
Machine Learning & Computer Vision
History of Computer Vision
Computer Vision: Emulates the human visual system, interpreting images via sensing. Applications include self-driving cars, surveillance, and biomedical imaging.
Classical Era vs. Deep Era
- Classical Era (1960s–2000s): Based on mathematical principles and handcrafted features (e.g., stereovision, projective geometry, SIFT). Rule-based and explicit.
- Deep Learning Era (2012+): Neural network–driven, data-centric, and end-to-end learning.
Computer Vision vs. Machine Learning
- Computer Vision (CV) is a subfield of Machine Learning (ML).
- Features: Measurements for object identification. In classical CV, features are handcrafted; in ML-based CV, models learn them automatically from data.
ML-based CV vs. Classic CV
ML-based CV: Train/test workflow; models learn mappings from data to results.

Classic CV: Predefined feature extraction + simpler classifiers.
Factors Leading to ML Rise
- Improved AI algorithms.
- GPUs enabling massive parallelism (3–4 orders of magnitude faster than CPUs).
- Large datasets (e.g., ImageNet).
- Open-source libraries (Jupyter, TensorFlow, PyTorch).
Computer Vision

Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning

History of Computer Vision
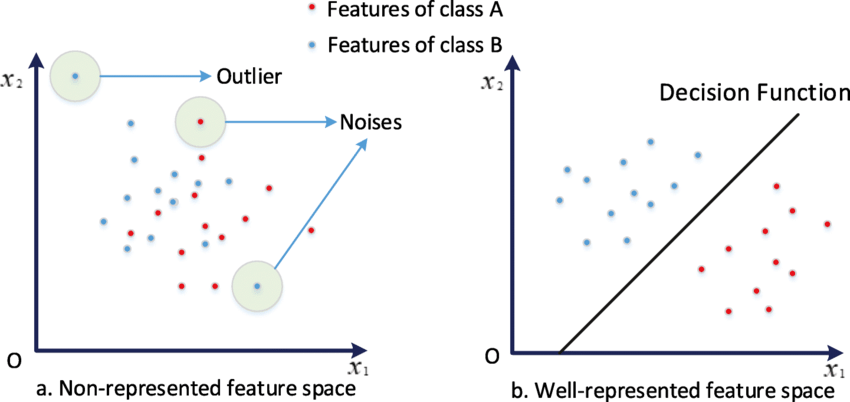
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
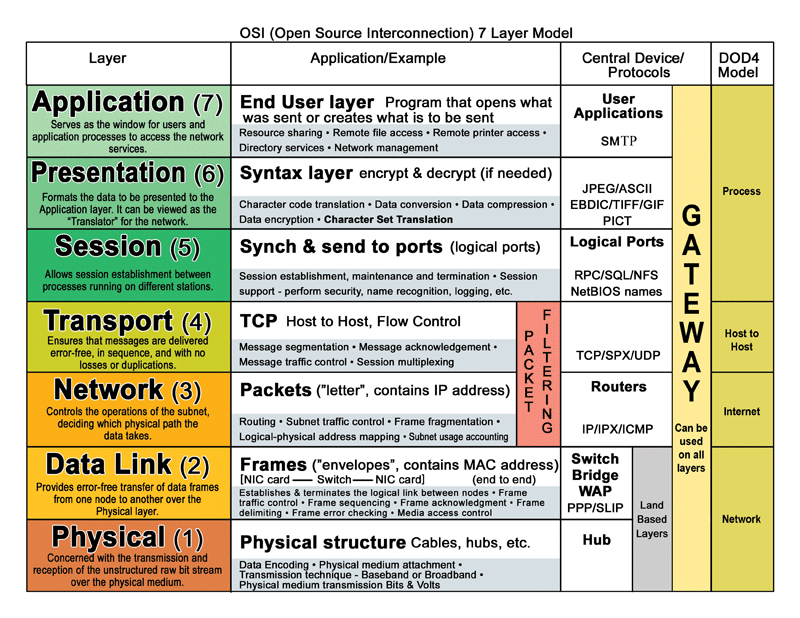
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
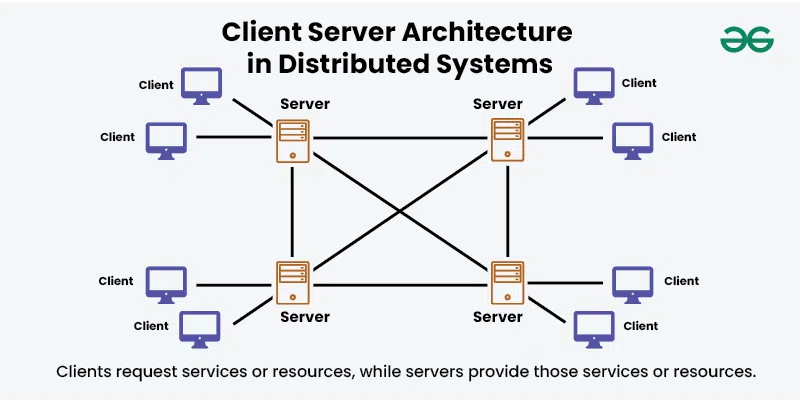
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
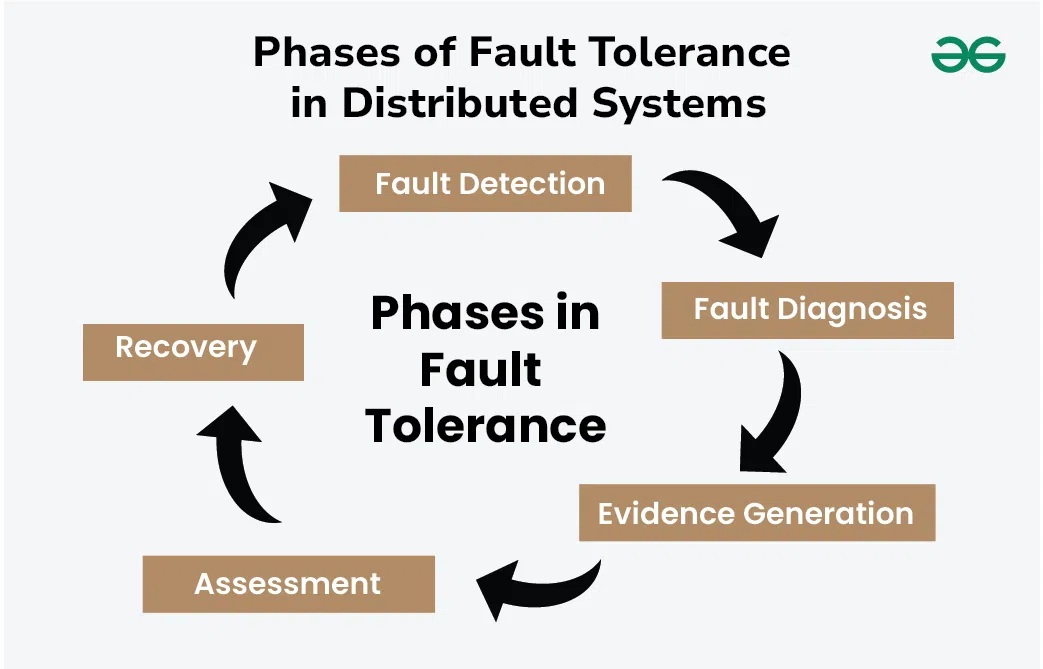
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
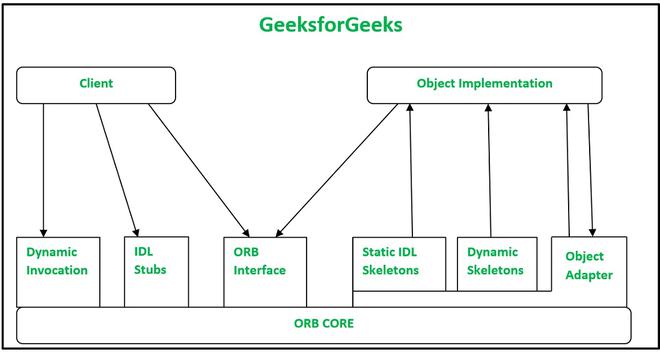
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
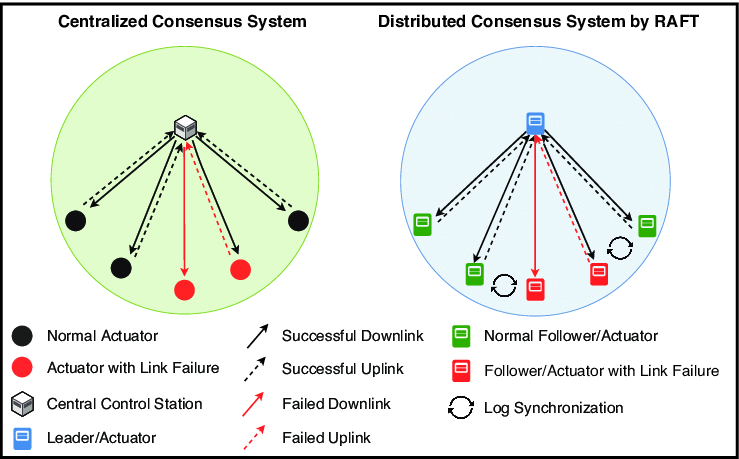
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
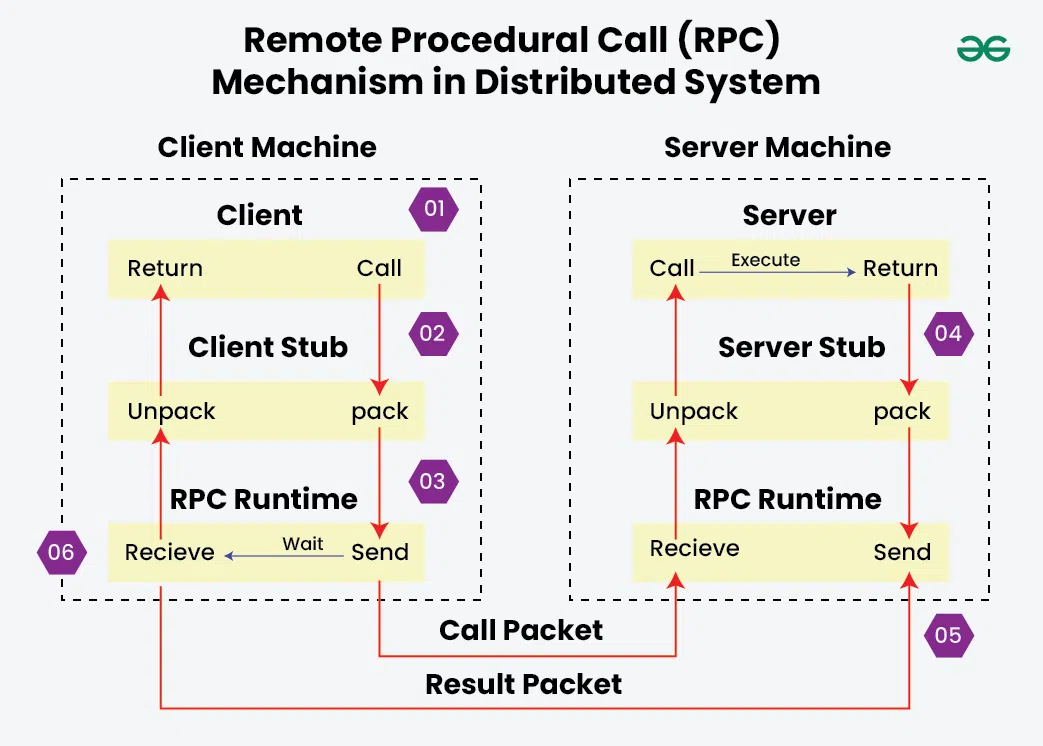
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
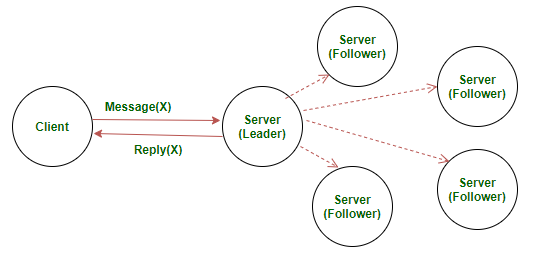
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
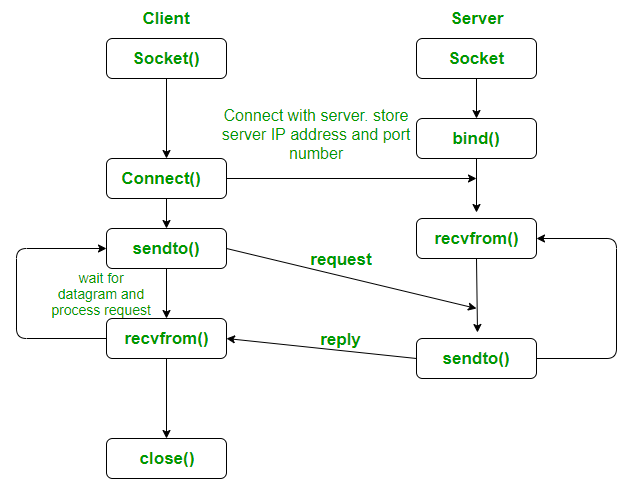
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
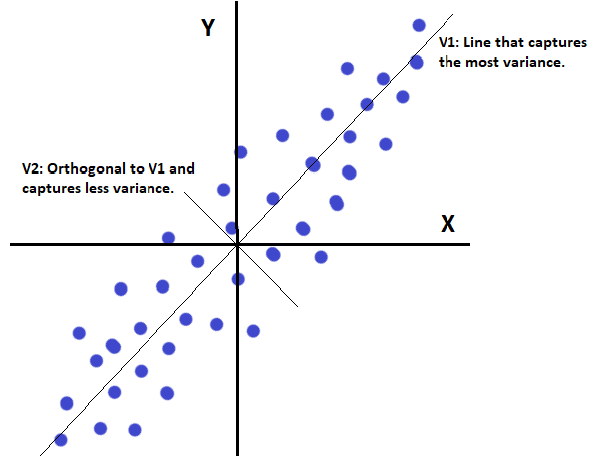
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
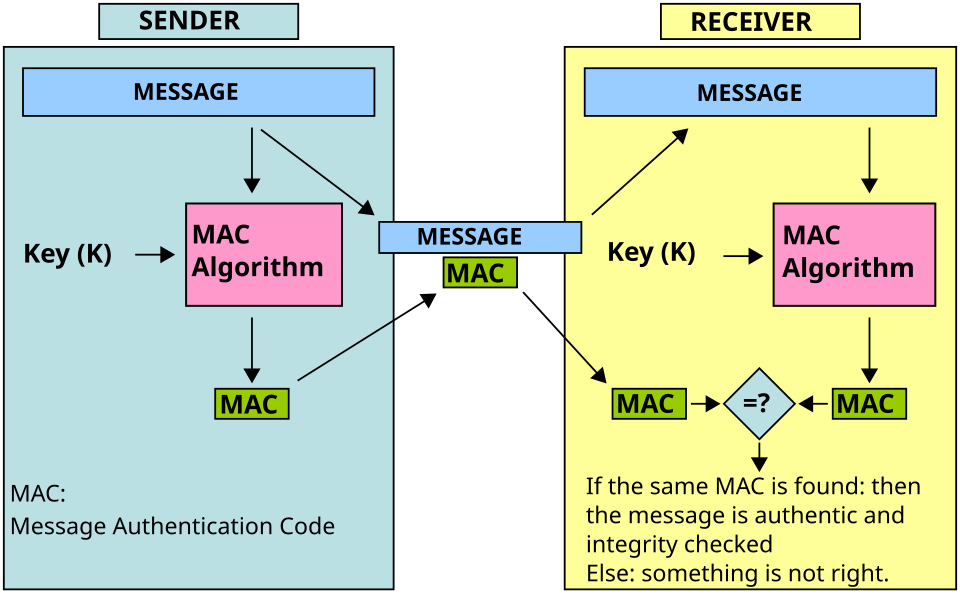
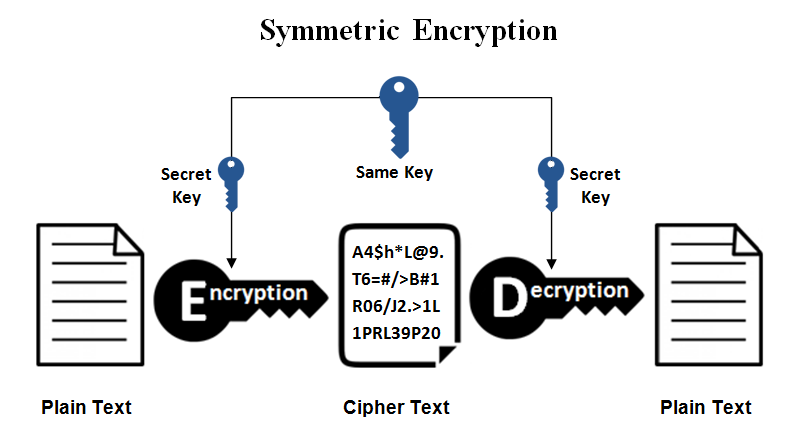
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
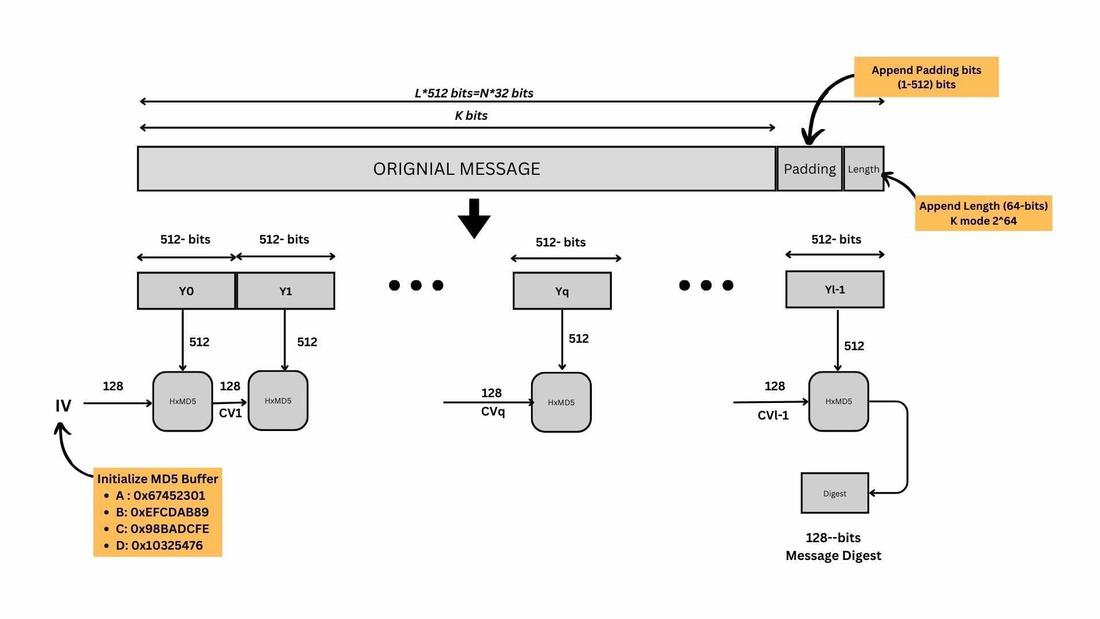
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
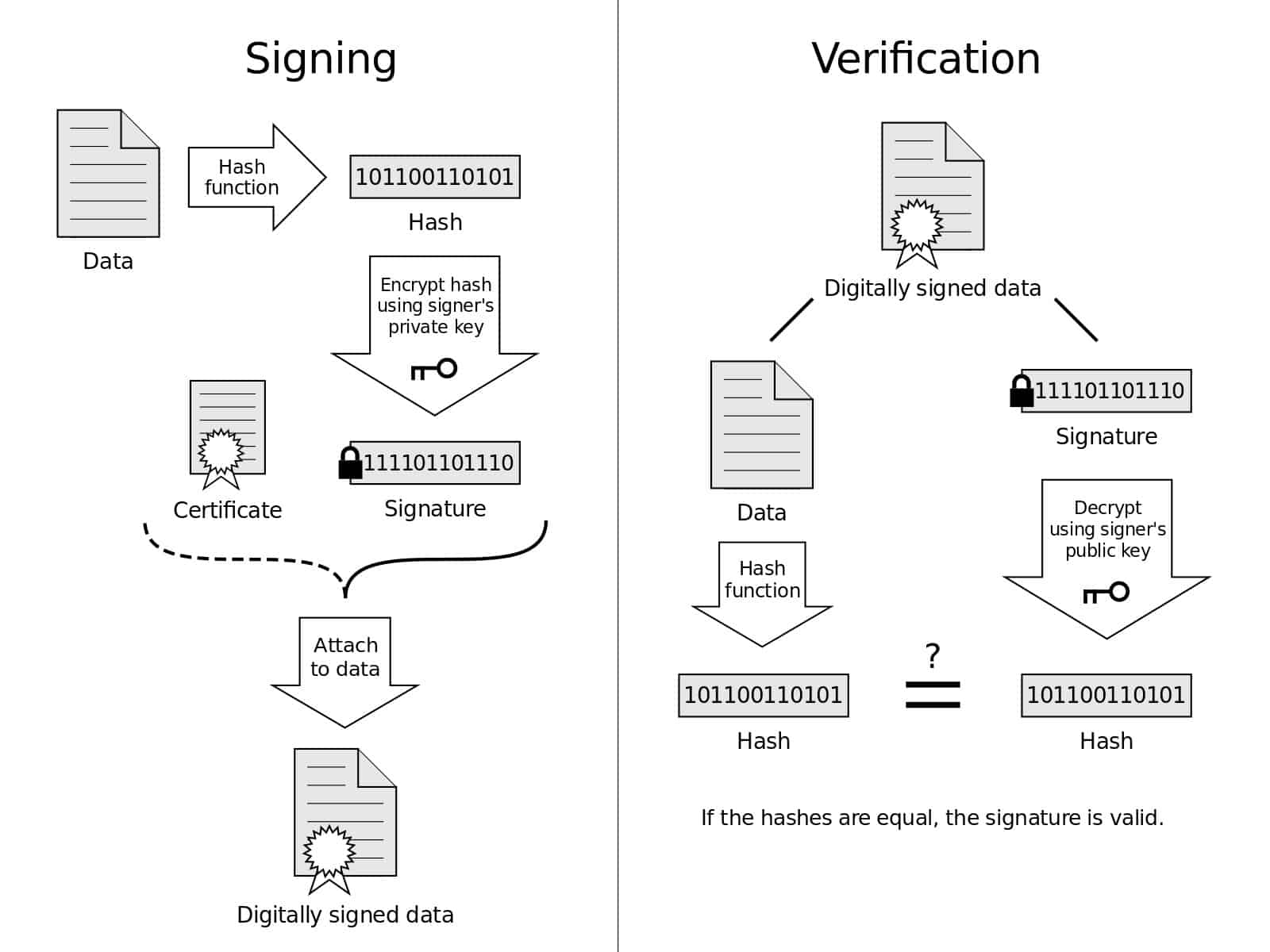
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
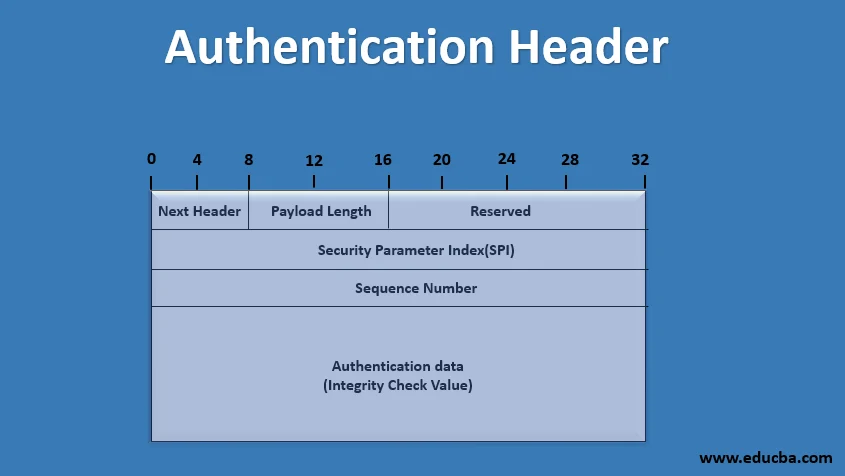
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes