
Symmetric Cryptography
Overview
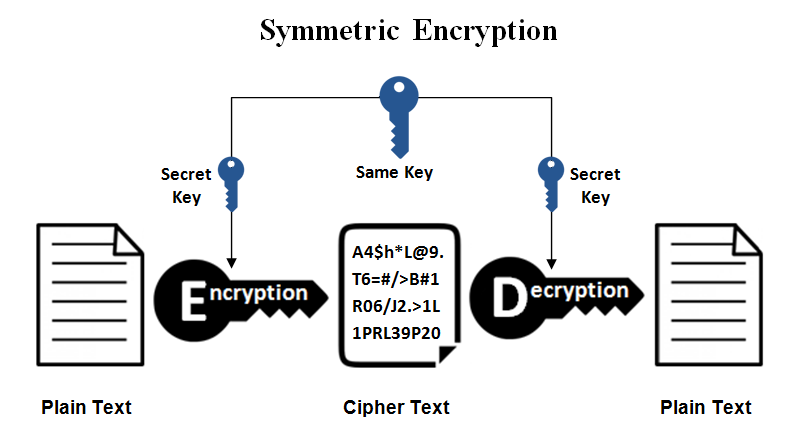
Symmetric cryptography uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, or for generating and verifying message authentication codes.
Basic Structure:
- y = (k,m) ; D(c,k) = m
- E: (k,m) ; D: (c,k)
m →|E|→ c →|D|→ m
↑k ↑k
MAC (Message Authentication Codes)
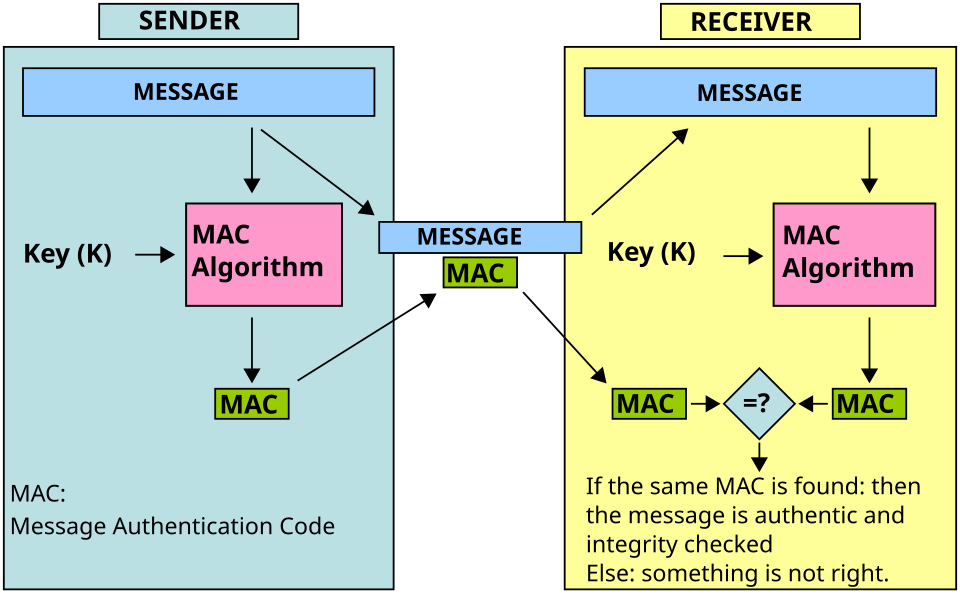
Fundamentals
Symmetric key → if attacker has Mₖ, Cₖ(M). Contains M’ for Cₖ(M')
- NO confidentiality - that is hasn’t been tampered with
- Cₖ(M) is uniformly distributed over Cₖ(M)
|tag| message m|
Generate tag:
- tag = Sₖ(m)
- tag’ = MAC(k,m')
- tag = MAC(k,m)
- If tag’ = tag ∴ m = m’ - passed!
Hₖ: M → T
Uses key (k) to map msg to tag with fnc. Hₖ
- Tag is fixed length
- If attacker had key - would pass verification
Security Properties
Integrity: Bob knows msg wasn’t modified.
Authenticity: Bob knows msg is with someone with the key
Confidentiality: Bob doesn’t know Alice sent the msg - if key is intercepted - attacker (in some cases) can send msg.
Condition: → If attacker has M & Cₖ(M) → getting K is hard beyond Integrity - Was msg sent by right person? → Cₖ(M) is uniformly distributed over Cₖ(M) → NO confidentiality - that is hasn’t been tampered with
One-Key MAC - DES with CBC
→ MAC can persist on any size msg so separate msg into 64-bit blocks, pad it to do DES
→ Compress msg into 64bit · 2⁶⁴ crumb.
→ Oₙ = Eₖ(Dₙ ⊕ Oₙ₋₁)
Attacks on MAC
1) Exhaustive Search - Total Break
→ If attacker has key → total break → Given M || Cₖ(M) = MAC, find K
2) Fake Message for Given Auth. Tag - Don’t Need Key
∴ Msg input can have any size but tag space is fixed, multiple msgs have same tag d. where tag = MAC(k,m)
Bob won’t know msg is faked b/c tag passes auth.
Exhaustive Key Search
Round 1) For all 2ᵏ keys - given M₁ & MAC₁
- do search to find N tags where MACᵢ = Cₖ(M₁) many keys would hold.
Round 2) Round 1 has 2ᵏ⁻ⁿ possibilities, do search for M₂, MAC₂ on 2ᵏ⁻ⁿ to yield 2ᵏ⁻²ⁿ
Example:
- n: |k| = 80 Round 1 = 2⁸⁰⁻³² = 2⁴⁸
- |n| = 32bit Round 2: 2⁴⁸⁻³² = 2¹⁶
- Round 3 - find key.
Forge Message Attack
ECB-DES: 56 bit keysize, 64 bit MAC.
- ΔM = X₀X₁⊕…Xₙ (XOR all msg)
- If attacker does reuse XOR - they can forge a new msg → for ECB: NOT DES
3 Types of MAC
a) Msg Authentication
Cₖ[M]
b) Auth & Confidentiality: Auth in Plaintext
Eₖ₂[M] || Cₖ(M)
c) Auth & Confidentiality: Auth on Ciphertext
Cₖ₂(Eₖ₁[M])
Secret Key Systems
Secret Key - MAC used -
- The person’s name managed is in the MAC (per session) b/c secret key K is shared so either can make MACs
Key Concepts Summary
Authenticity - Is msg mod’d Integrity - Was msg sent by right person?
If key is intercepted - attacker can send msg, and they’ll pass!
Computer Vision
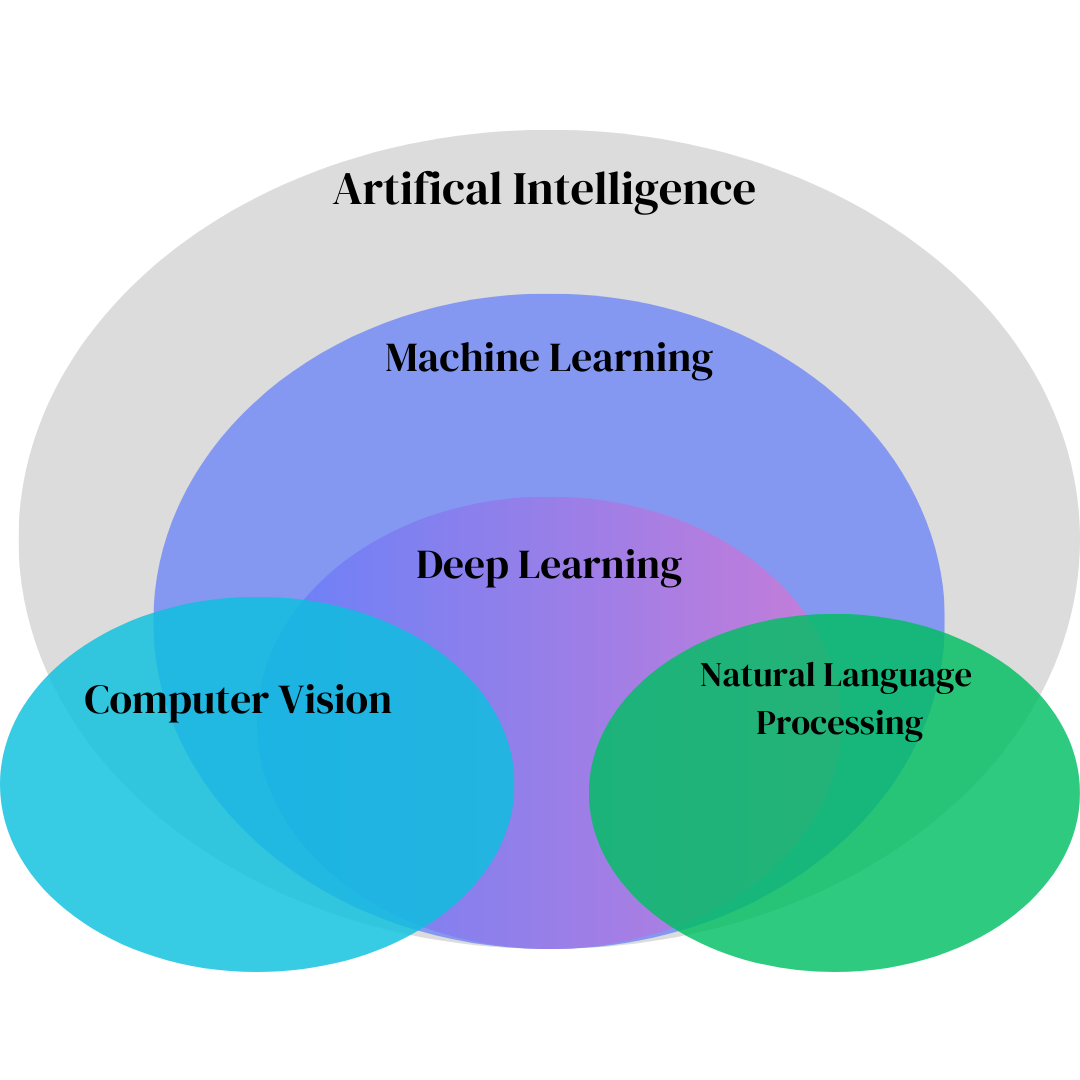
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
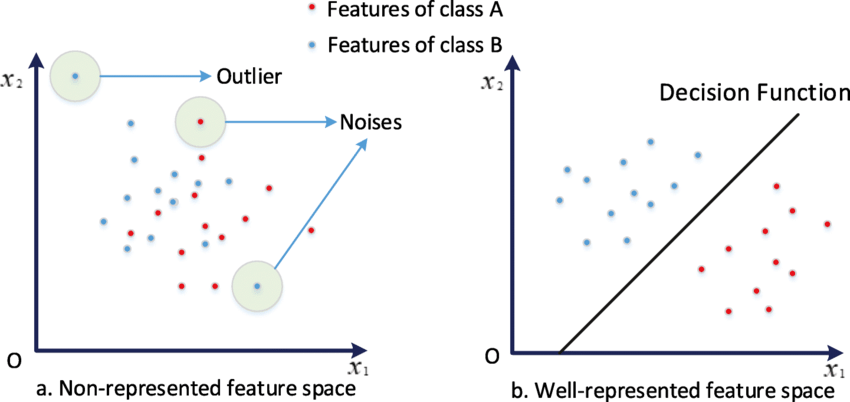
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
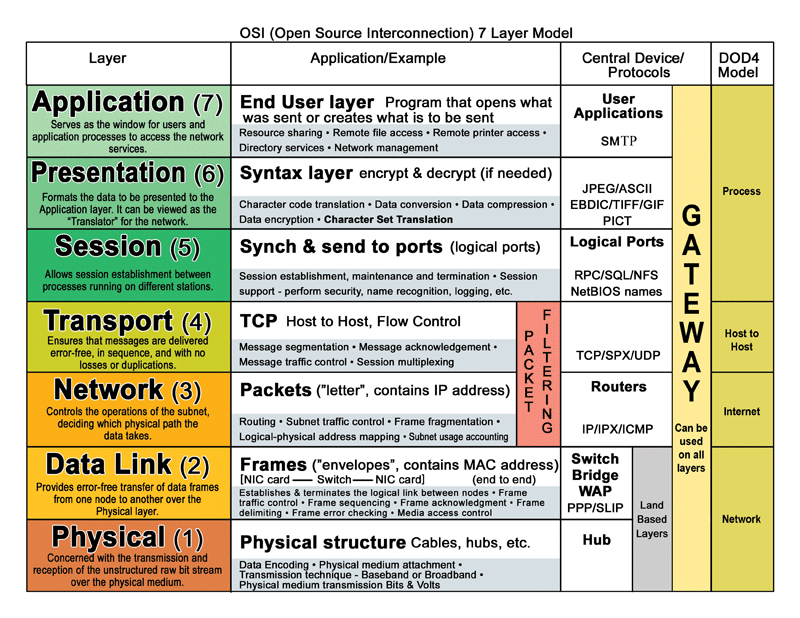
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
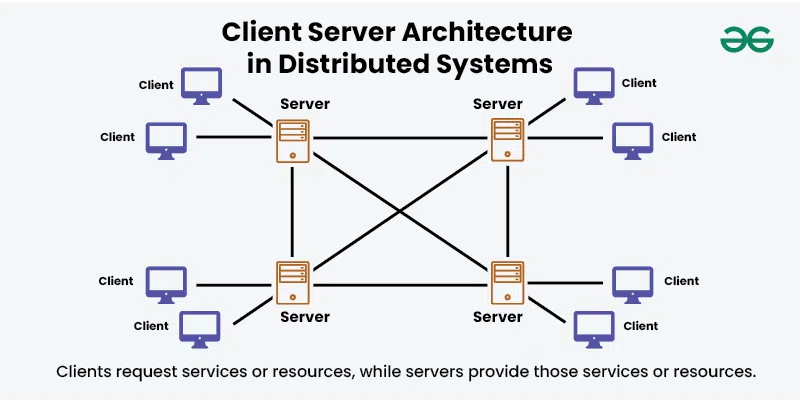
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
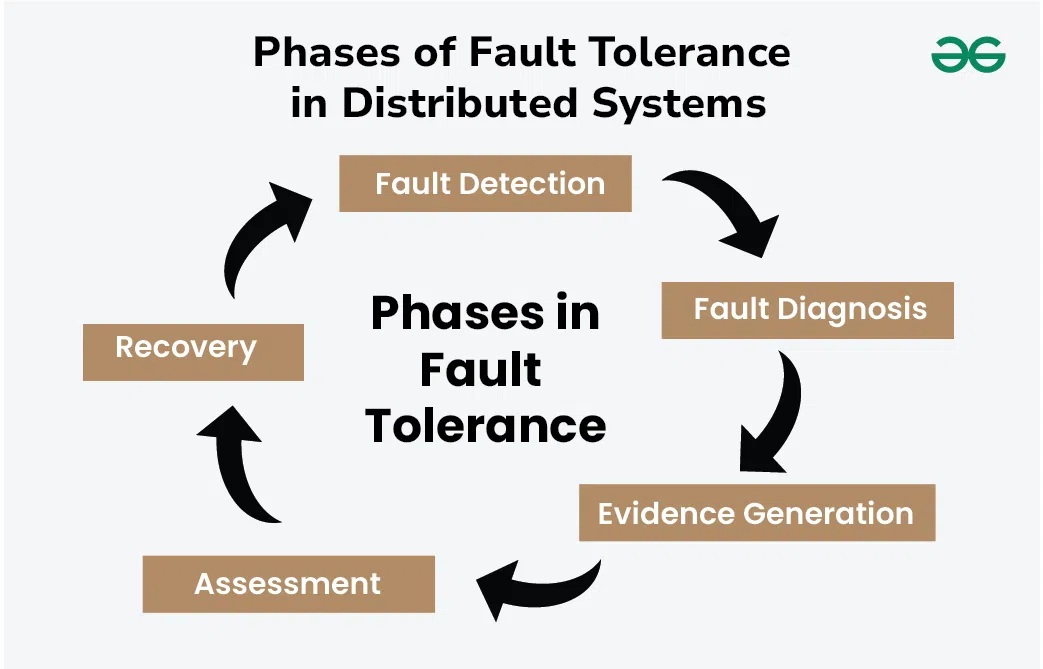
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
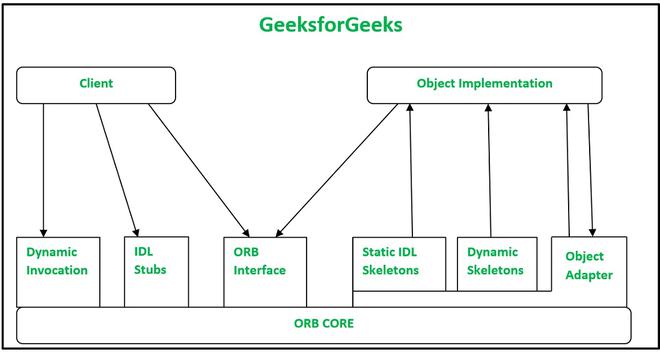
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
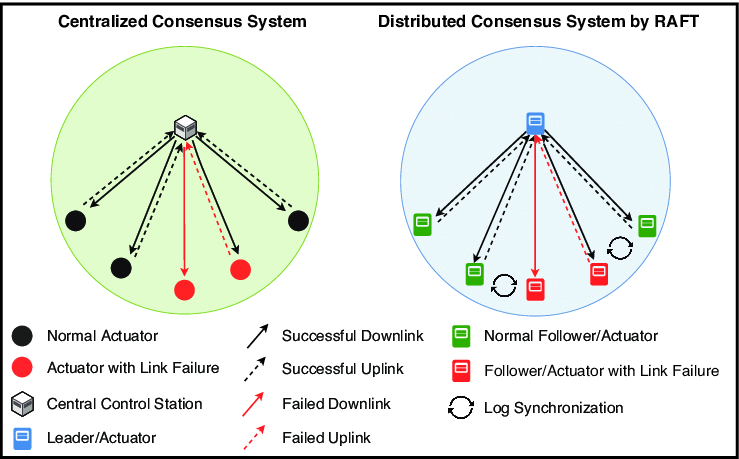
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
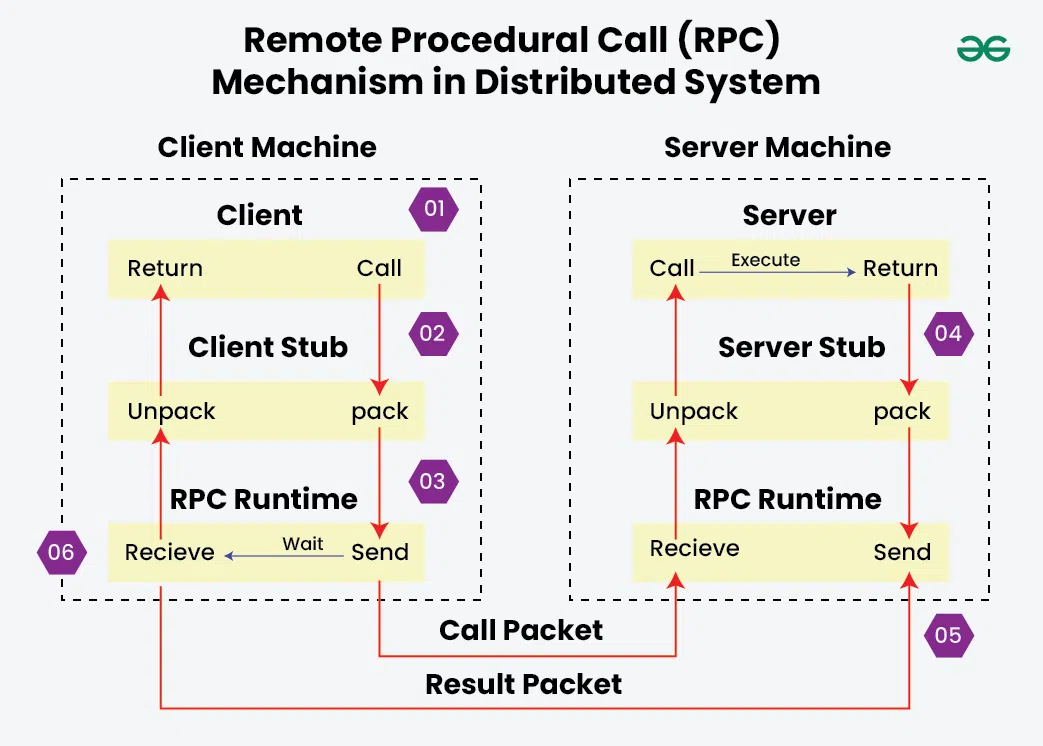
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
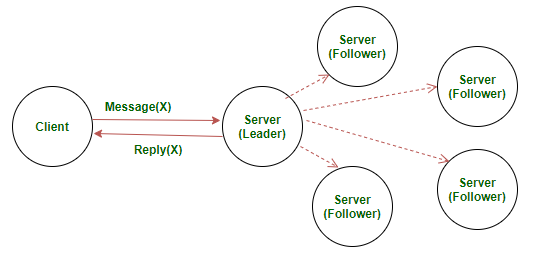
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
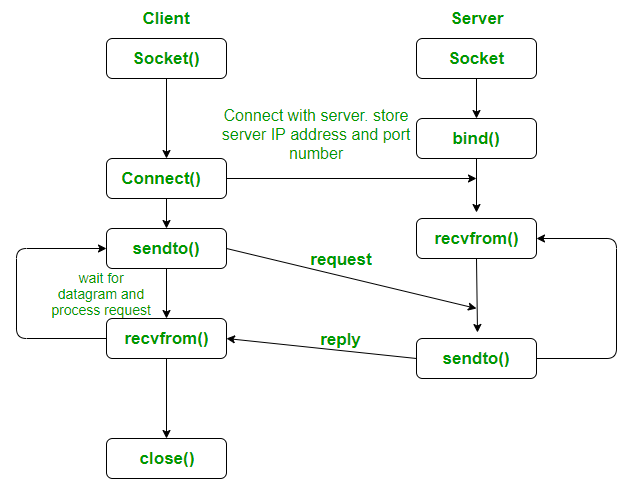
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
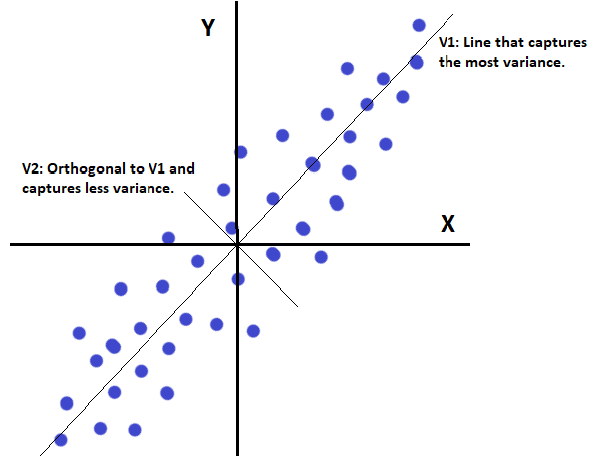
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems

Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
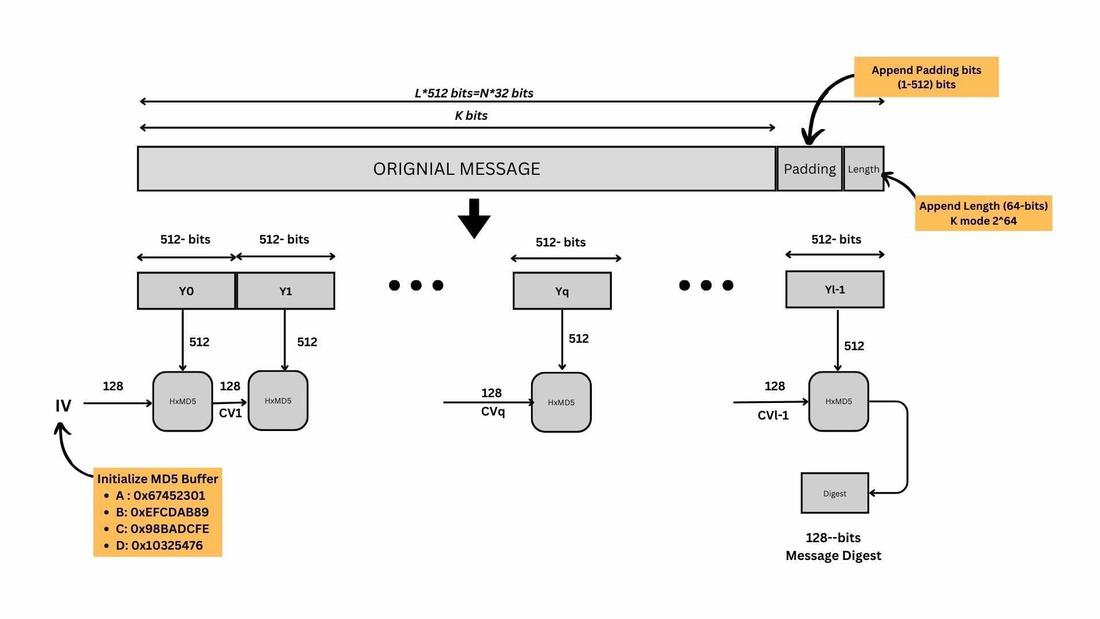
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
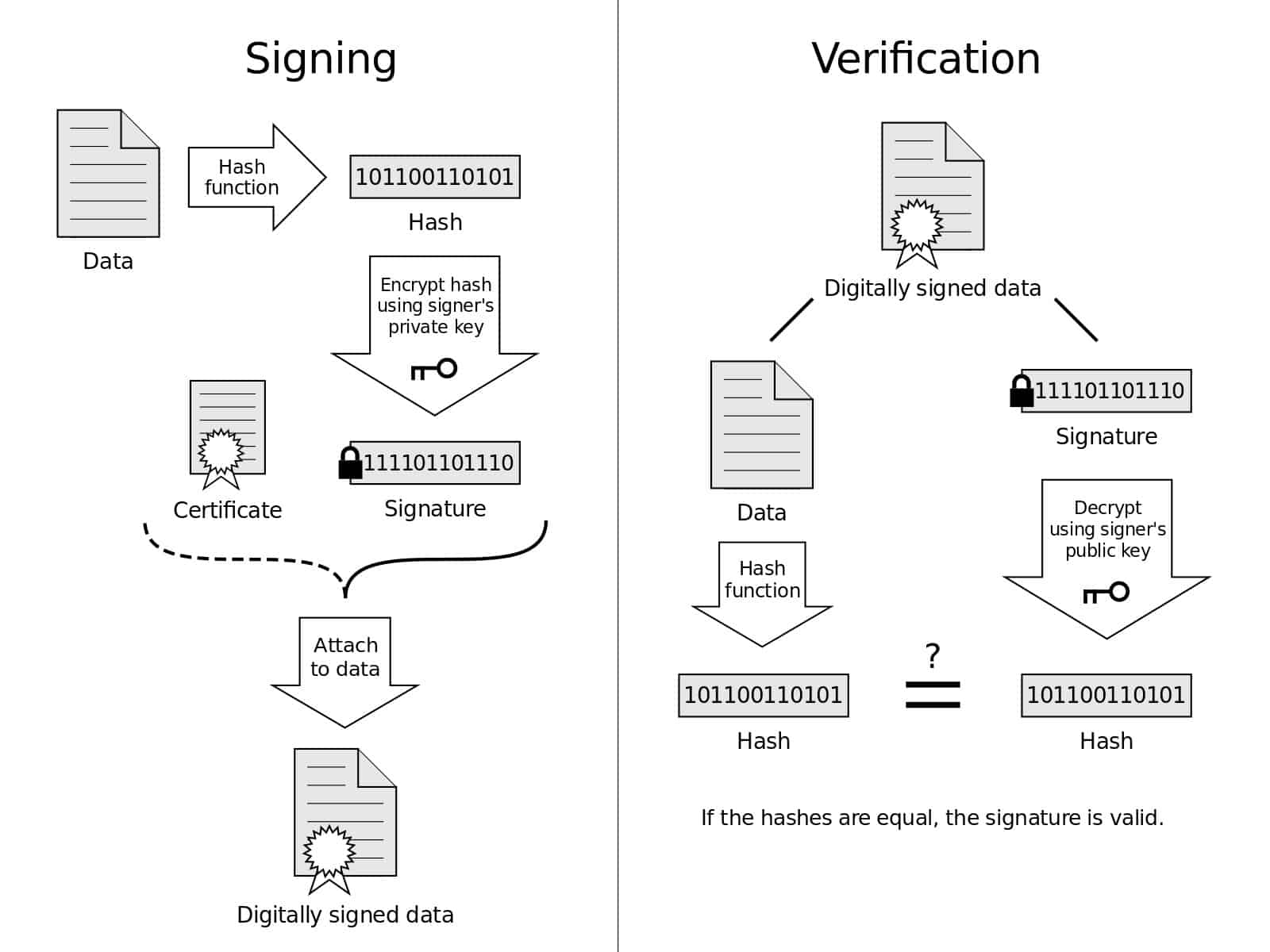
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
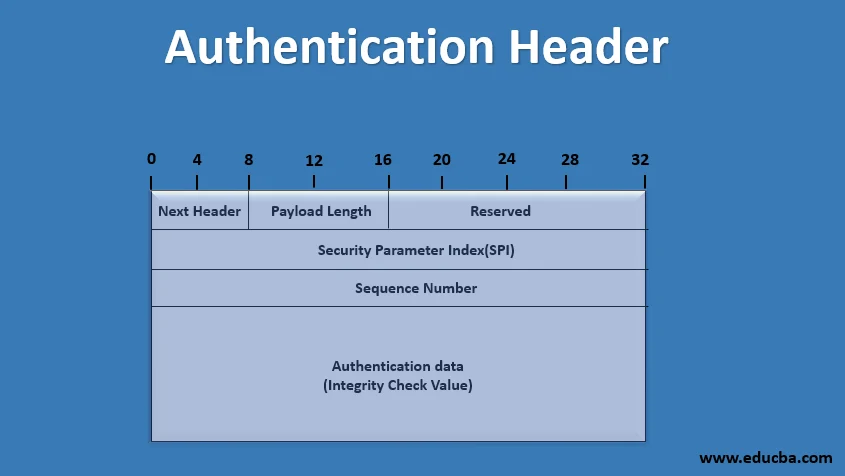
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes