
Dependability
Dependability is a measure of how much users can trust a system to function correctly. It’s a key metric for fault tolerance in distributed systems.
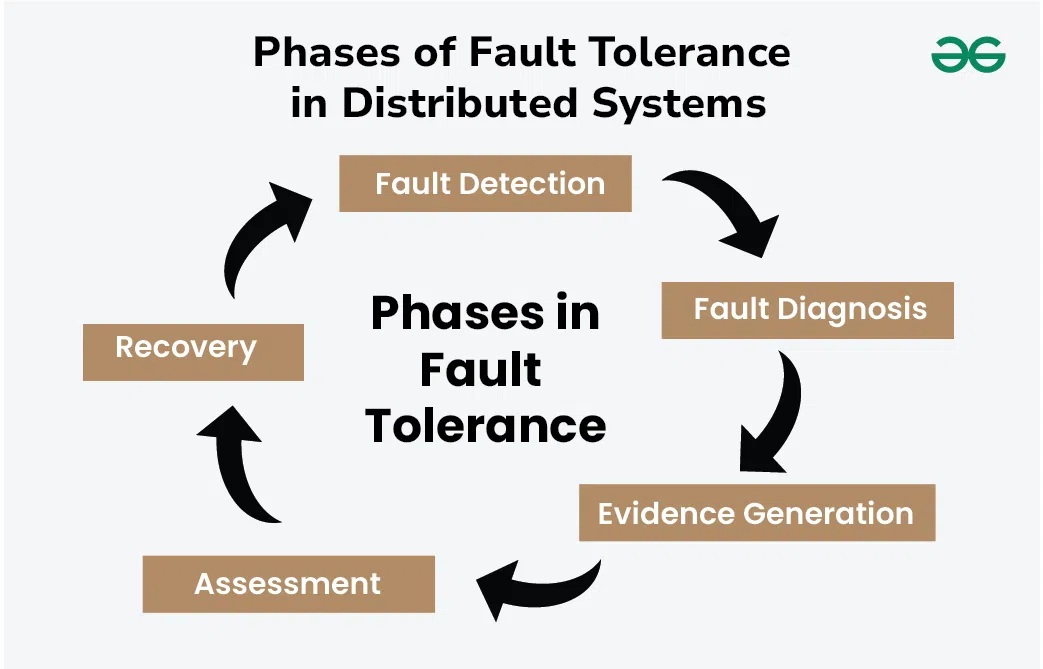
Metrics for Dependability
- Availability – The proportion of time the system is operational and delivering service (e.g., uptime at a given instant).
- Reliability – The probability that the system runs correctly for a given period of time (e.g., a system that fails once every hour has high availability if it quickly restarts, but low reliability).
- Safety – The system should minimize the impact of faults so they don’t cause catastrophic failures.
- Security – Protection of data and services, including confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA triad).
- Maintainability & Recoverability – The ease with which the system can be repaired and restored after a failure.
Fault Tolerance (Hardening against Faults)
A fault-tolerant system continues to operate, possibly at a reduced level, even when some components fail. This involves:
- Fault prevention – Designing to avoid faults.
- Fault removal – Detecting and fixing faults during development or runtime.
- Fault forecasting – Predicting the likelihood of future faults.
Types of Faults
- Transient faults – Temporary errors that occur once and then disappear. (squirrel chews wire)
- Intermittent faults – Errors that reappear sporadically. (bad contact wire)
- Permanent faults – Persistent issues that remain until repaired.
Failures & Faults
- A failure occurs when the system cannot provide its service.
- An error is the incorrect part of the system state that may cause a failure.
- A fault is the underlying cause of the error.
Failure Models
Note: All models can be deliberate or unintentional failures – omission and commission are usually deliberate (security issue) but it’s difficult to tell.
- Crash Failure – The component stops running unexpectedly.
- Omission Failure – A component fails to provide an expected response (e.g., dropping a message).
- Commission Failure – A component takes incorrect actions (e.g., sending the wrong result).
- Timing Failure – The response is correct but delivered too late (missed deadline).
- Response Failure – The response is incorrect.
- a) Value Failure – Singleton response value is wrong.
- b) State Transition Failure – The system transitions into an incorrect state.
- Arbitrary (Byzantine) Failure – The component behaves in completely unpredictable ways (e.g., sending random or malicious data).
Process Resilience
To tolerate faults, systems introduce redundancy:
- Information redundancy – Extra error-checking data (e.g., checksums).
- Time redundancy – Retrying operations after a failure.
- Physical redundancy – Extra hardware or backup servers.
To protect against faulty processes, computations are often distributed among groups of processes.
Process Groups
Groups are dynamic – members can join, leave, or fail. To the outside, the group looks like one entity.
Two main types:
- Flat groups – All members are equal, decisions are made collectively by voting (peer-to-peer style).
- Hierarchical groups – One coordinator (leader) manages workers (followers). Example: RAFT consensus algorithm.
K-Fault Tolerant Groups
If there are k failures, how many group members are needed? Assume all members are identical, all updates occur in the same order i.e. assume each component executes the same updates in the same order as every other component → consensus occurs.
- To tolerate K halting failures, at least K + 1 members are needed (majority ensures service continues).
- To tolerate K arbitrary (Byzantine) failures, at least 2K + 1 members are needed (majority voting ensures correct results).
Consensus
Consensus means all non-faulty processes agree on the same system state and the same sequence of updates. This ensures consistency across distributed components.
Computer Vision
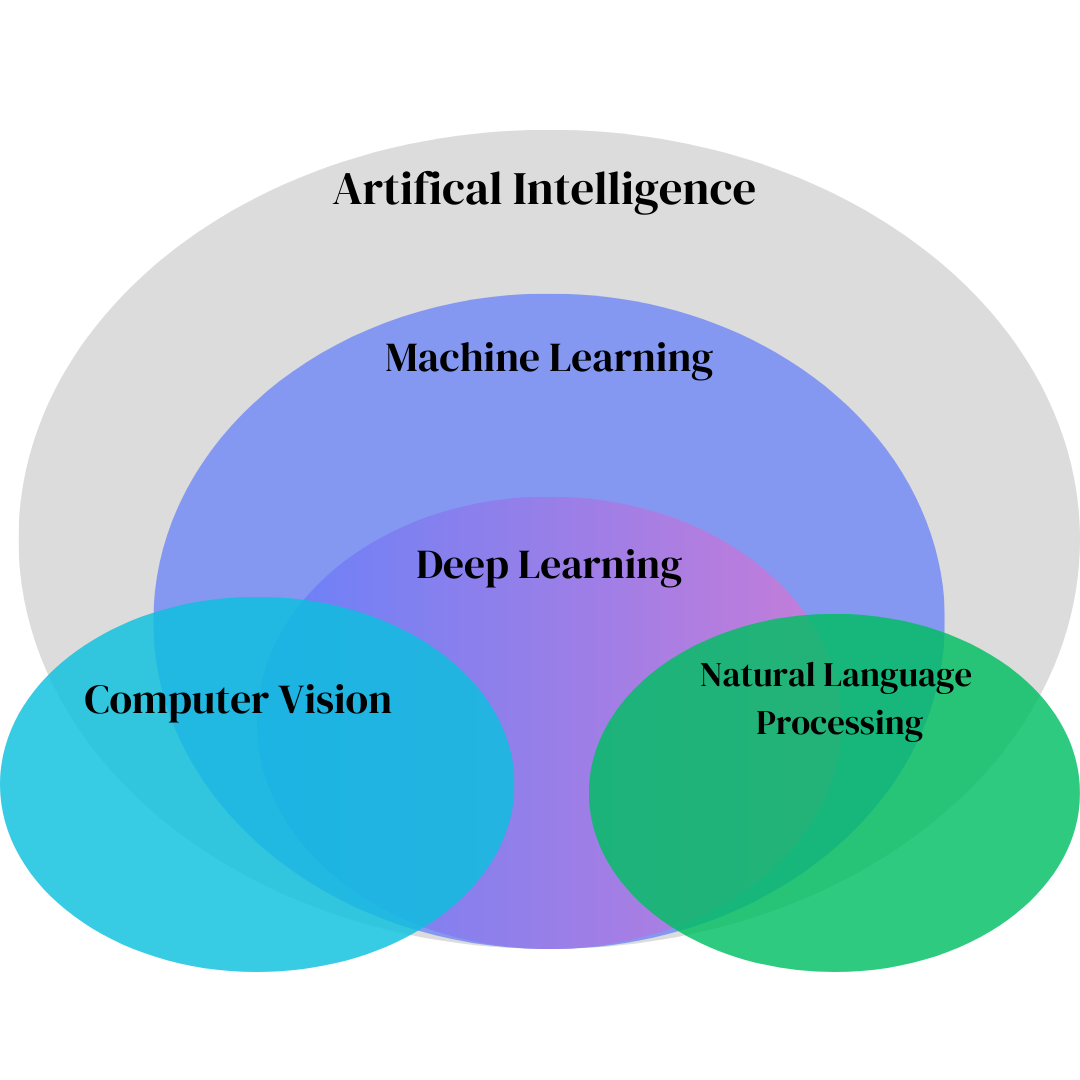
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
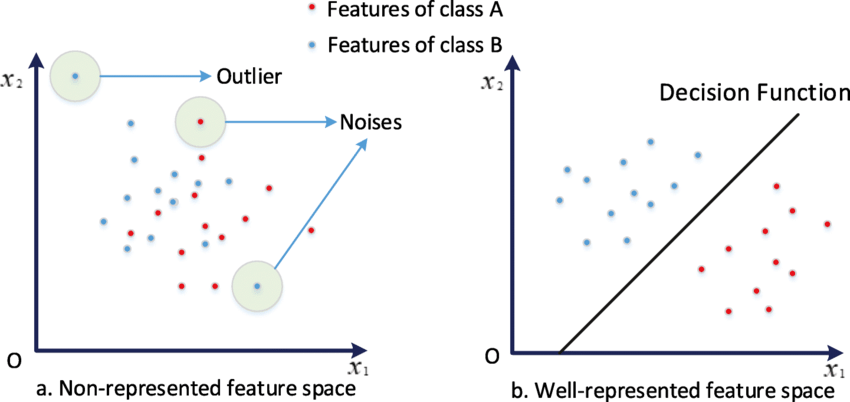
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
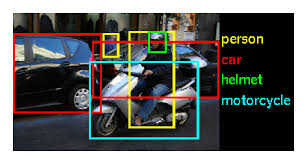
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
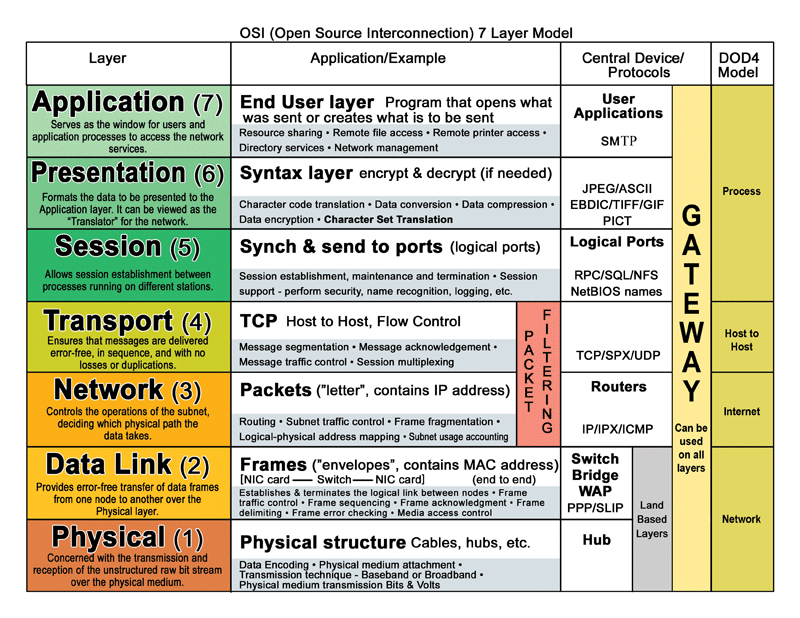
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
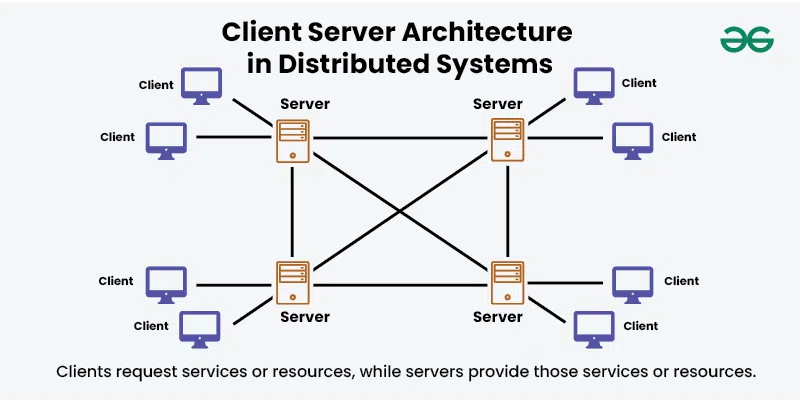
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems

Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
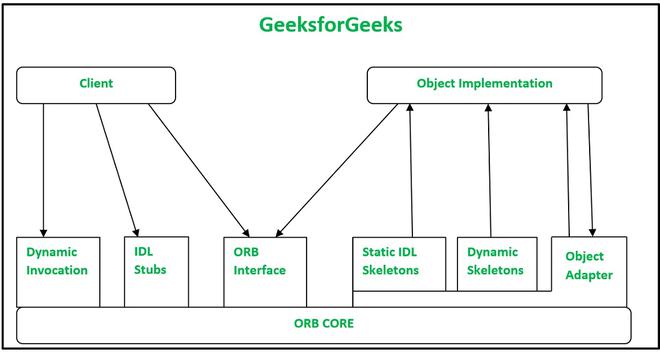
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
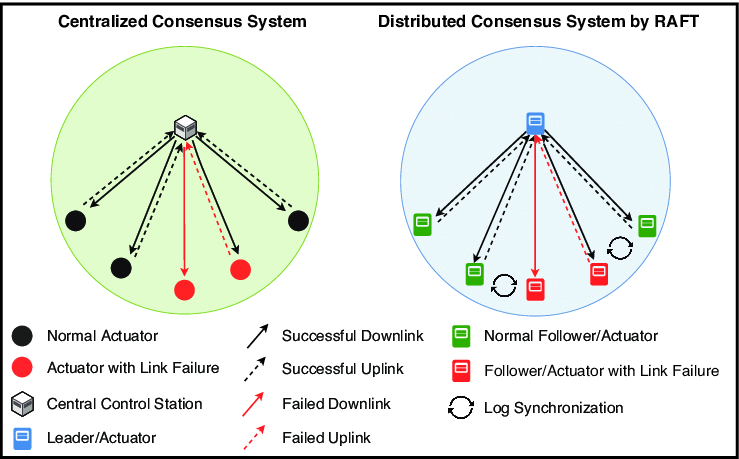
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
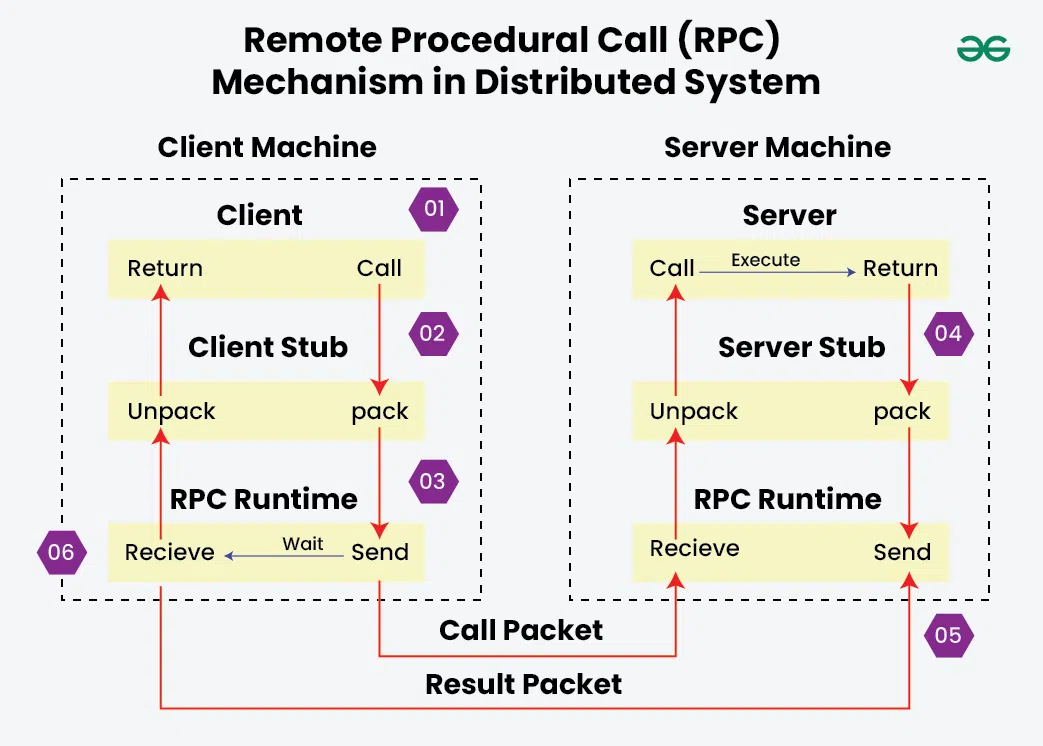
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
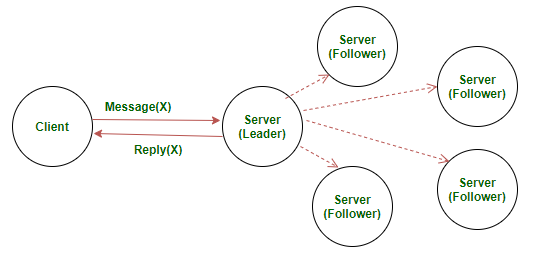
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
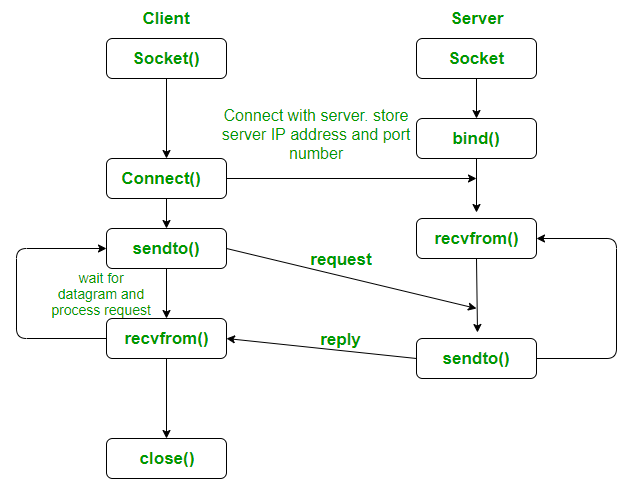
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
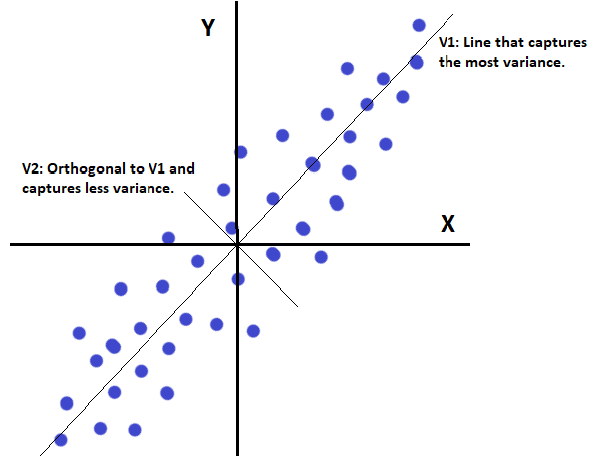
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
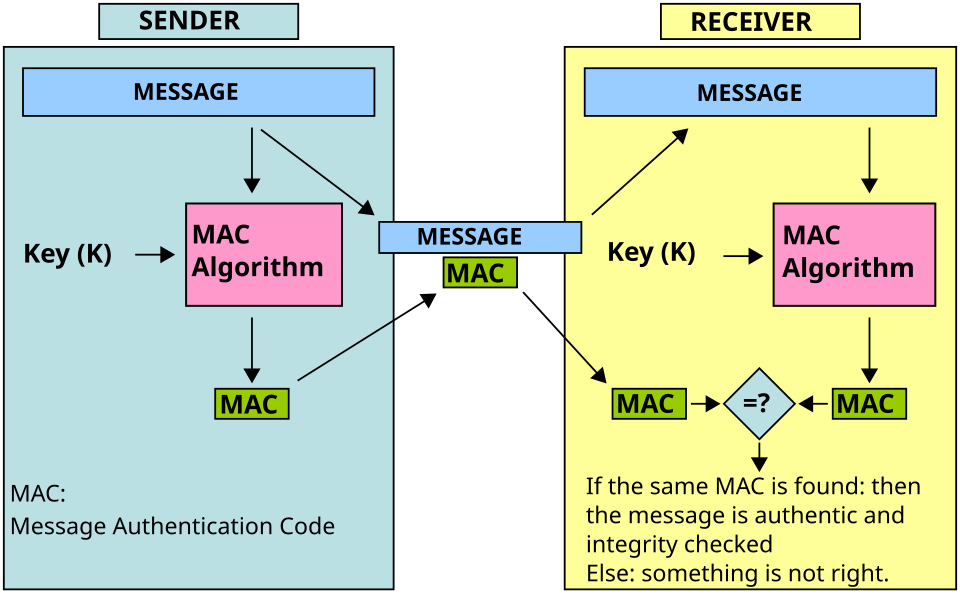
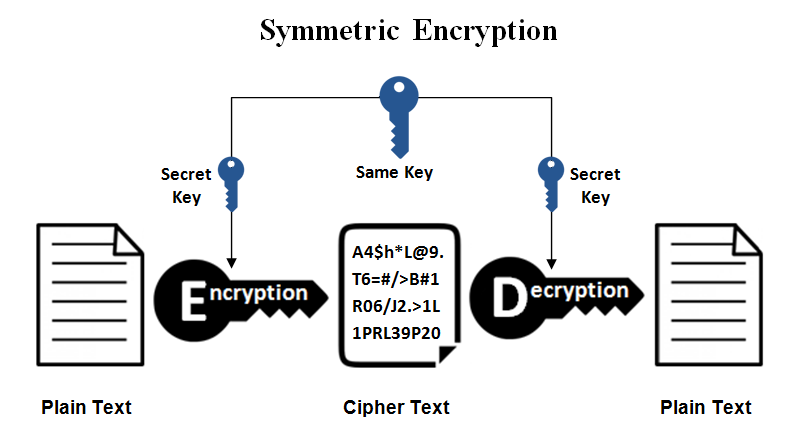
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
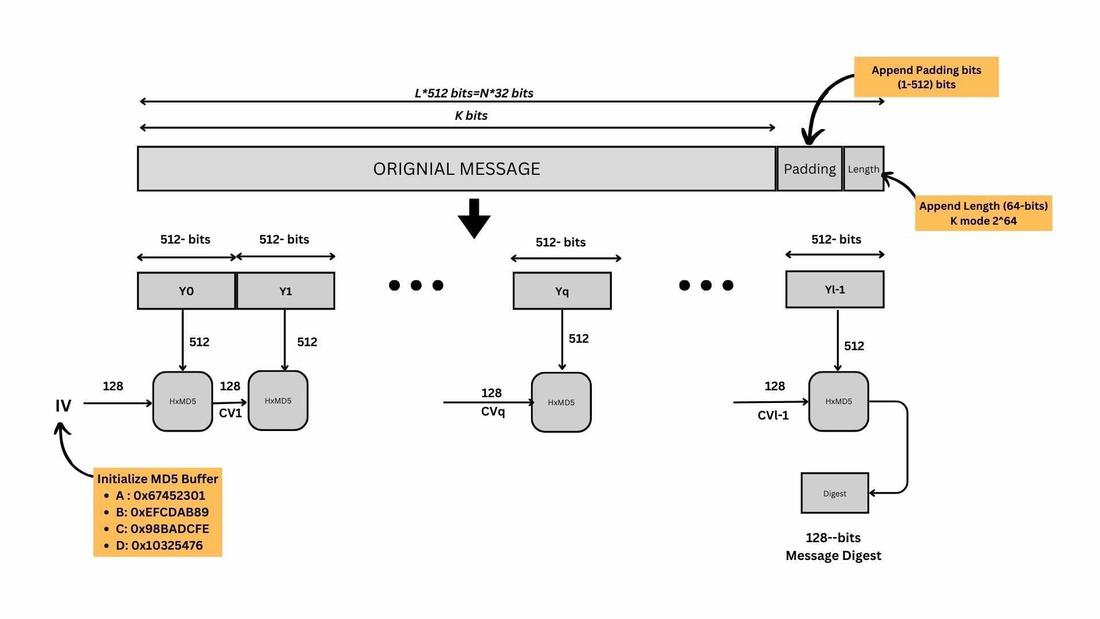
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
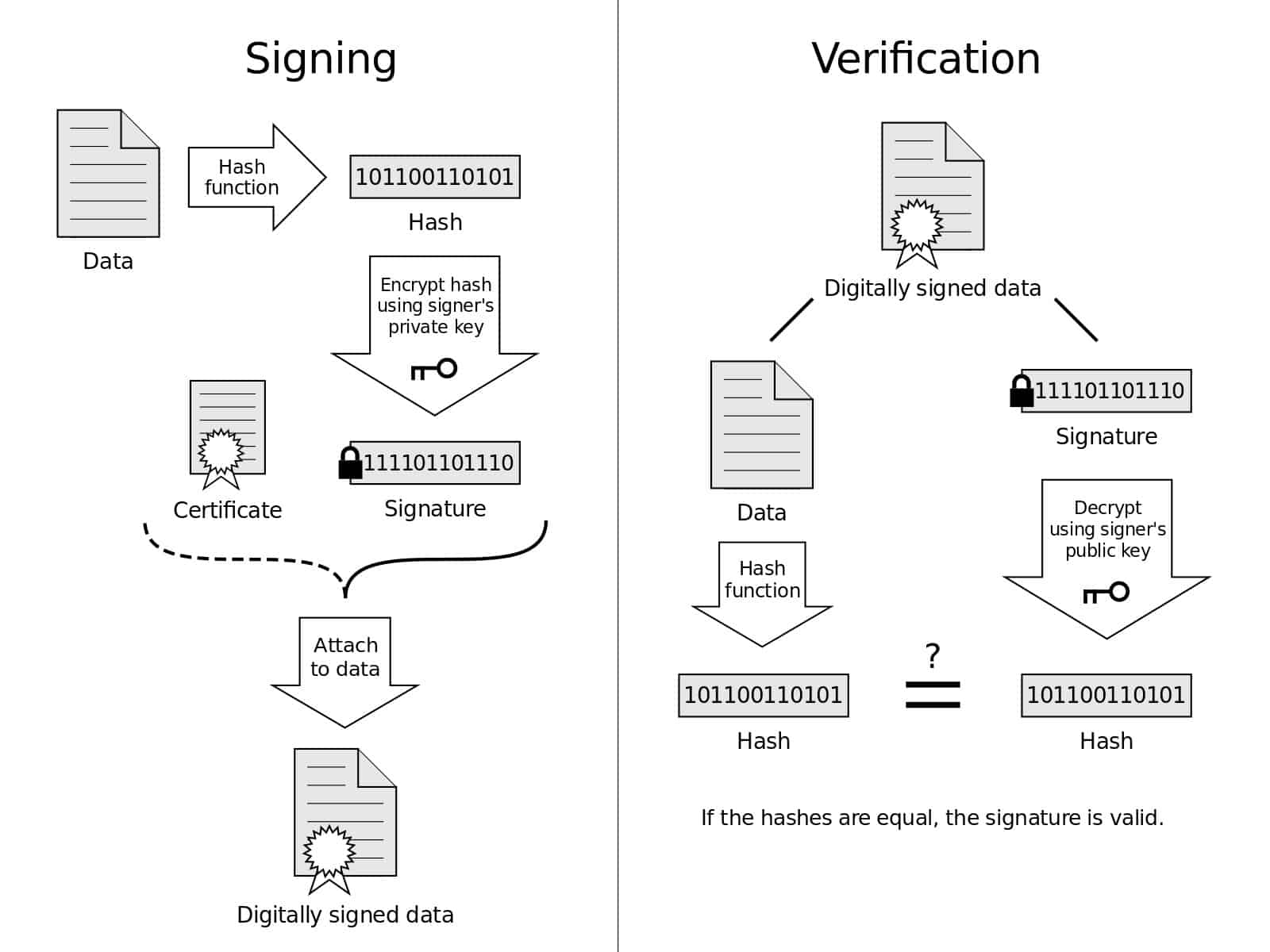
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
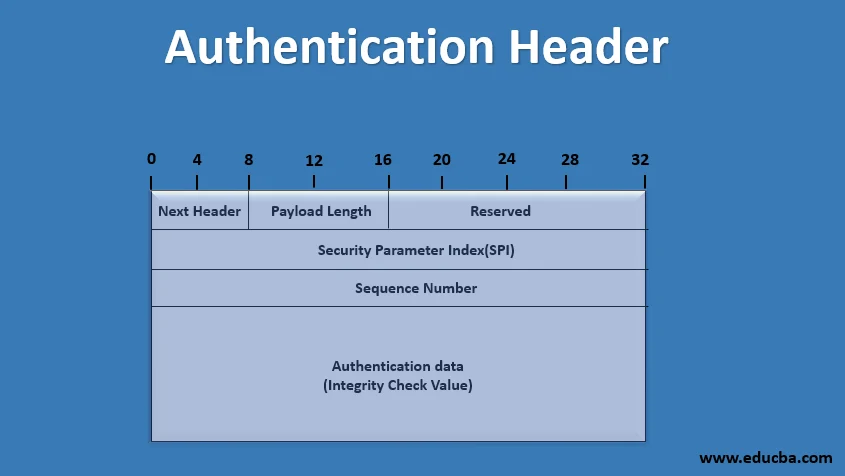
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes