
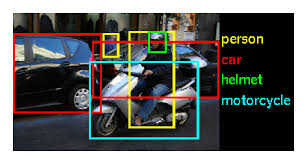
R-CNN (Region-based Convolutional Neural Network)
Task: Object detection (not just classification)
Approach: Two-stage detectors → first propose regions, then classify them (Alternative to one-stage detectors like YOLO, SSD which detect objects in single pass (faster but historically less accurate) )
R-CNN (2014)
- Runs CNN separately on ~2000 region proposals per image
- Uses selective search (external algorithm) for proposals
- Trains SVM classifiers separately from CNN features
- Bottleneck: Feature extraction happens 2000+ times per image
Cons of R-CNN
- Slow training time → requires lots of annotated & labelled data → multi-stage pipeline where you train multiple components separately
- Slow inference time → feature extraction happens independently for each ROI, meaning tons of redundant computation
- Not end-to-end → 4 different networks (region proposal, CNN feature extractor, SVM classifier, bounding box regressor) that need to be trained separately
Fast R-CNN (2015):
- Runs CNN once on whole image, extracts features from feature map
- Still uses selective search for proposals
- Replaces SVM with FC layers → end-to-end for detection part
- Bottleneck: Selective search still external and slow
Fast R-CNN (Pipeline)
- CNN over entire image → run convolutions once on the whole image instead of per region
- Feature extraction used to propose ROIs → the feature map is reused for all region proposals
- ROI extractor (with selective search algorithm) → still uses external algorithm to find candidate regions
- ROI pooling → max-pooled into downsampled subwindows → all ROIs same size regardless of input dimensions
- Fully Connected (FC) layers → processes the pooled features for classification and localization
Outputs: Softmax classifier → predicts object class Bounding box regressor → refines box coordinates K+1 categories for class → K object classes plus 1 background class (x, y, w, h) coordinates for each of the K categories → bounding box for every possible class
- The output of the feature map is spatially the same dimension as the input image.
Fast R-CNN Improvements
- feature extraction on the whole image → whole feature space → only need 1 CNN instead of running it thousands of times
- Replace SVM with FC layers for classification → now end-to-end trainable with backprop through the whole network
Cons of Fast R-CNN
- Computational complexity → still expensive overall Fixed input size → images need to be resized to standard dimensions K = number of objects to classify → K elements in classifier output vector
- Selective search is slow → region proposal still happens outside the network
Faster R-CNN (2016):
- Introduces RPN to learn region proposals inside the network
- Fully end-to-end trainable
- RPN and detector share convolutional features
- Everything is learned, nothing external
Faster R-CNN Architecture
Backbone → Detector Branch (VGG-16 or similar)
RPN (Region Proposal Network):
Responsible for proposing regions likely to contain objects → replaces selective search Predicts:
Objectness scores → is there an object here? (binary) Bounding box coordinates → where exactly?
Uses anchor boxes (r, c, w, h) → predefined boxes at different scales and aspect ratios
Faster R-CNN Improvements
Removed selective search algorithm → no more external preprocessing step Uses Region Proposal Network → single, unified network that learns to propose regions
Outputs:
Bounding box coordinates → refined positions Class predictions (C-dimensional vector) → probabilities for each class
Anchor Boxes
Hyperparameters defining shapes for underlying size & aspect ratio (e.g., 1:1, 1:2, 2:1 ratios at multiple scales) Associated with objects → different anchors for different object types Act as reference boxes to help network learning → network predicts offsets from anchors rather than absolute coordinates
Training Shared Features
Updating classifier + bounding boxes concurrently → both networks train at the same time They share / learn from the same features → RPN and detector use the same backbone conv layers
Alternate Training Method
(To train shared features across separate networks)
Train RPN branch → pre-trained backbone (e.g., ImageNet weights) Train detector → disconnect RPN, train backbone + detector using RPN’s proposals Train RPN → fix parameters of detector branch → train only RPN features with fixed backbone Alternate between steps 2 & 3 until loss converges → iteratively improve both components
Pros of Faster R-CNN
Faster → significantly reduced inference time End-to-end → single network, single training process More accurate → shared features improve both proposal and detection RPN doesn’t use external algorithms (e.g., selective search) → everything is learned
Multi-task Training
Fast R-CNN & Faster R-CNN do multi-task learning:
Asking two questions: classification → what is the object? bounding box localization → where is it?
Multitasking gives better performance for each task because:
tasks are correlated → knowing what something is helps locate it bounding box size correlates to image size / classifier → features useful for one task help the other
Optimized in parallel → single loss function combines both tasks, train together
Computer Vision
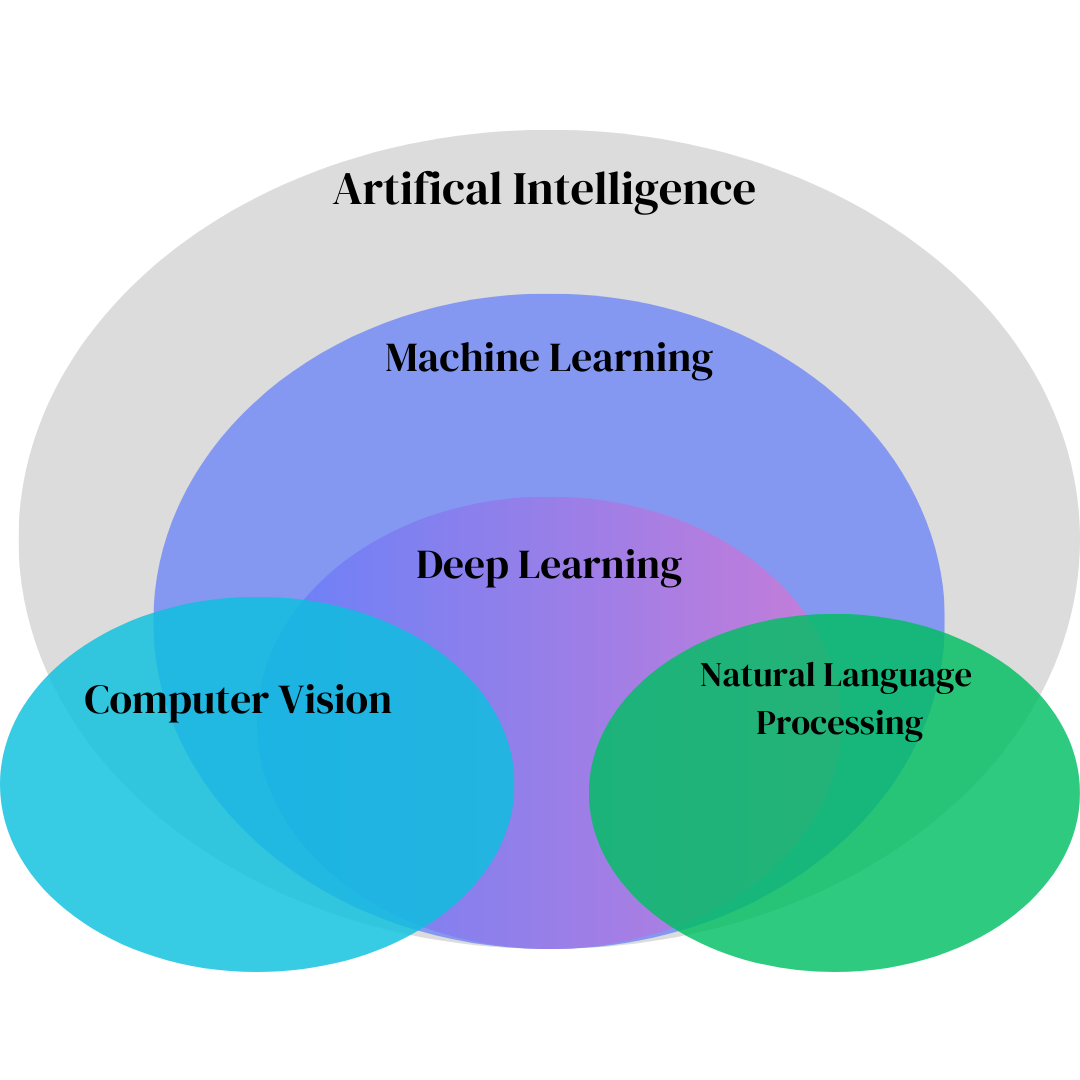
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
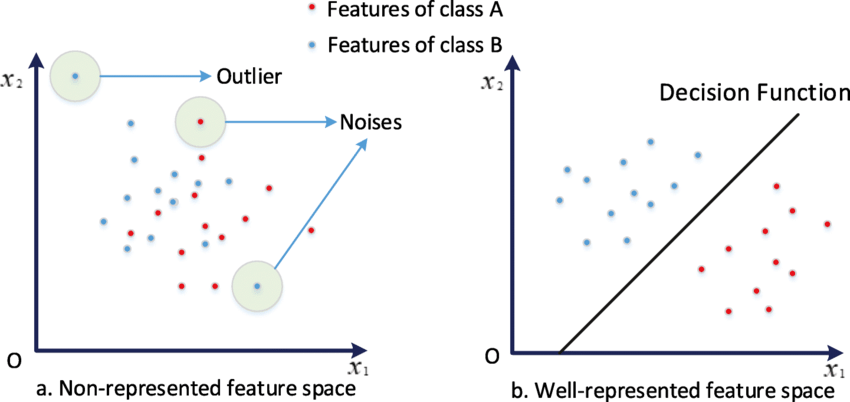
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
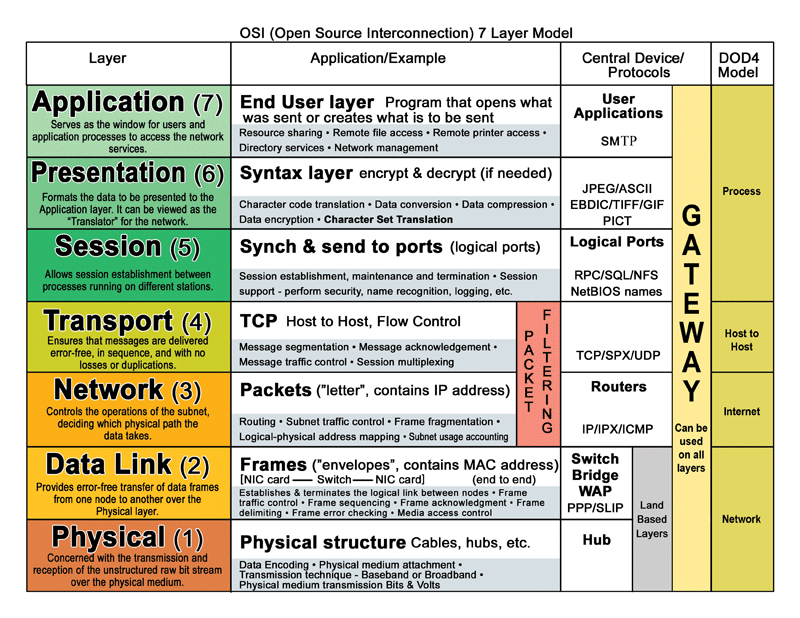
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
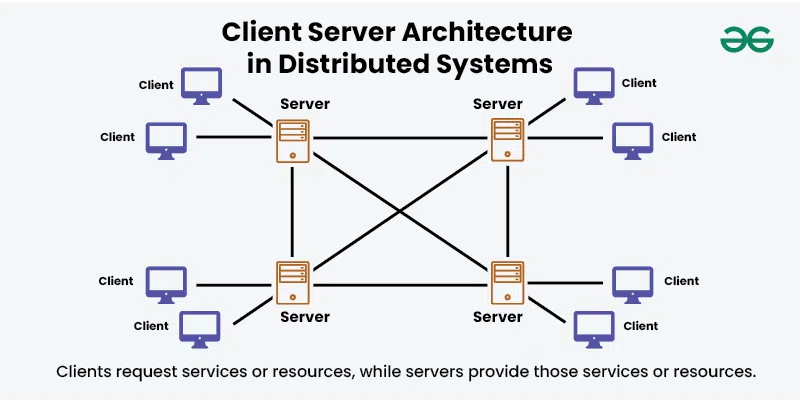
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
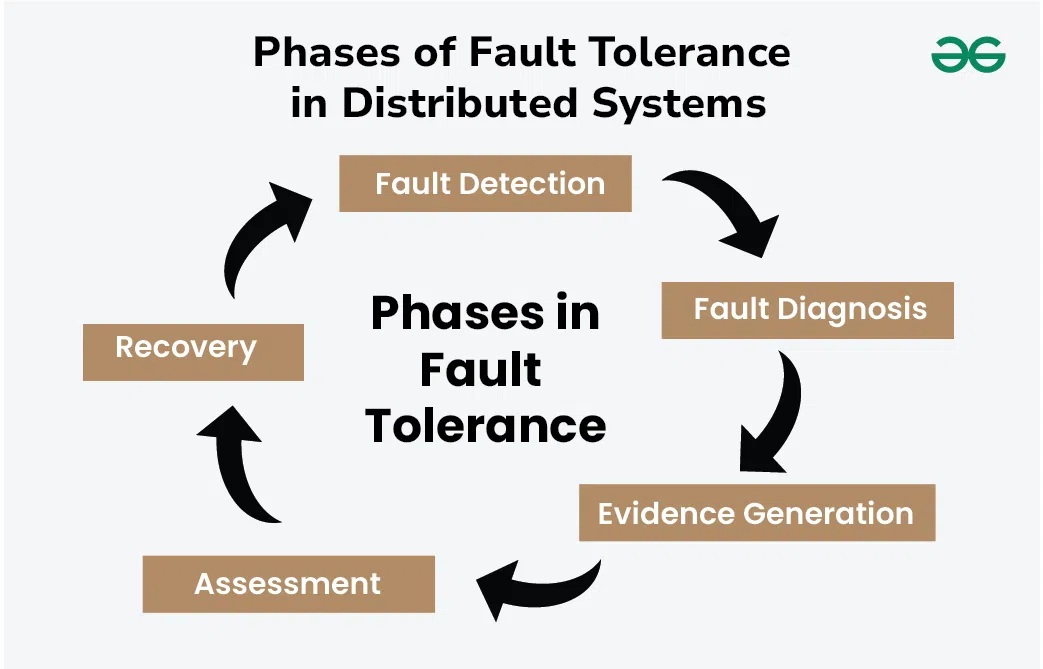
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
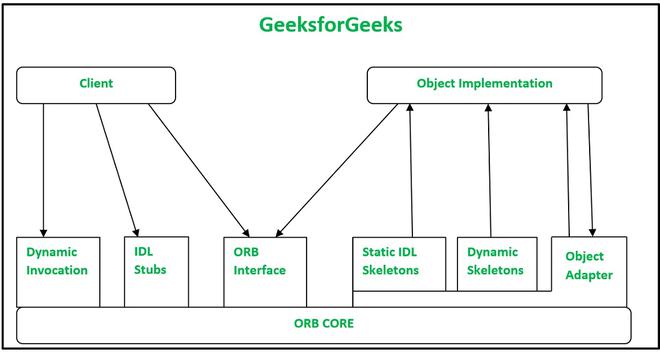
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
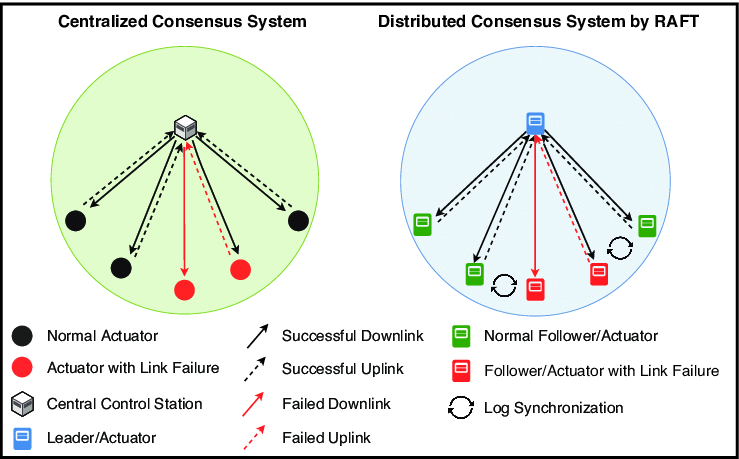
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
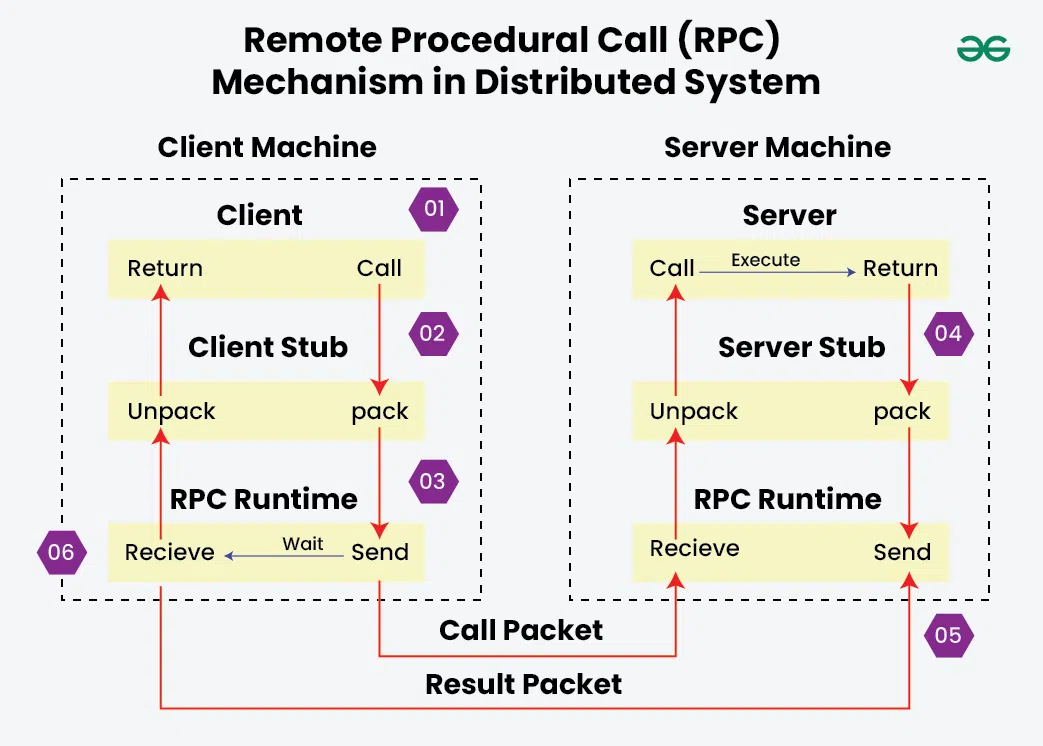
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
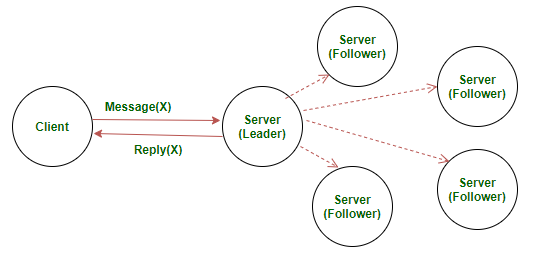
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
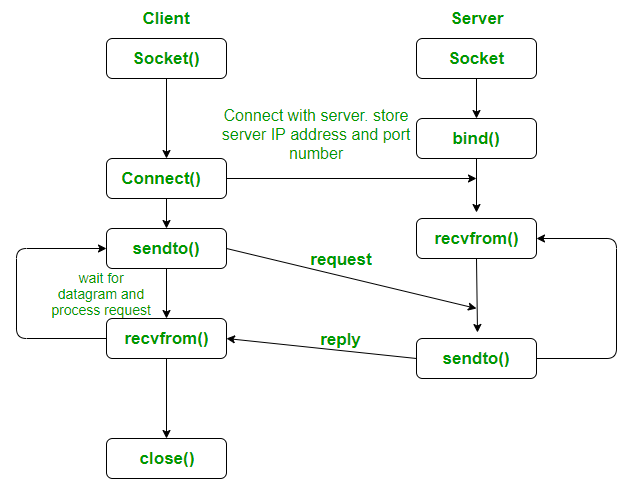
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
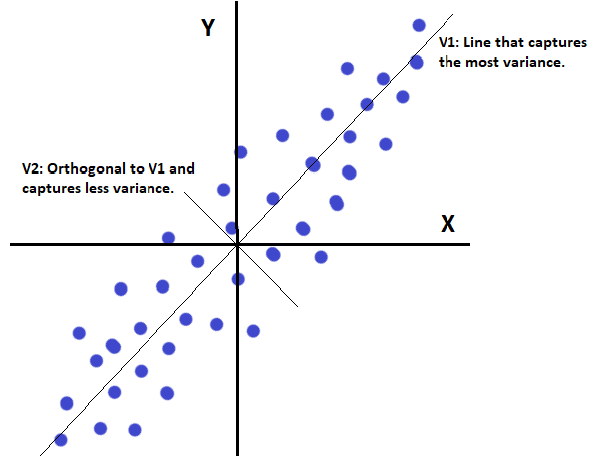
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
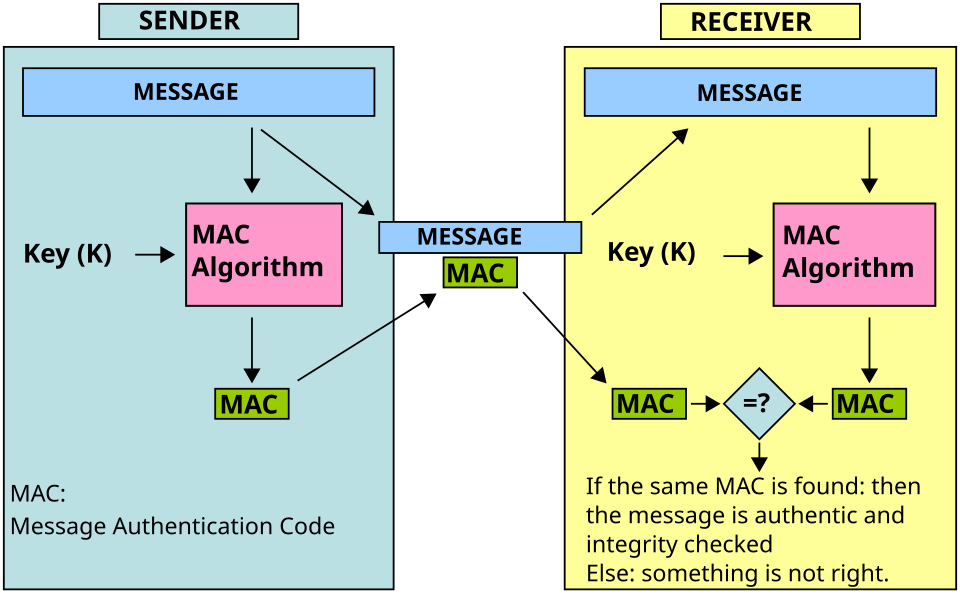
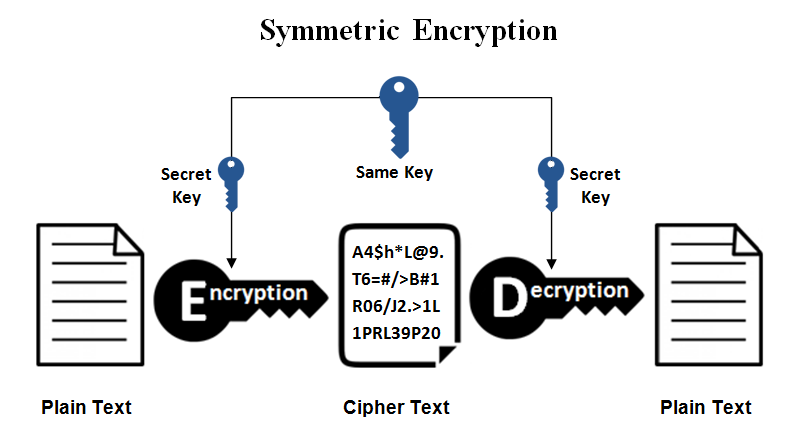
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
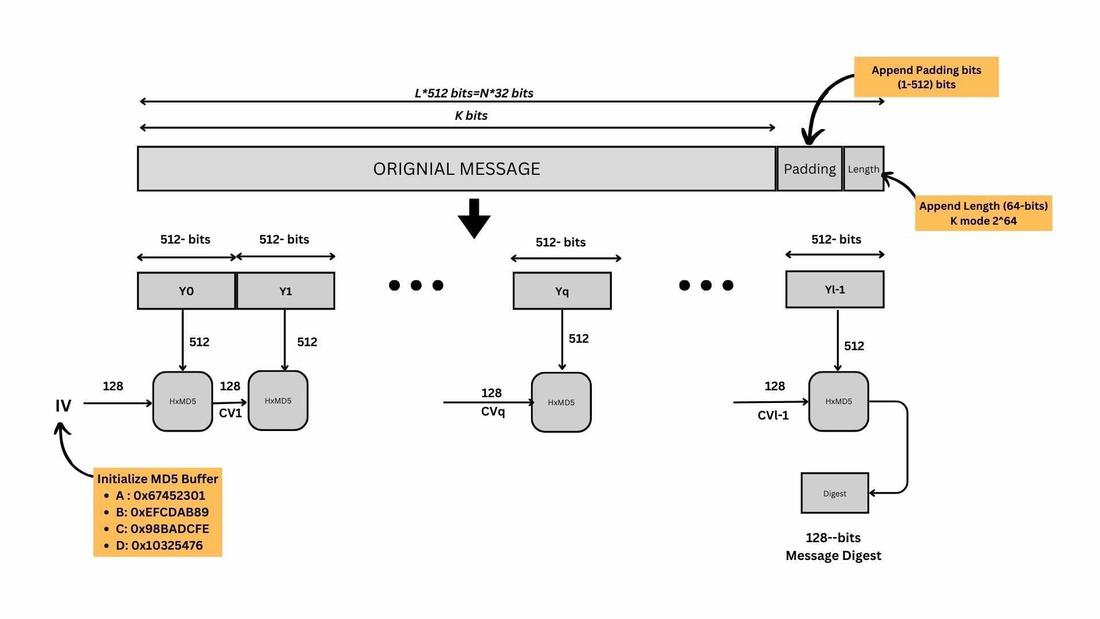
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
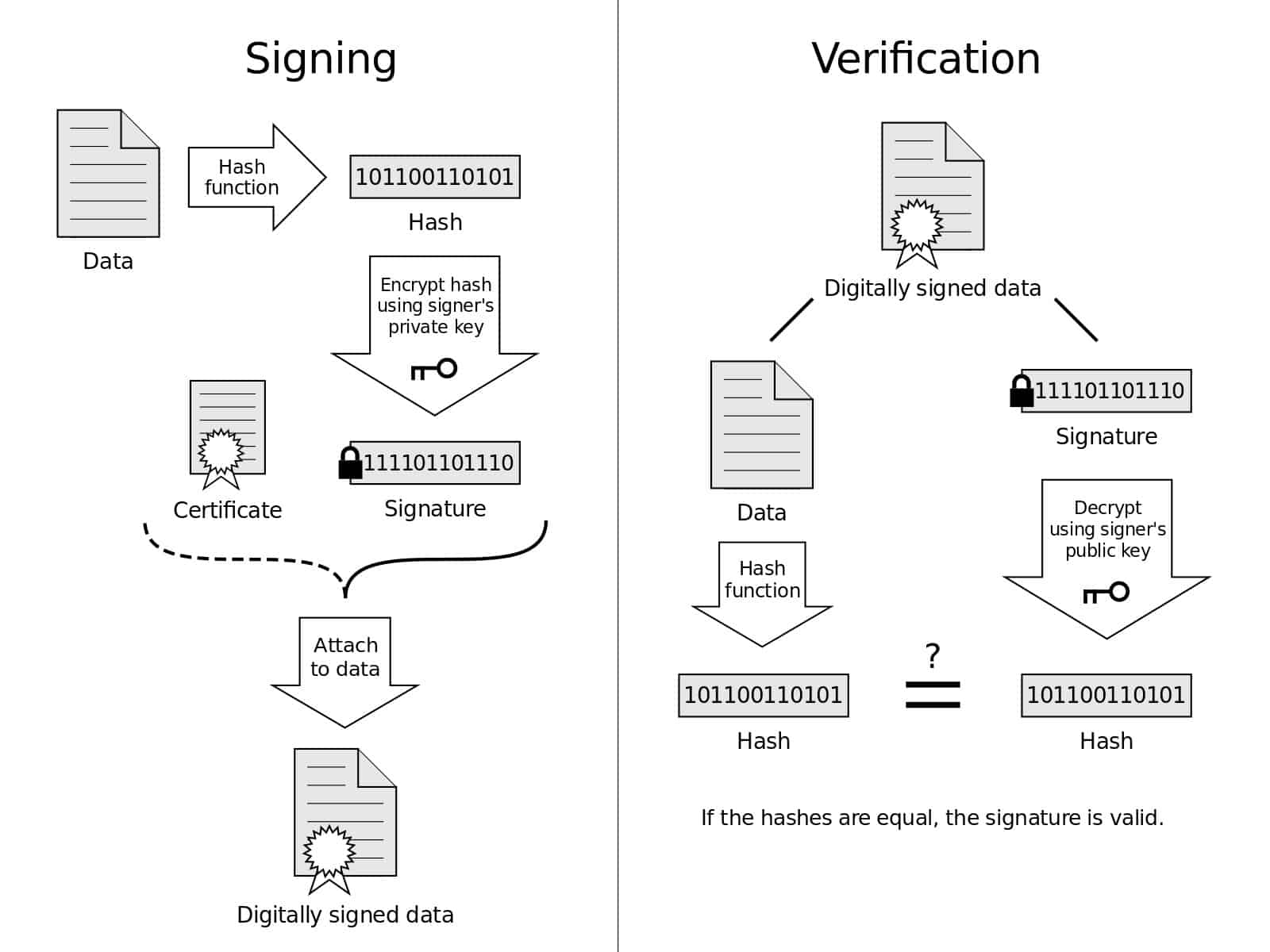
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes