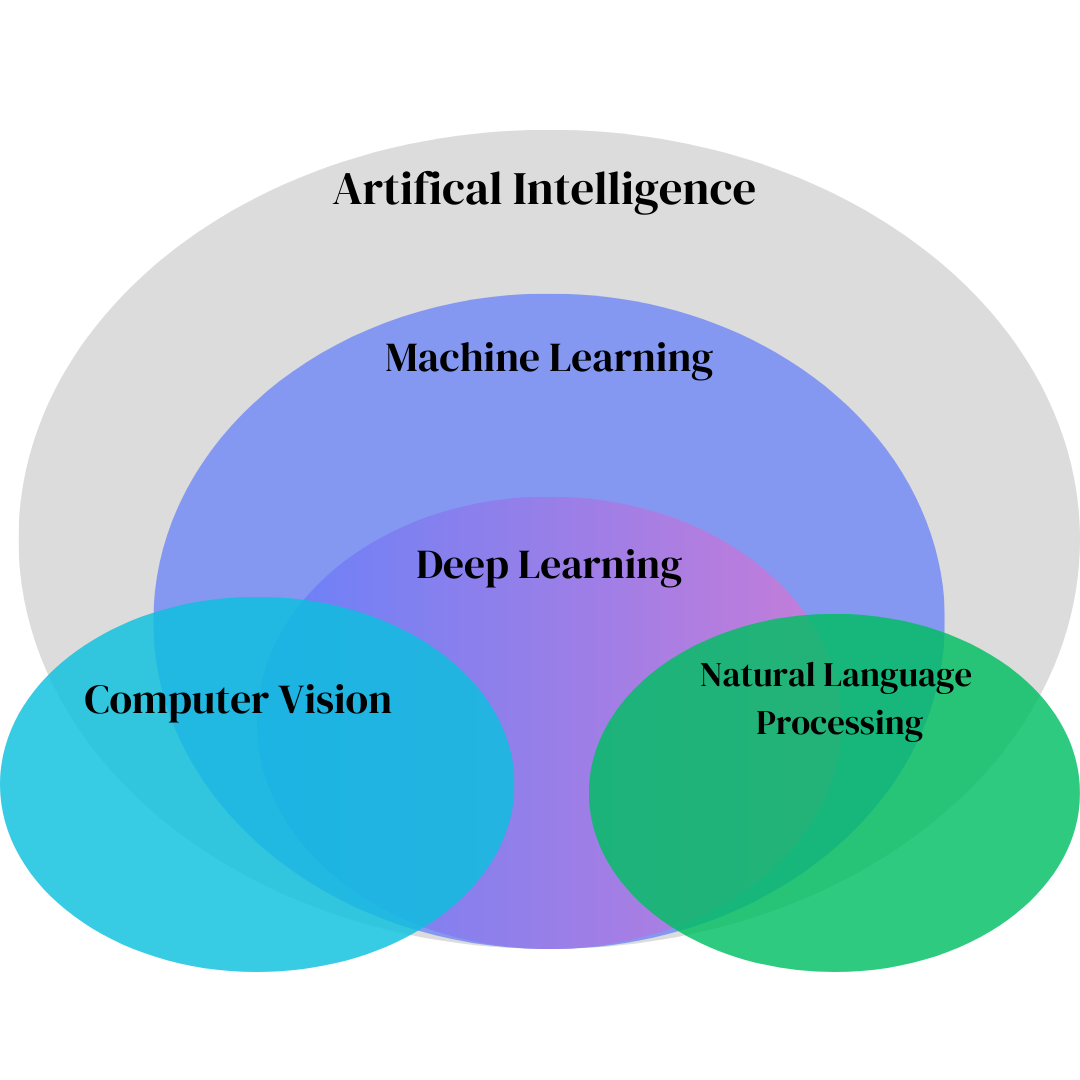
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
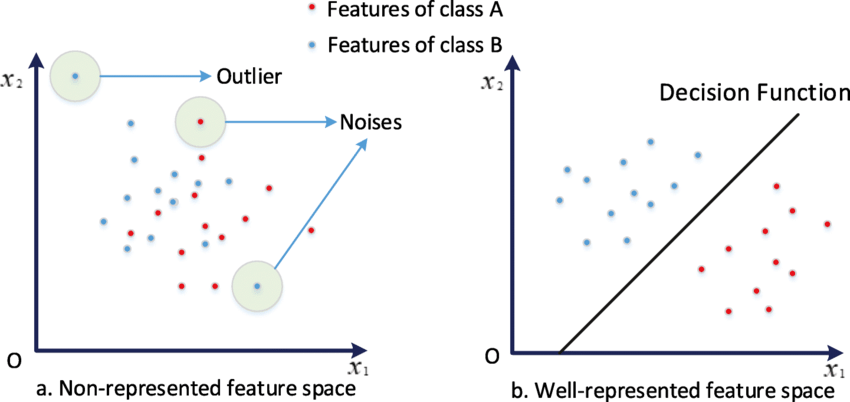
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
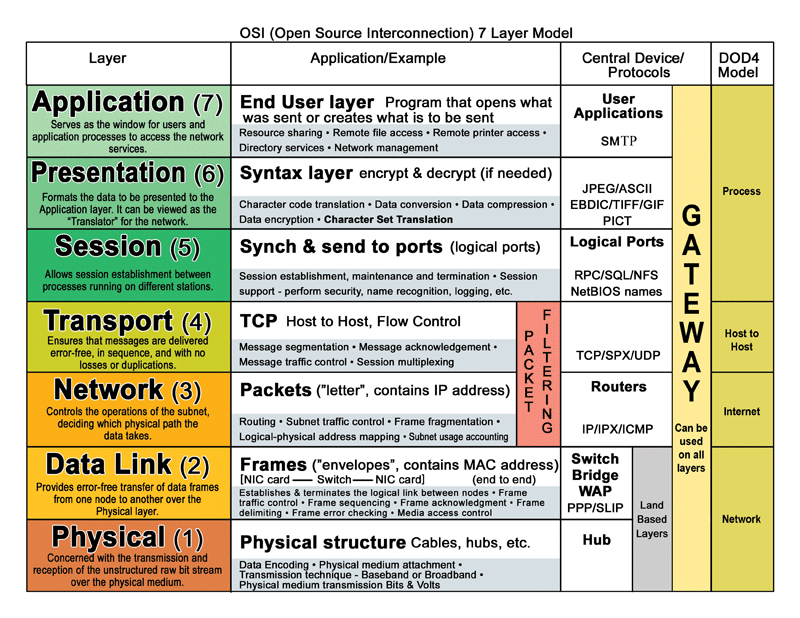
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
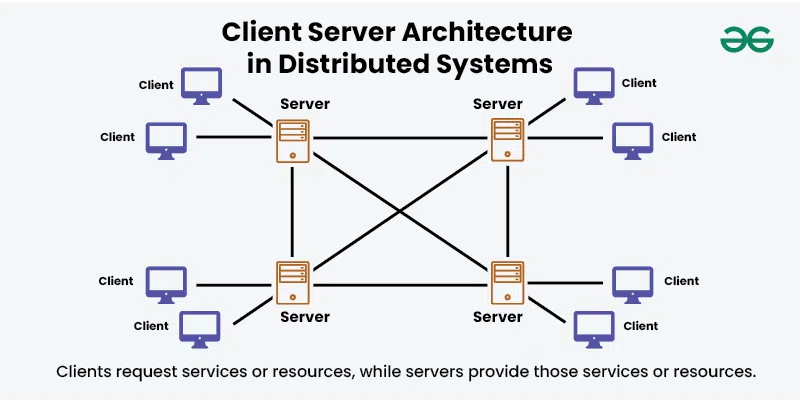
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
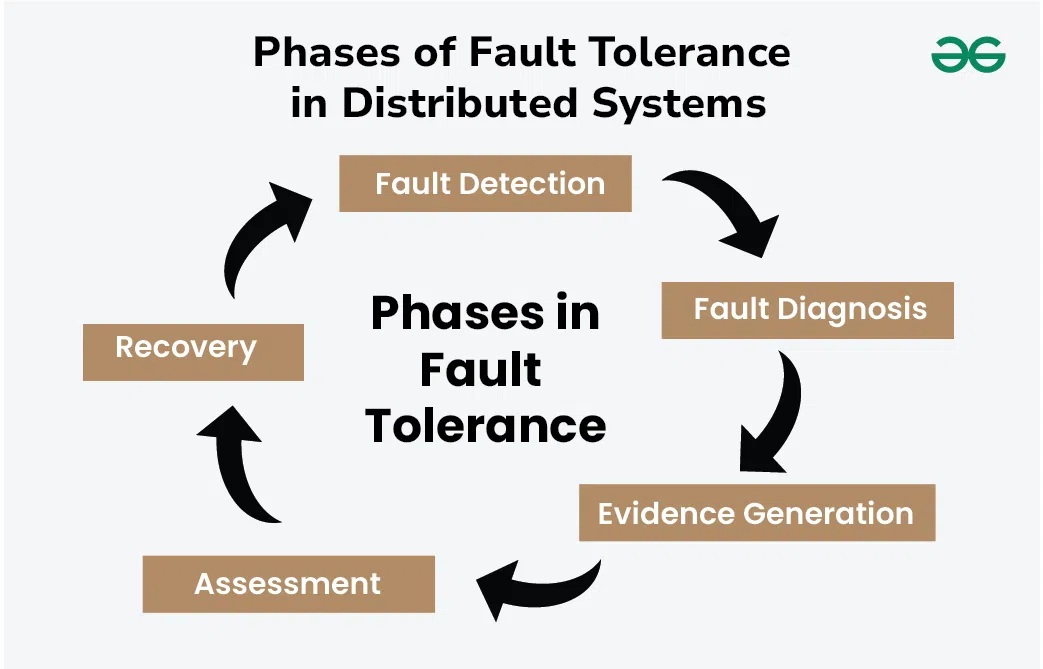
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
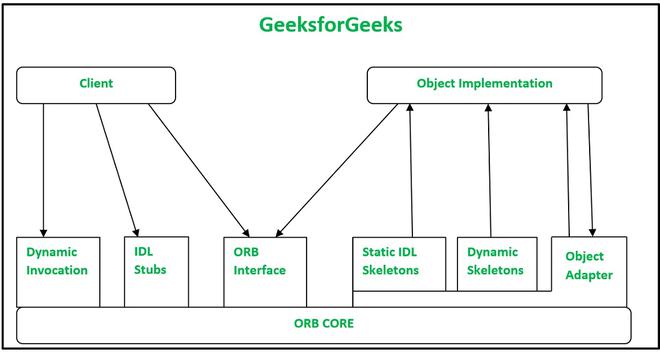
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
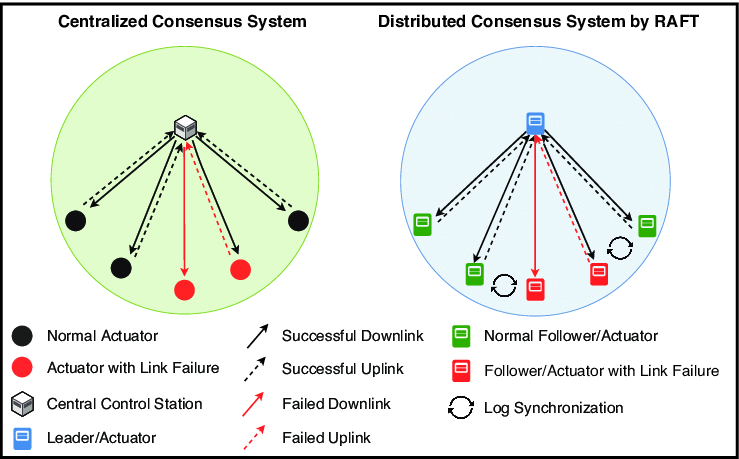
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
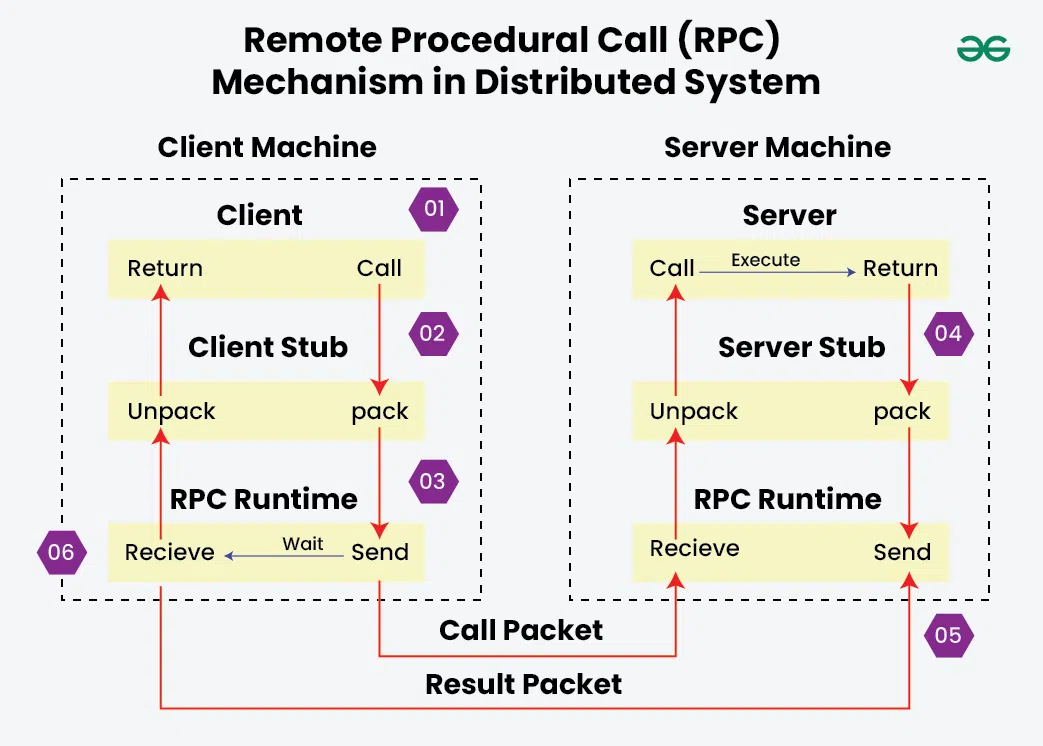
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
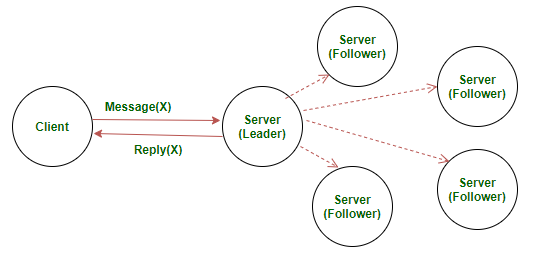
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
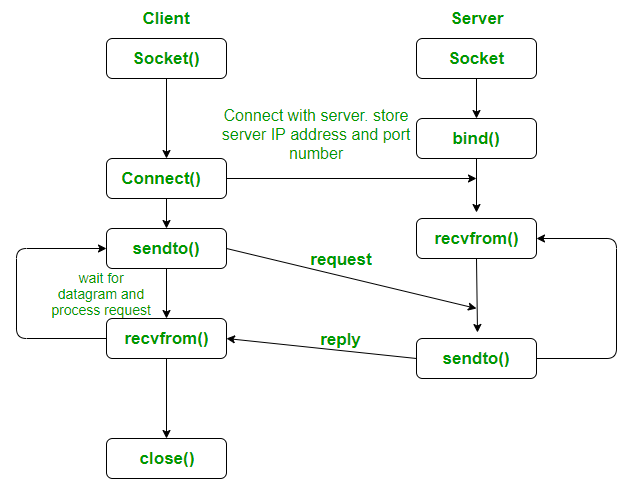
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
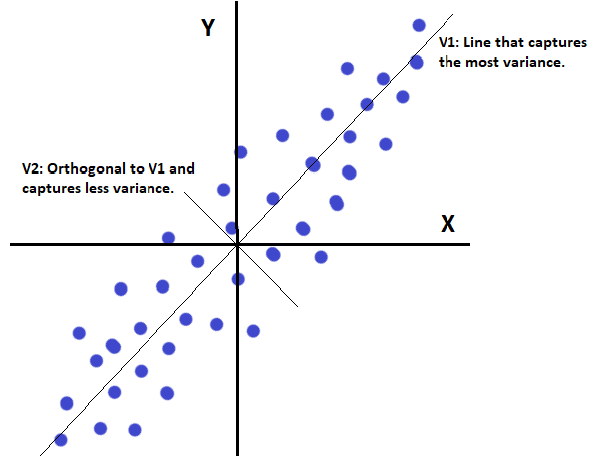
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
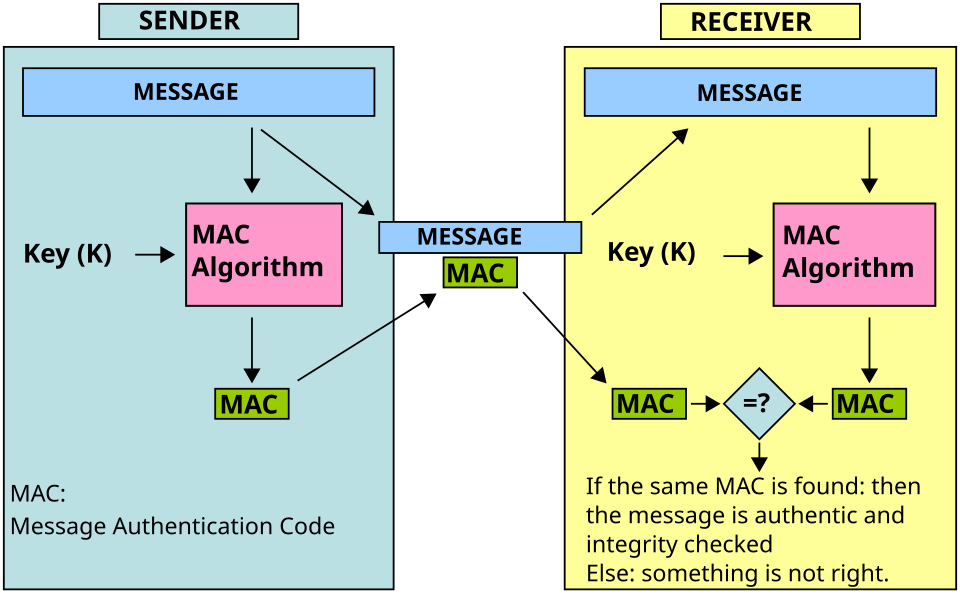
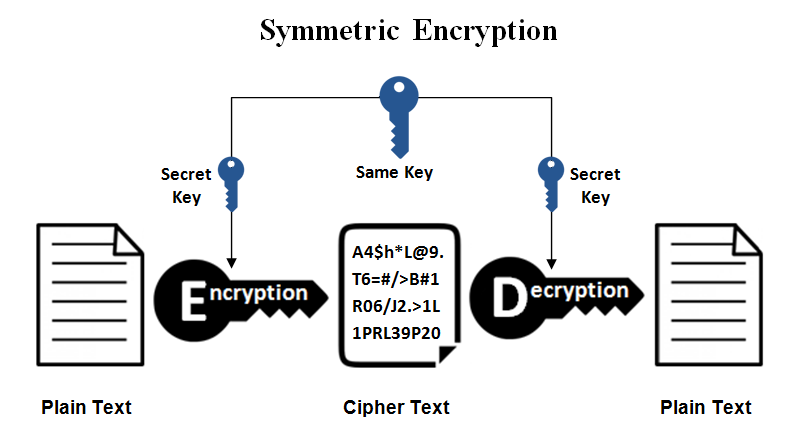
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
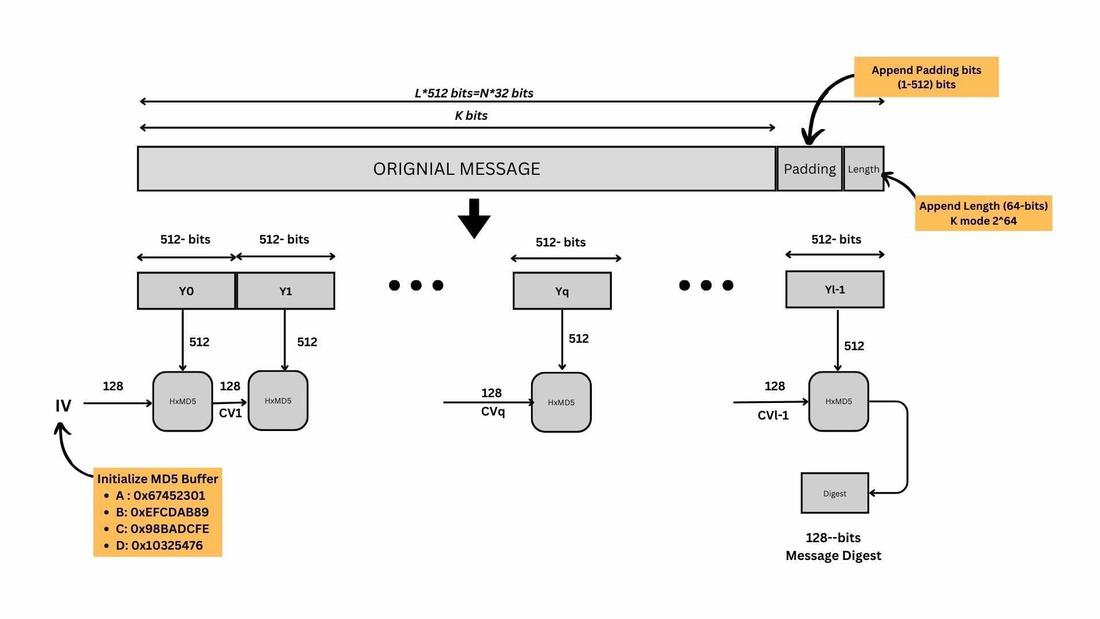
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
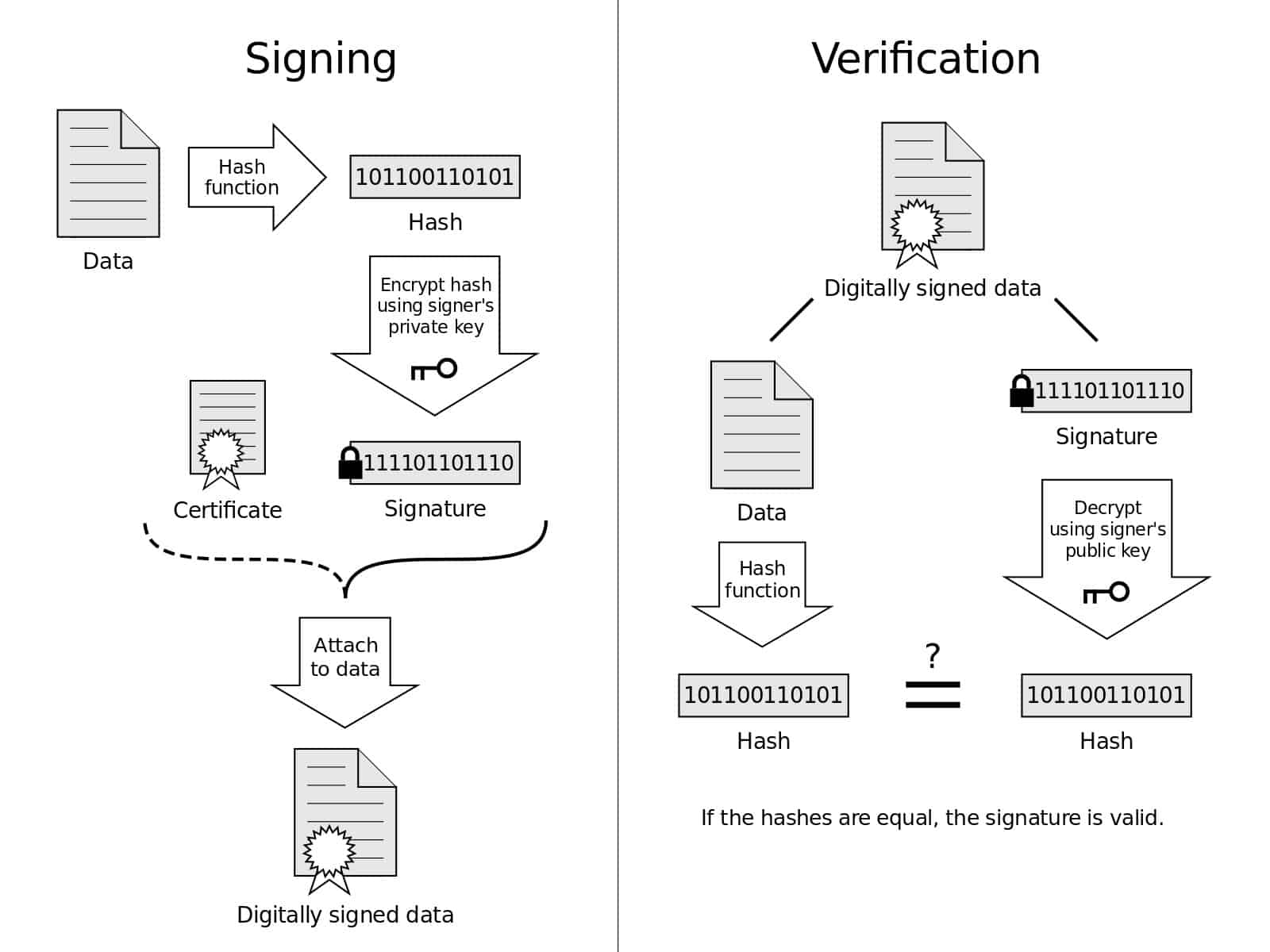
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
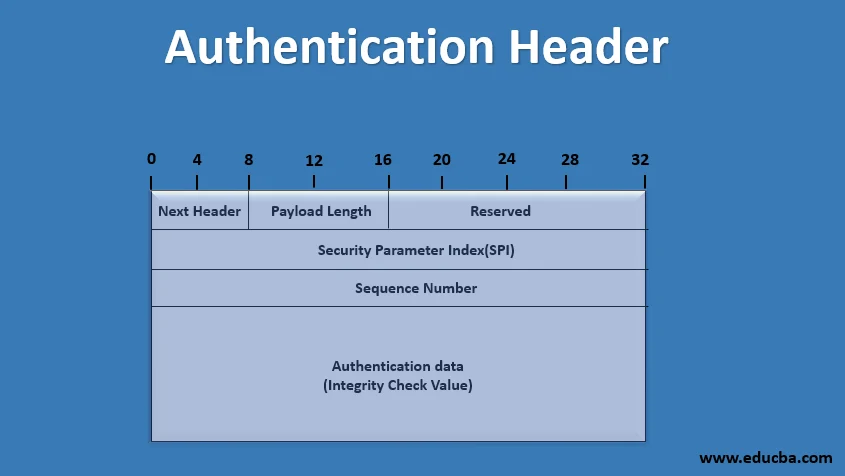
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes