
Public-Key Encryption
Overview
Public-key encryption uses asymmetric key pairs: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
RSA
Key Generation
Find d, d·e¹ mod P(n)
Public key → (n,e) Private key → d
Encryption & Decryption
Encrypt → c = mᵉ mod n
Decrypt → m = cᵈ mod n
Correctness of RSA (𝒫, 49)
Euler’s Theorem → aᵖ⁽ⁿ⁾ = 1 mod n
- gcd(a,n) = 1
- σ = H(n)ᵈ mod n.
Since pq = n, ed ≡ 1 mod P(n) ← Prove this:
σᵉ ≡ H(m)ᵉᵈ ≡ H(m)¹ᵐᵒᵈᵏ⁽ⁿ⁾⁺¹ ≡ H(m)¹ᵏ⁽ⁿ⁾ᵏ⁺¹ ≡ H(m)ᵏᵖ⁽ⁿ⁾ᵏ · H(m) ≡ H(n) mod n
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
Key Pair
public key, private key = (pk, sk) = (a, a·P)
- P = generator
- Example: a = 5, · (5, 5P)
- P: (2,7)
Encryption & Decryption
ciphertext = (u, v)
encrypt:
- u = gᵇ
- v = m·(pk_a)ᵇ = m·gᵃᵇ
Note: mod 𝒫 when doing with generator
decrypt:
- m = v·u⁻ᵃ
- = m·(gᵇᵃ)·(gᵇ)⁻ᵃ
- = m·(pk_a)ᵃ·(gᵇ)⁻ᵃ
Note: mod E(a) when doing encryption/decryption
Functions:
- E(pk = (a, pk), m)
- D(sk, rec(u,v))
- C = (u,v)
ElGamal
Key Pairs
2 pairs = (sk_a, pk_a) = (a,gᵃ), (sk_b, pk_b) = (b,gᵇ)
Encryption & Decryption
Ciphertext = (u,v)
encrypt:
- u = gᵇ
- v = m·(pk_a)ᵇ = m·gᵃᵇ
decrypt:
- m = v·u⁻ᵃ
- = m·(gᵇᵃ)·(gᵇ)⁻ᵃ
Functions:
- E(pk = (g, pk), m)
- D(sk, rec(u,v))
- C = (u,v)
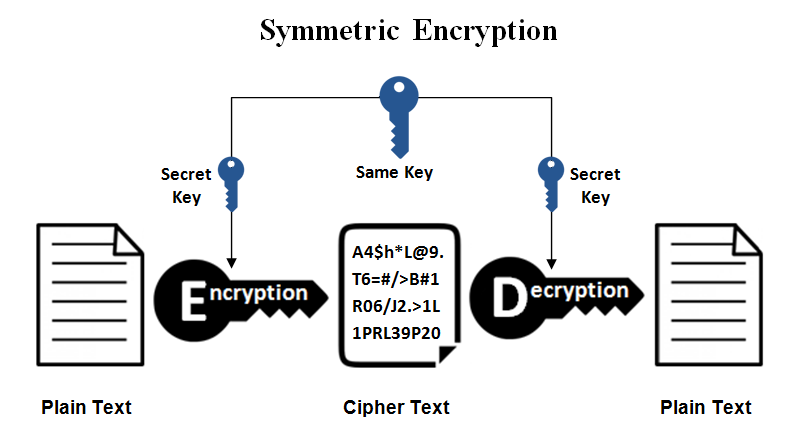
Symmetric Ciphers Diagram
For comparison with public-key systems:
m →|E|→ c →|D|→ m
↑k ↑k
In symmetric: same key k In asymmetric: different keys (public/private)
Computer Vision
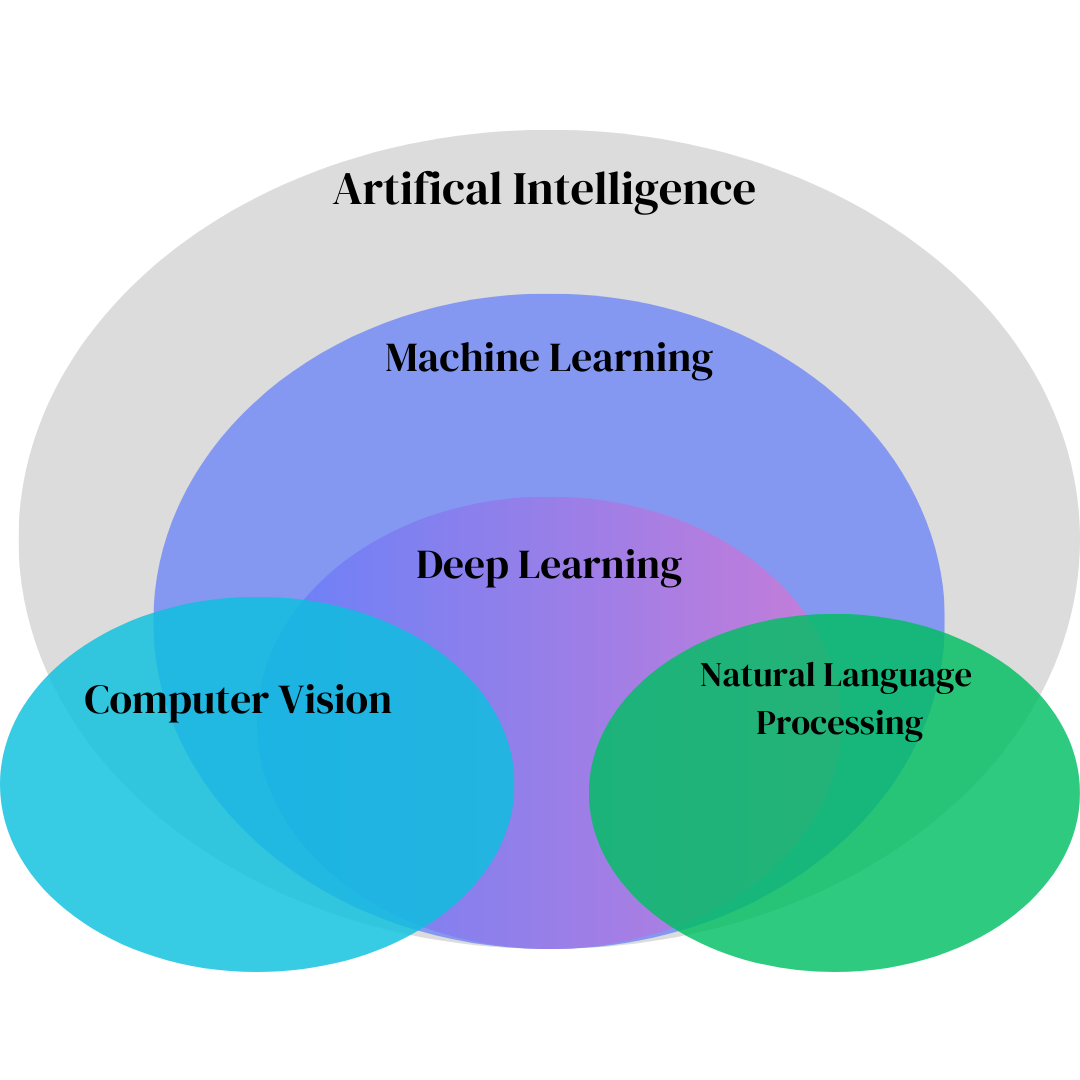
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
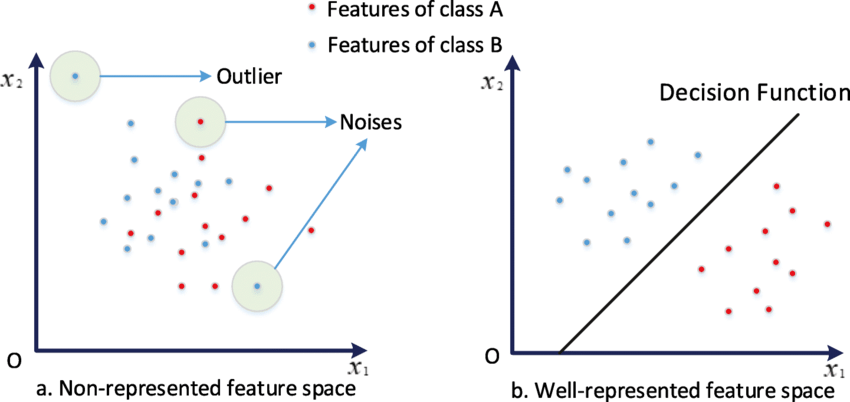
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
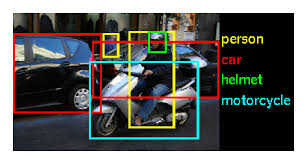
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
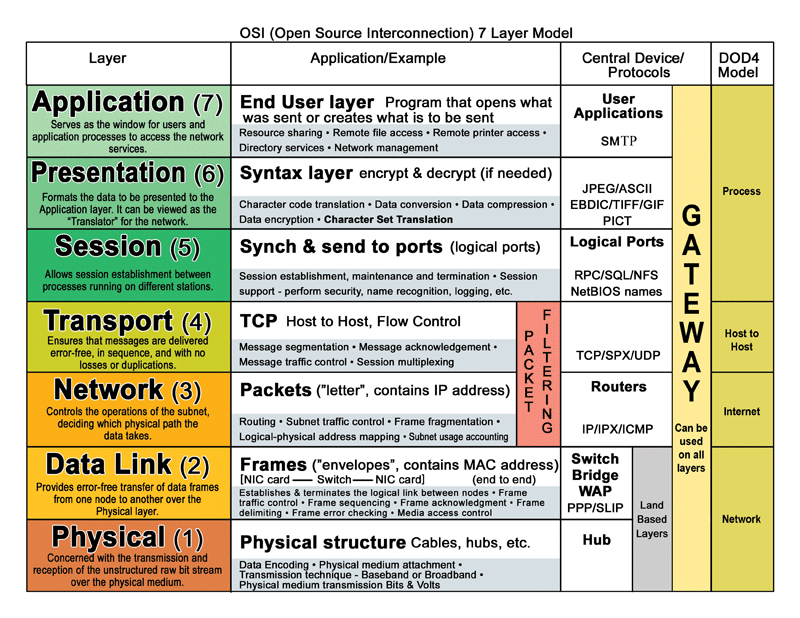
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
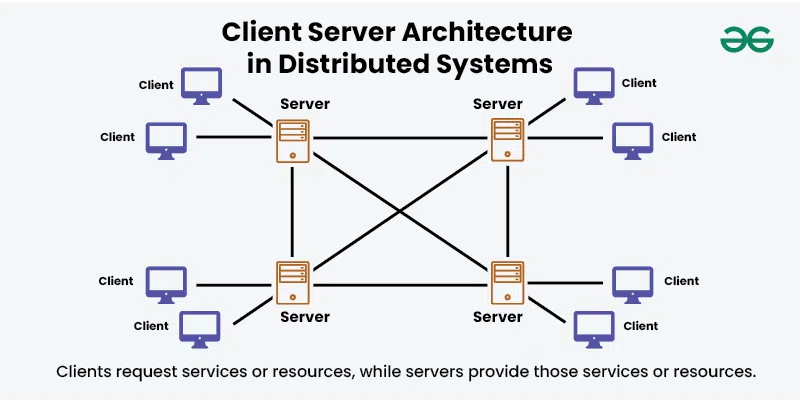
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
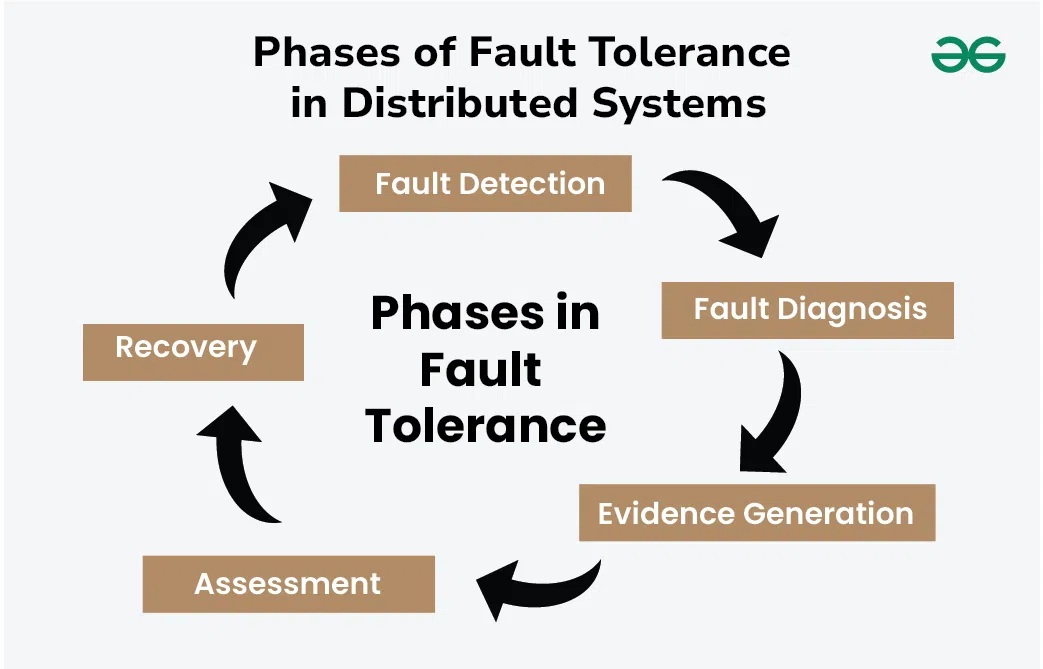
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
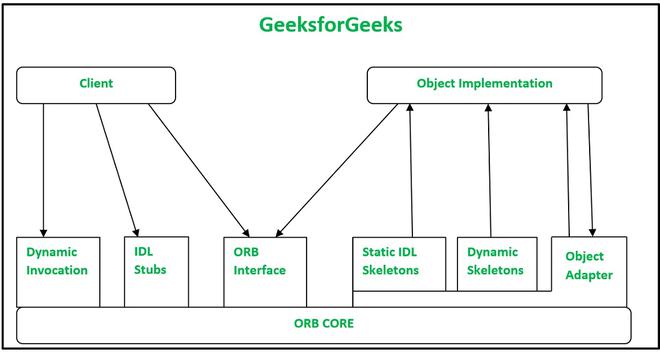
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
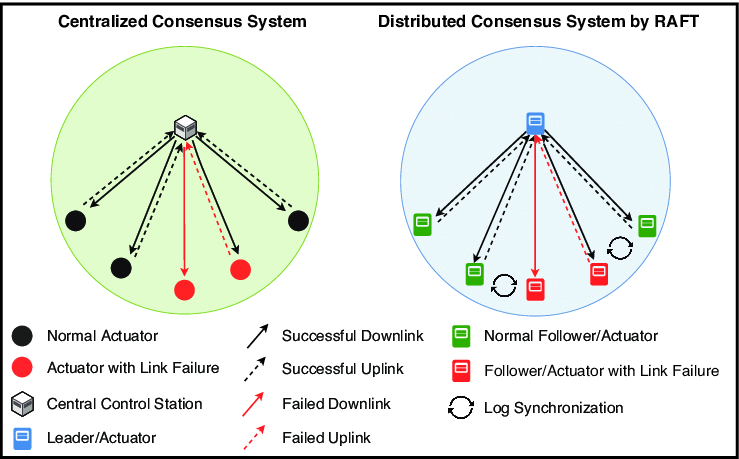
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
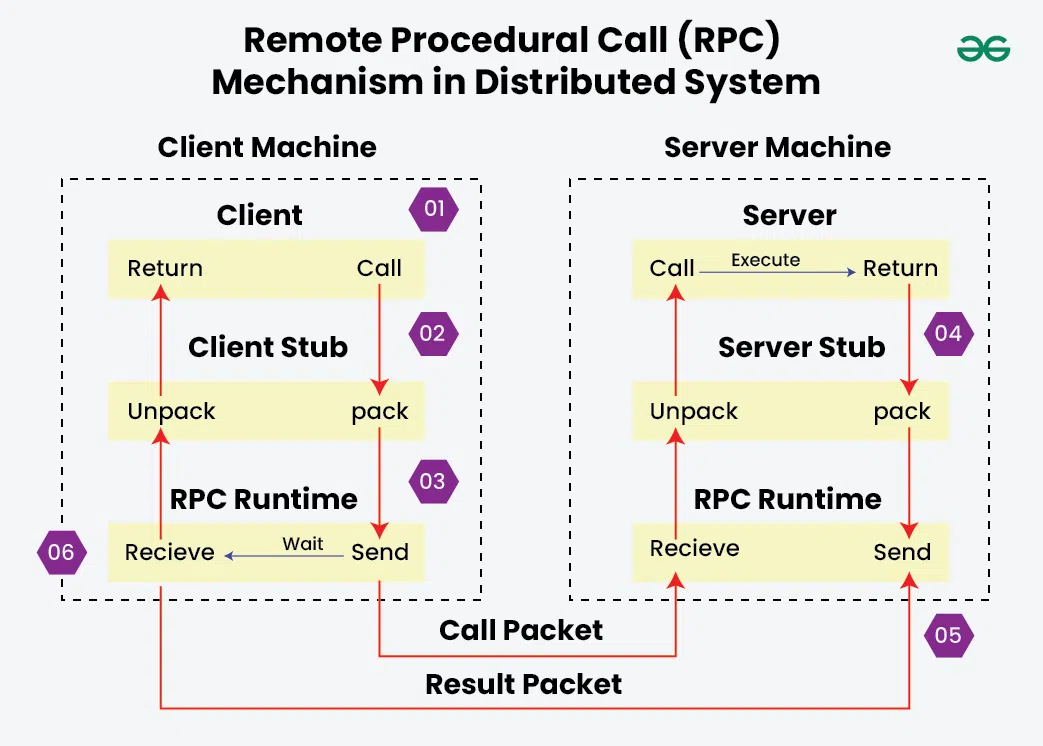
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
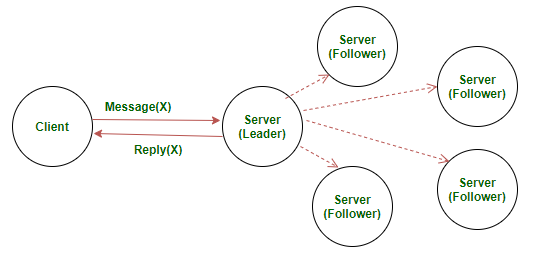
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
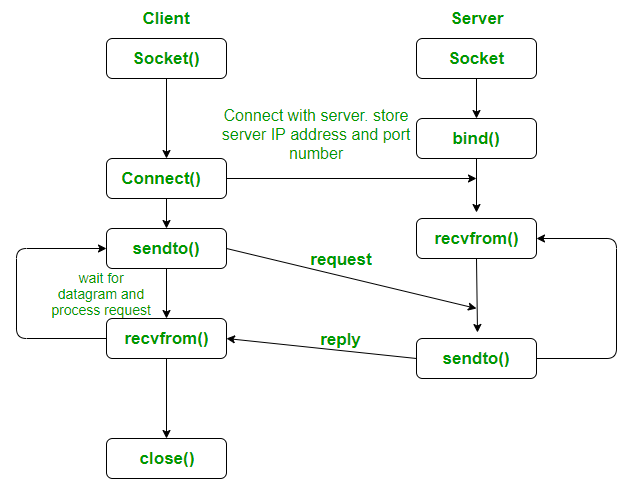
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
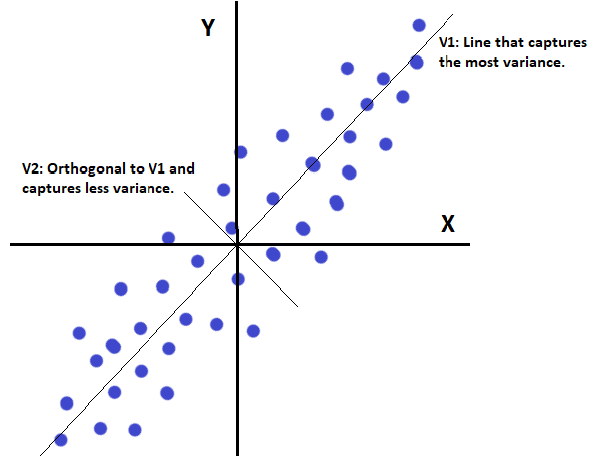
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
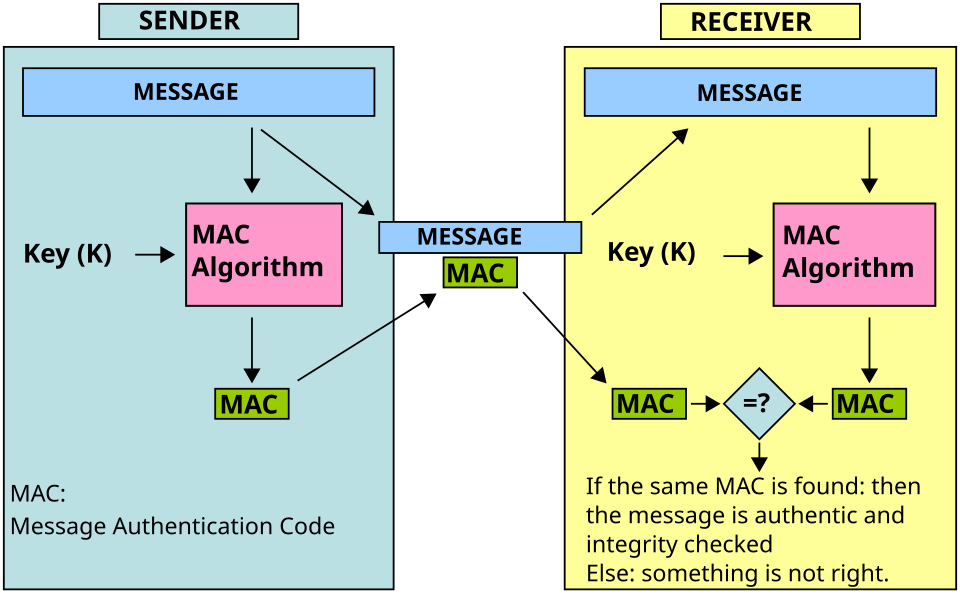
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
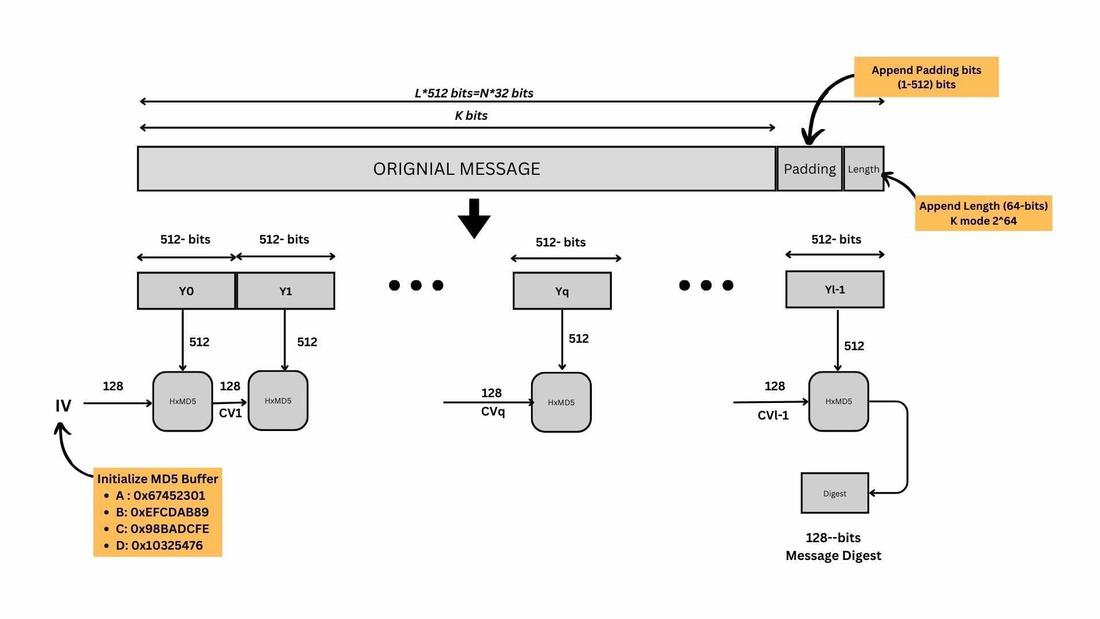
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)

Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
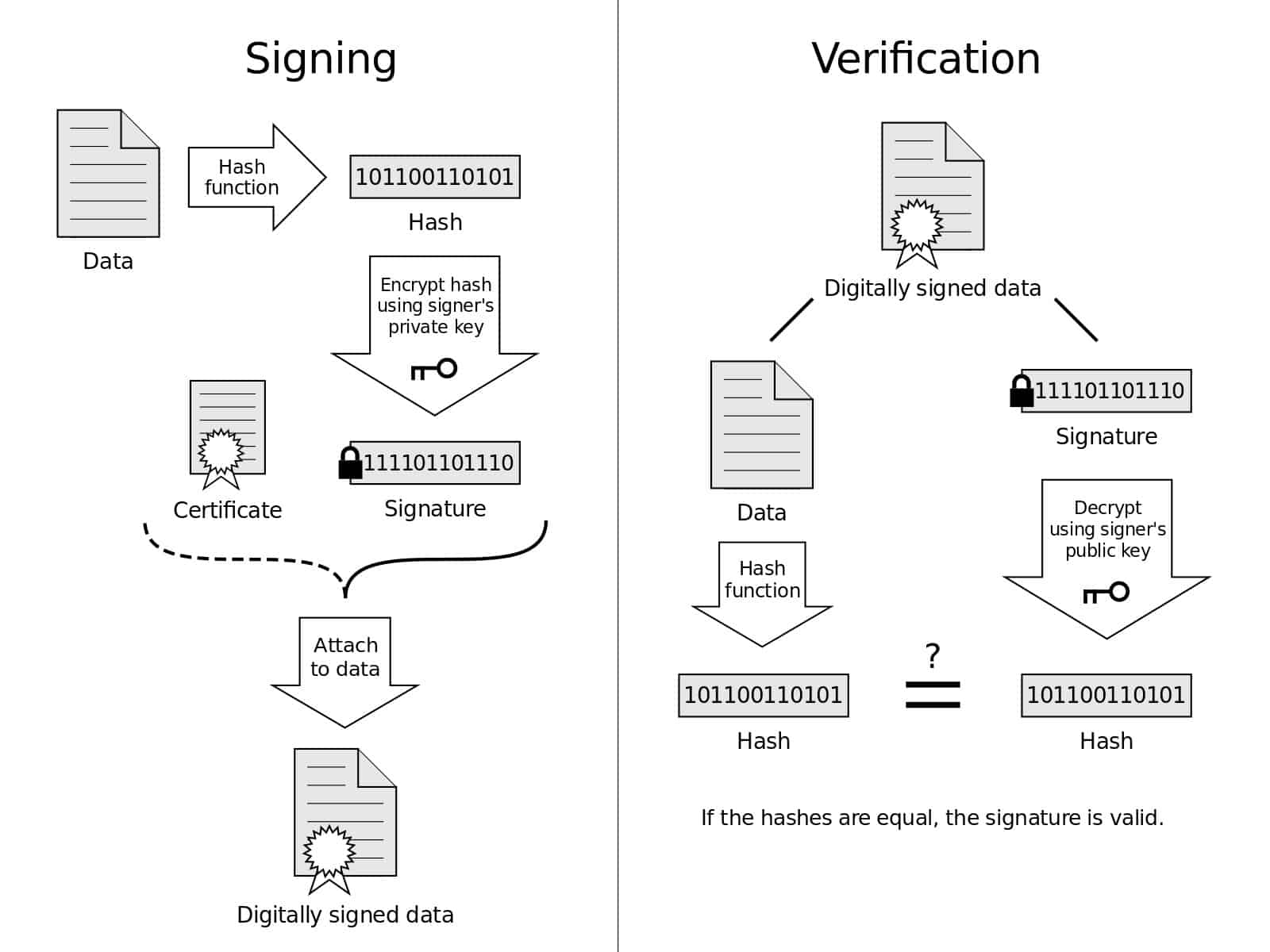
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
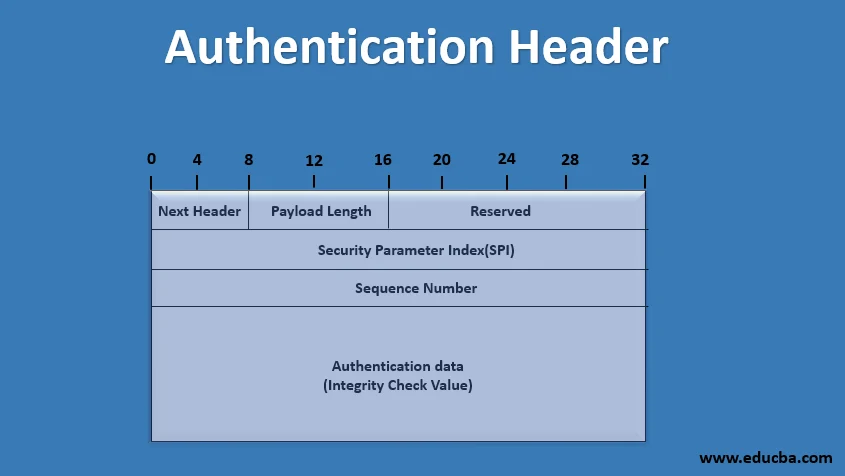
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes