
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC)
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC)
- Main Objective: Advance state-of-the-art in image classification, object detection, and localization at scale.
- Competition Timeline: Ran annually from 2010–2017.
- Organized by: The ImageNet project, at Princeton and Stanford.
- Dataset: Subset of the full ImageNet database, covering 1,000 object categories with over 1.2 million training images, 50,000 validation images, and 100,000 test images.
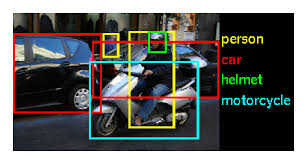
Tasks
- Image Classification: Assign a single class label to an image. Top-1 and Top-5 accuracy were standard metrics.
- Object Localization: Predict both the class label and the bounding box of the primary object in the image.
- Object Detection: Detect and localize multiple objects of different categories in an image with bounding boxes (2013–2017).
- Scene Parsing (later years): Pixel-wise labeling of scenes into object categories.
Impact of ILSVRC
- Catalyst for Deep Learning: ILSVRC popularized deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which outperformed traditional hand-crafted feature methods.
- Benchmarking: Provided a standardized benchmark for comparing algorithms in computer vision.
- Industrial Relevance: Progress at ILSVRC directly influenced advances in self-driving cars, facial recognition, and large-scale image search.
Winners and Breakthroughs
- 2010–2011: Non-deep learning methods (SIFT, HOG, bag-of-words) dominated before the deep learning breakthrough.
- 2012: AlexNet by Krizhevsky, Sutskever, and Hinton — reduced Top-5 error from ~26% to ~15% using deep CNNs and GPUs.
- 2013: ZFNet refined AlexNet with visualization-guided improvements; VGG also appeared with deeper networks.
- 2014: GoogLeNet (Inception) — introduced inception modules for efficient depth and parameter reduction.
- 2015: ResNet — introduced residual connections, enabling networks over 100 layers deep; achieved ~3.6% Top-5 error (surpassing human-level performance).
- 2016–2017: Variants of ResNet, Inception-ResNet, and ensemble methods. Less inventive so the challenge concluded.
Evaluation Metrics
- Top-1 Accuracy: Percentage of times the top predicted label matches the ground truth.
- Top-5 Accuracy: Percentage of times the ground truth label is among the top 5 predictions.
- mAP (mean Average Precision): Standard metric for object detection tasks.
ZFNet
- Motivation: Improve upon AlexNet using feature visualization as diagnostic feedback.
- Technique: Introduced deconvolutional visualization to “look inside” CNNs and understand feature activations.
Key Concepts Introduced in ZFNet
Convolutions
- Linear operations, theoretically invertible.
- Inversion achieved with transposed filters (transpose convolution).
Deconvolution (a.k.a. Transposed Convolution)
- Projects feature activations back to the input space.
- Highlights what patterns neurons in deeper layers respond to.
Unpooling
- Attempts to reverse max-pooling by using “switches” that record the position of maximum activations.
- Reassigns features to approximate original spatial structure.
Receptive Field
- Region of the input image influencing a neuron in a given layer.
- Determined by kernel size, stride, and depth of the network.
Ablation Studies
- Purpose: Assess contribution of model components.
- Examples in ZFNet:
- Occlusion tests with gray boxes measured robustness.
- Visualization revealed AlexNet’s large filters were suboptimal.
- Showed certain filters correspond to semantic object parts.
ZFNet vs. AlexNet
- Observations:
- AlexNet’s 11×11 first-layer filters with stride 4 caused aliasing and captured noise.
- ZFNet reduced filter size to 7×7 with stride 2 for sharper feature maps.
- Impact: Enabled clearer, more discriminative representations, guiding future architecture design.
Computer Vision
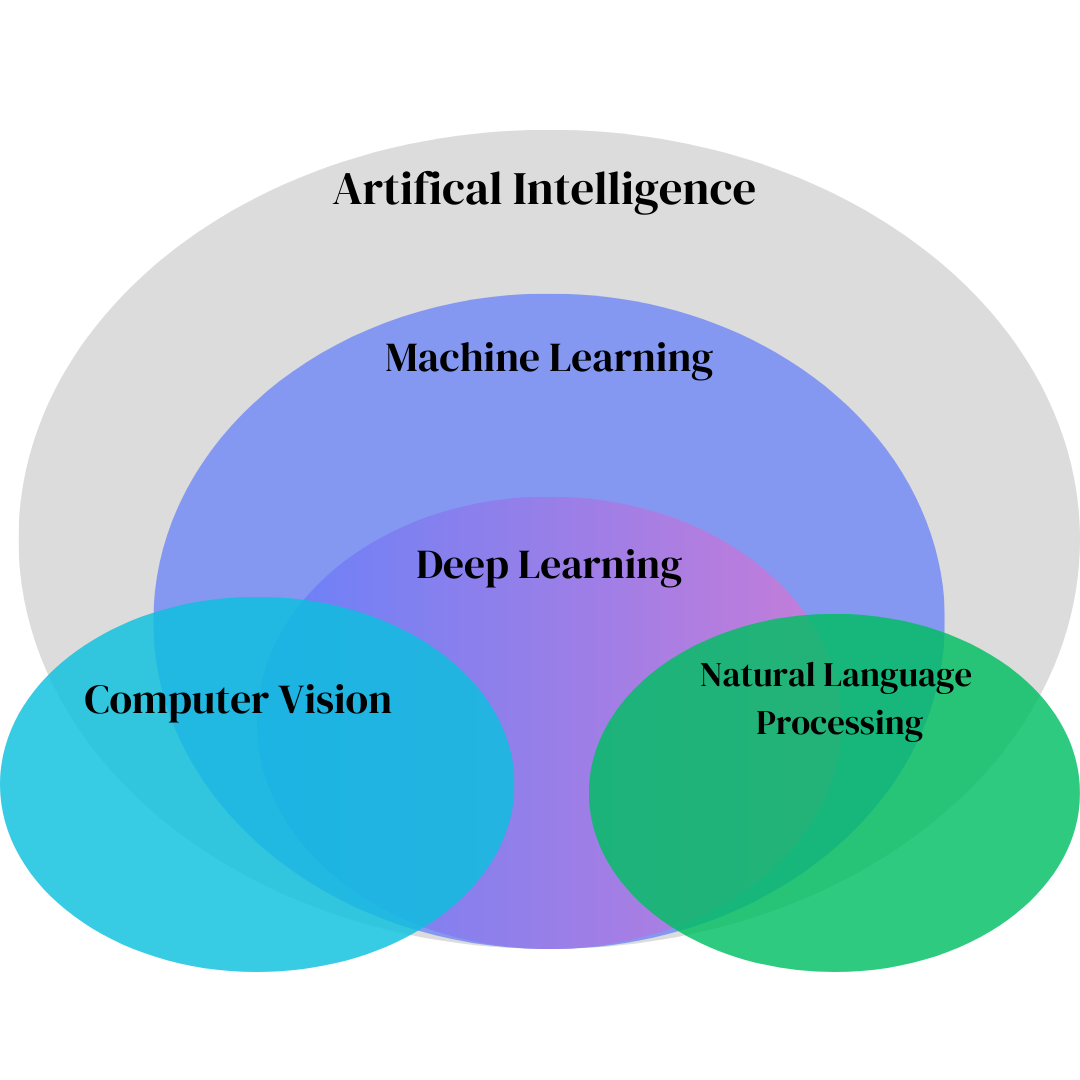
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
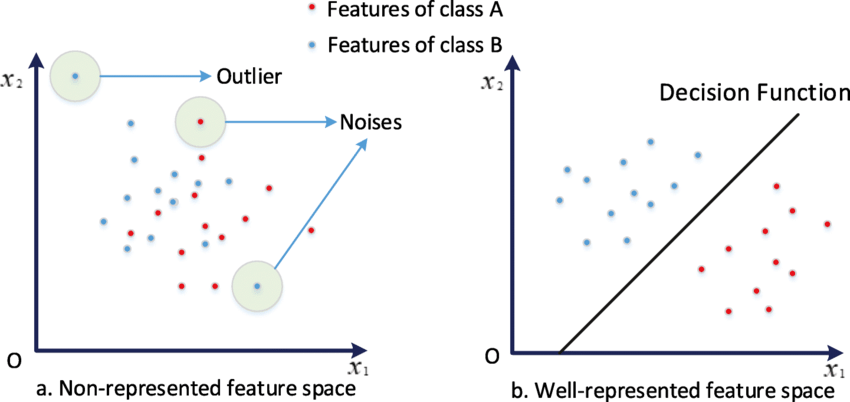
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces

ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
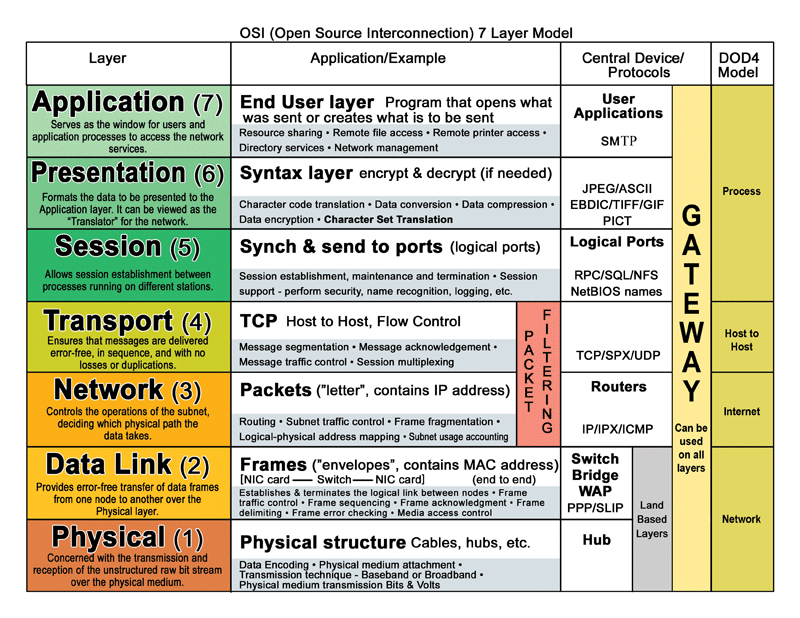
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
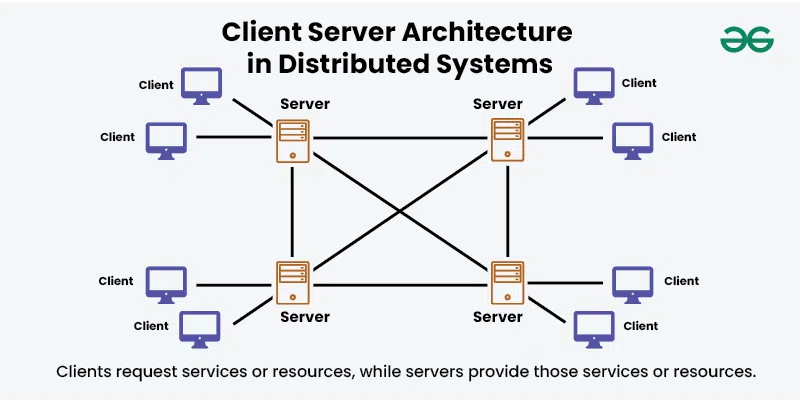
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
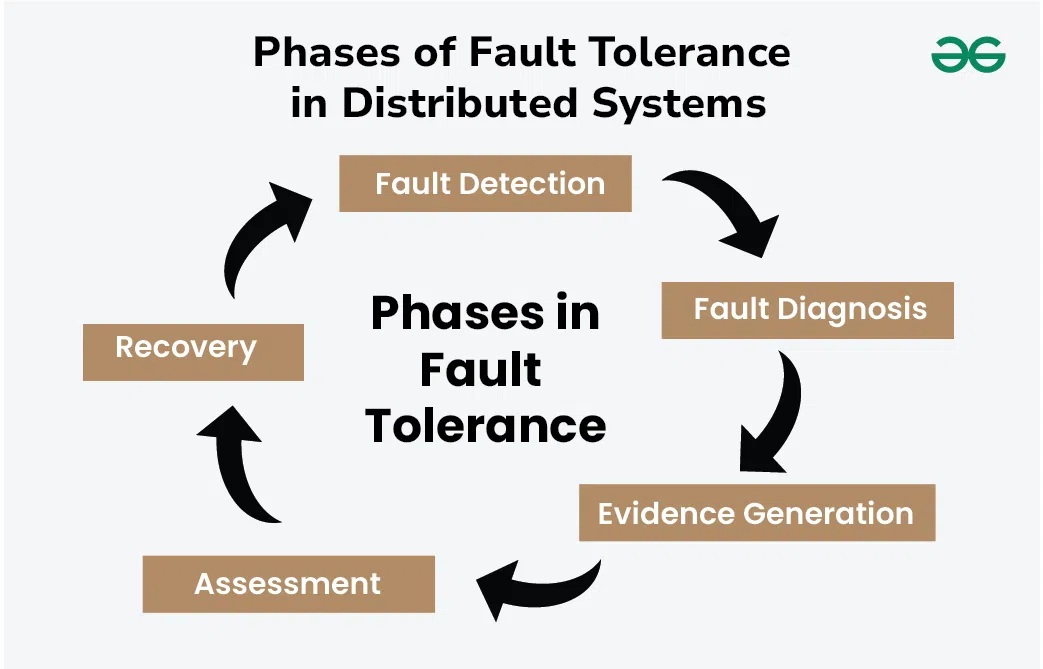
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
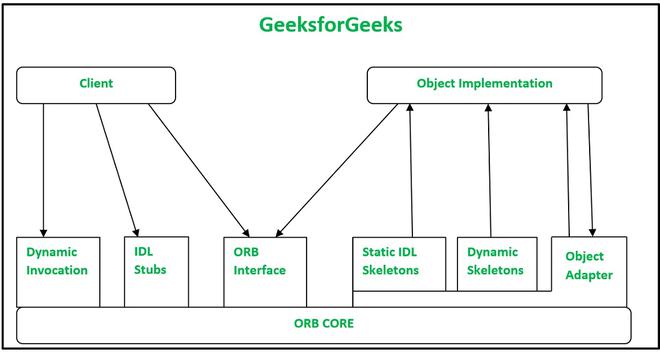
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
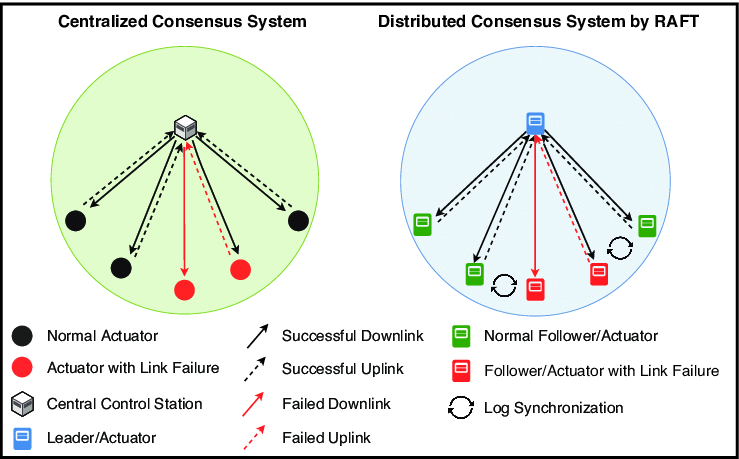
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
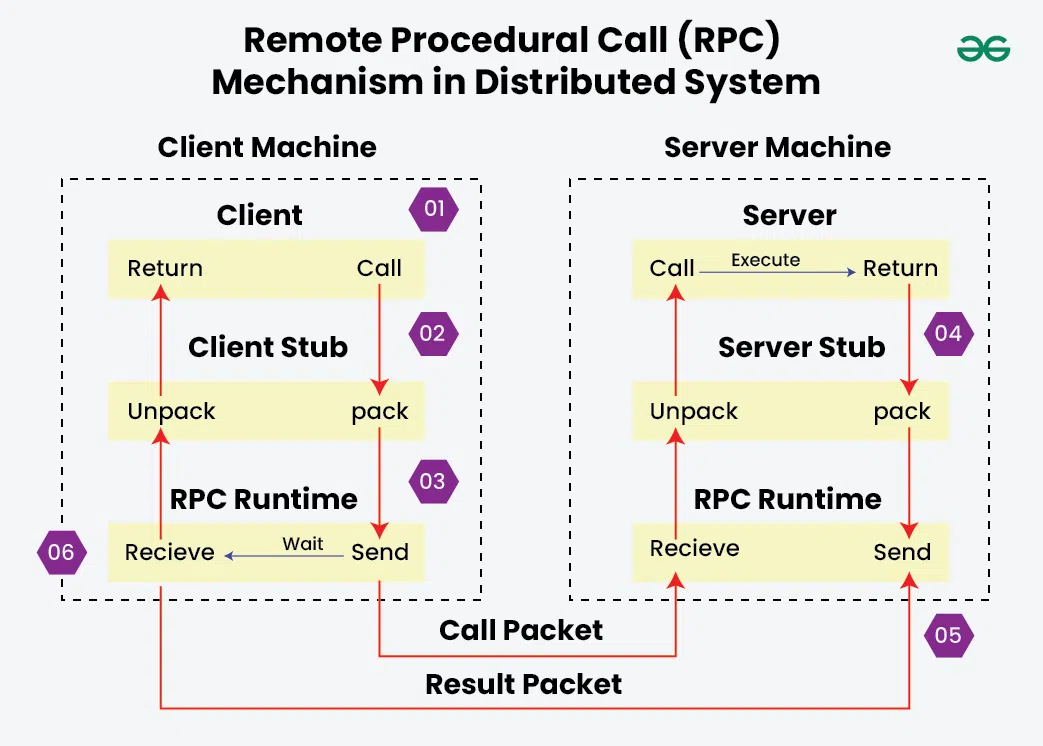
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
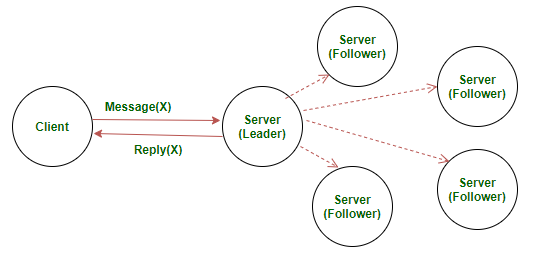
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
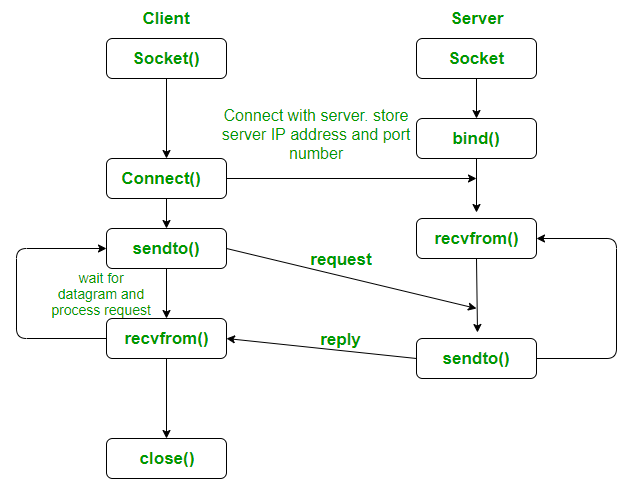
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
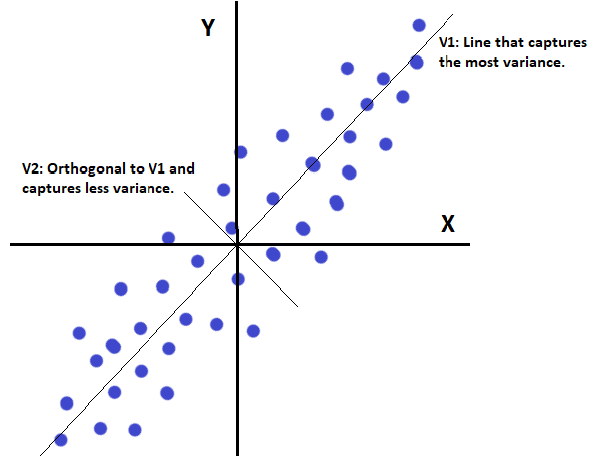
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
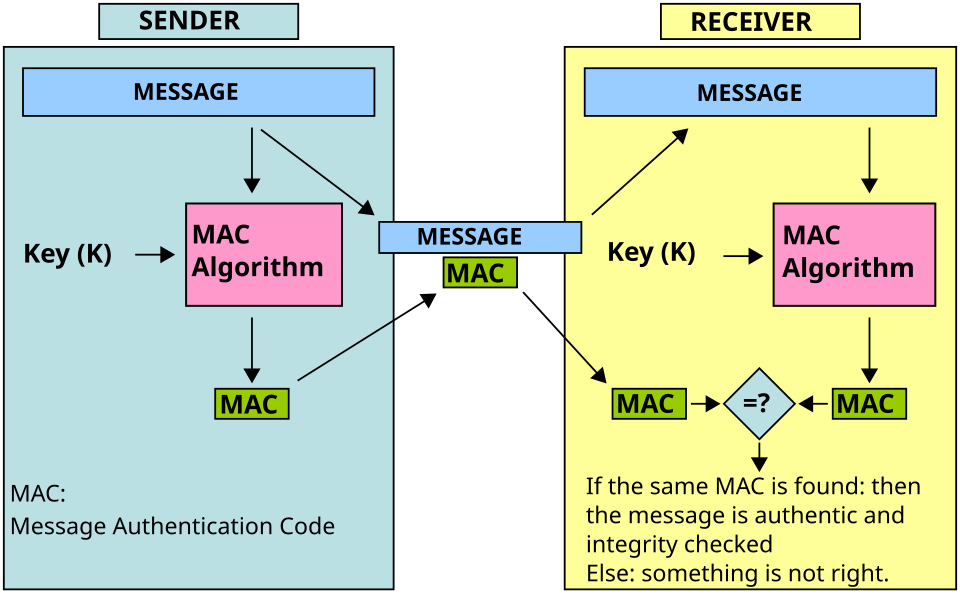
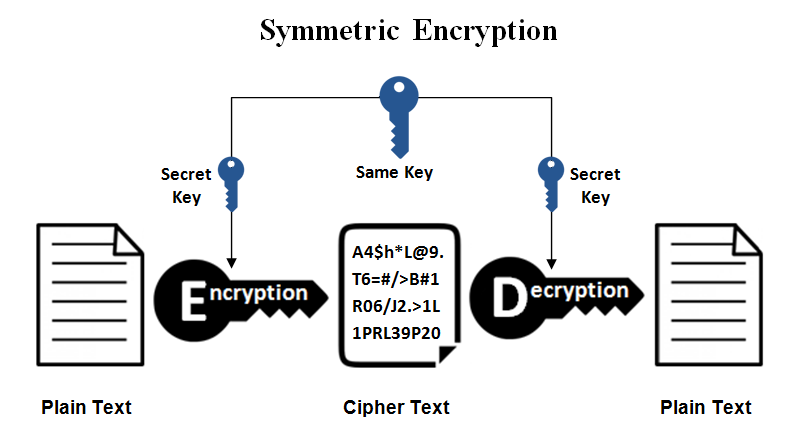
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
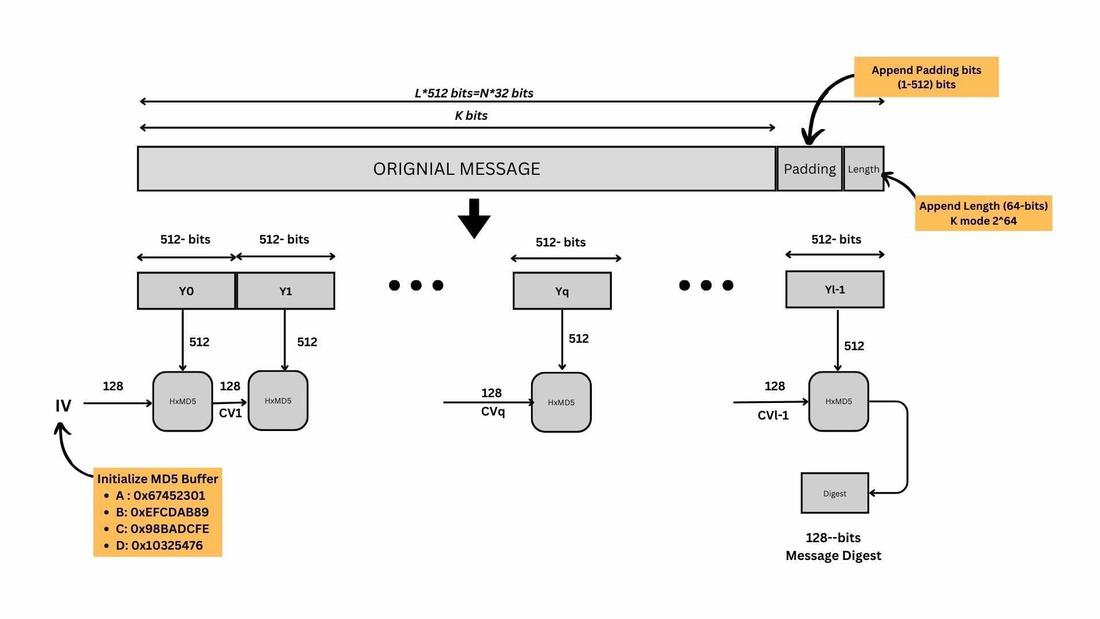
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
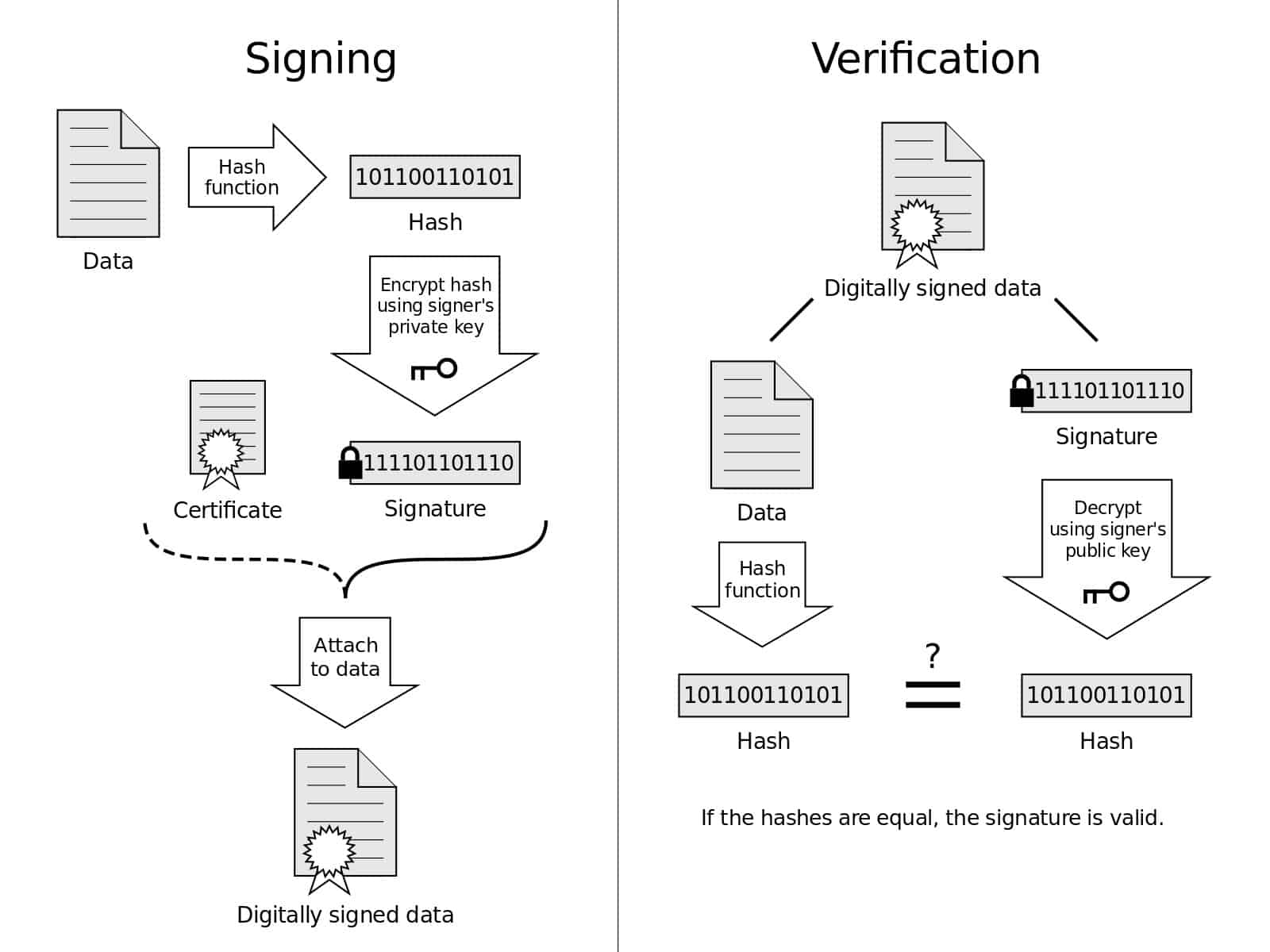
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
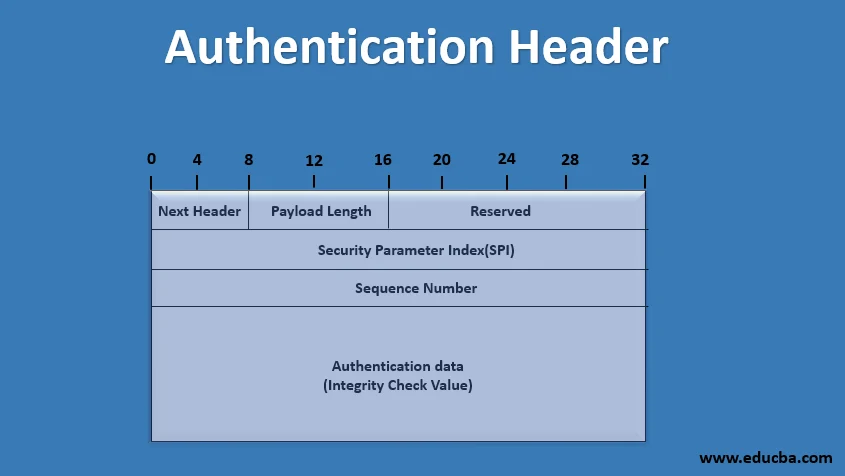
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes