
Instantiating Server (C++) Example
In distributed systems, it is common to model both servers and clients as specializations of a more generic Node abstraction.
This allows us to capture shared functionality (like initialization, naming, or lifecycle management) while leaving protocol-specific or role-specific logic to subclasses.
// Example: Object-Oriented Server Abstraction in C++ for a Distributed System
class Node {
protected:
std::string nodeName;
public:
explicit Node(const std::string& name) : nodeName(name) {}
virtual ~Node() = default;
std::string getName() const { return nodeName; }
virtual void start() = 0; // Force subclasses to implement startup logic
virtual void stop() = 0; // Force subclasses to implement cleanup logic
};
// Abstract interface for services handled by servers
class IService {
public:
virtual ~IService() = default;
virtual void handleRequest(const std::string& request) = 0;
};
// Concrete server implementation
class A1Server : public Node {
std::shared_ptr<IService> service; // Service instance handled by this server
std::string dbFilePath; // File path for persistence (e.g., metadata, state)
public:
explicit A1Server(const std::string& name, std::shared_ptr<IService> svc)
: Node(name), service(std::move(svc)) {}
void setDbFilePath(const std::string& path) { dbFilePath = path; }
std::string getDbFilePath() const { return dbFilePath; }
void start() override {
// Initialize resources (socket, threads, db connections, etc.)
std::cout << "Starting server: " << nodeName << std::endl;
if (!dbFilePath.empty()) {
std::cout << "Using database file: " << dbFilePath << std::endl;
}
// Imagine: bind socket, listen, accept connections, dispatch to service
}
void stop() override {
// Graceful cleanup of resources
std::cout << "Stopping server: " << nodeName << std::endl;
}
};
// Example of a concrete service implementation
class EchoService : public IService {
public:
void handleRequest(const std::string& request) override {
std::cout << "EchoService received: " << request << std::endl;
}
};
// Example usage
int main() {
auto service = std::make_shared<EchoService>();
A1Server server("DistributedNode1", service);
server.setDbFilePath("state.db");
server.start();
service->handleRequest("Hello, world!");
server.stop();
}
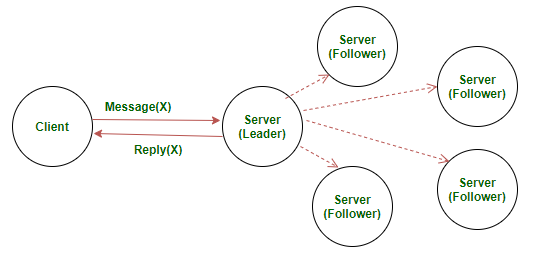
In practice, a real distributed server would replace the placeholder logic with:
- Socket setup: Binding to an IP and port, accepting client connections.
- Concurrency: Thread pools or async event loops to handle multiple requests in parallel.
- Persistence: Storing state in a database or replicated log for fault tolerance.
- Fault-tolerance mechanisms: Retry logic, leader election, or consensus protocols such as Raft.
Computer Vision
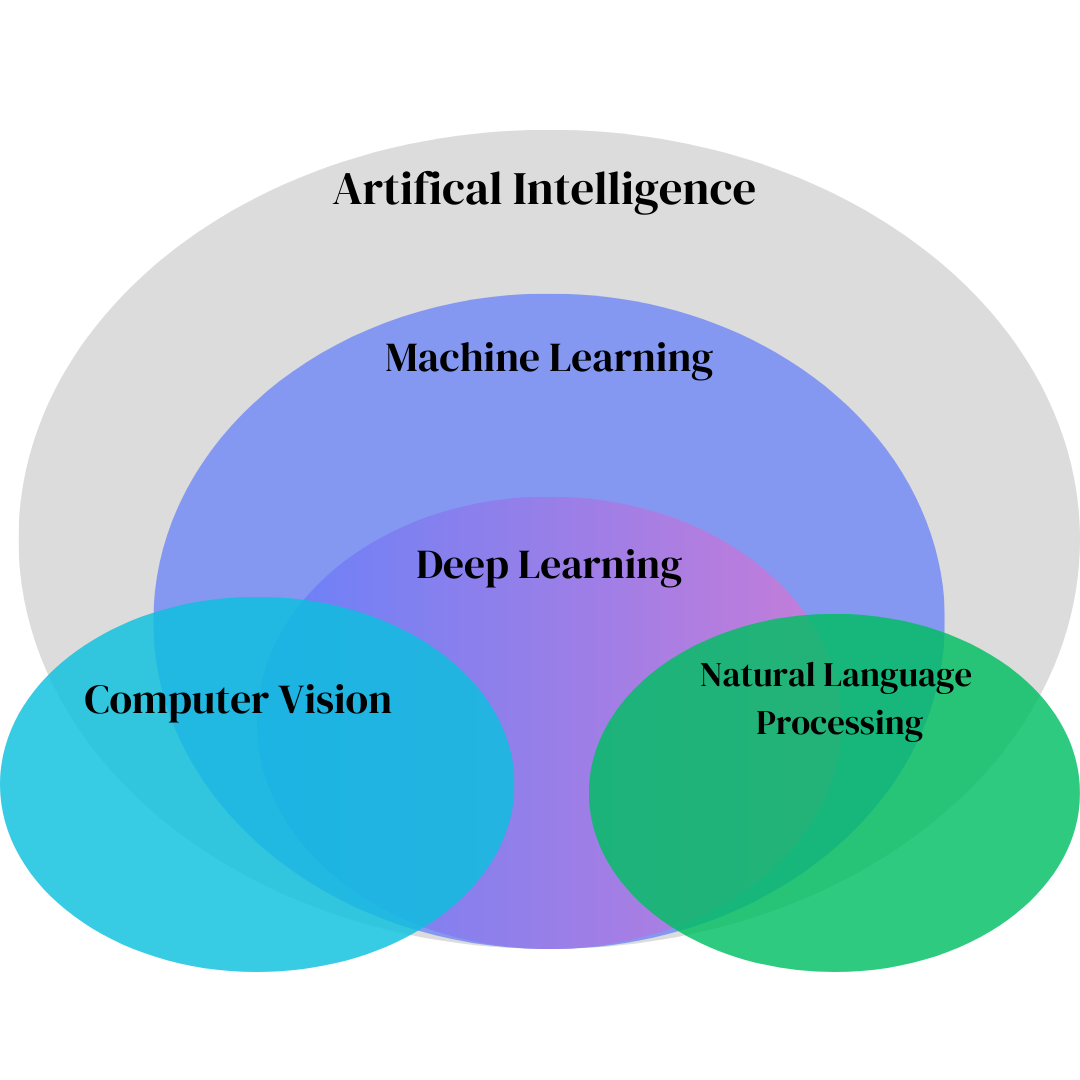
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
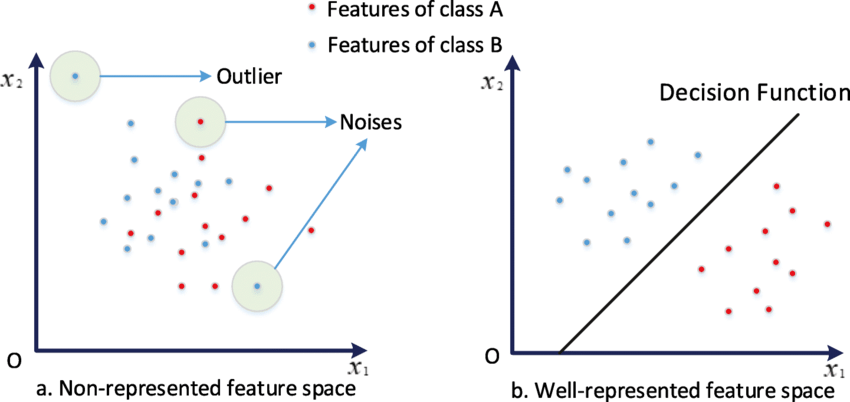
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
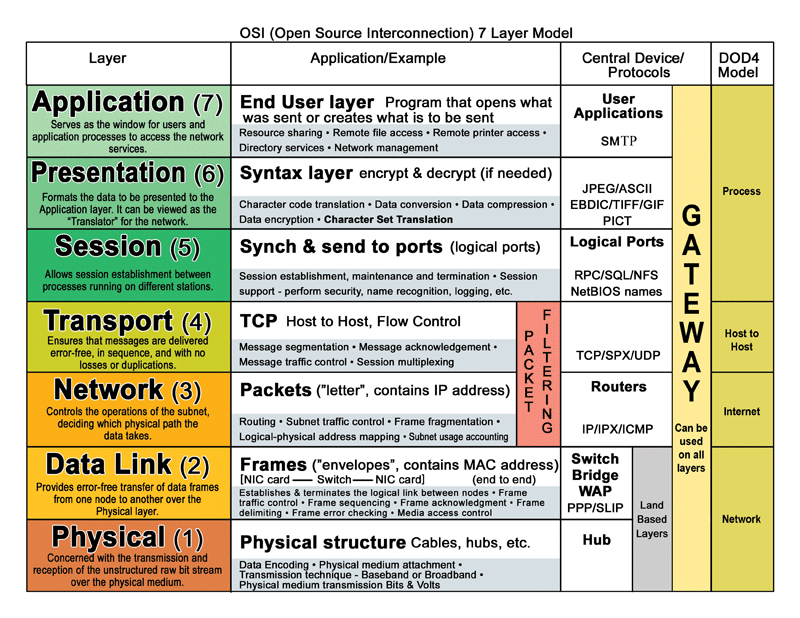
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
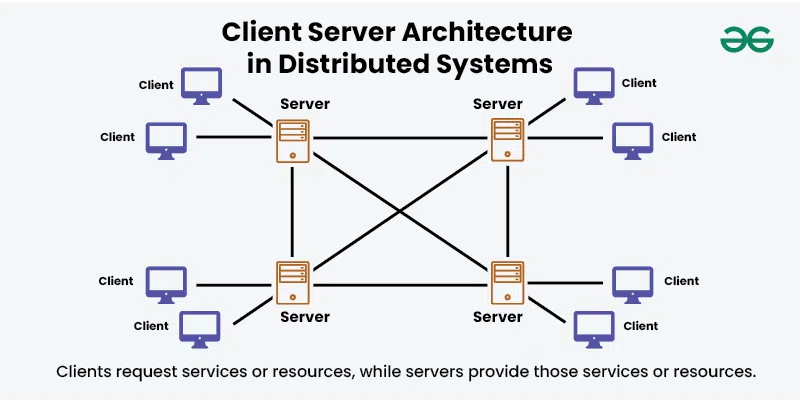
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
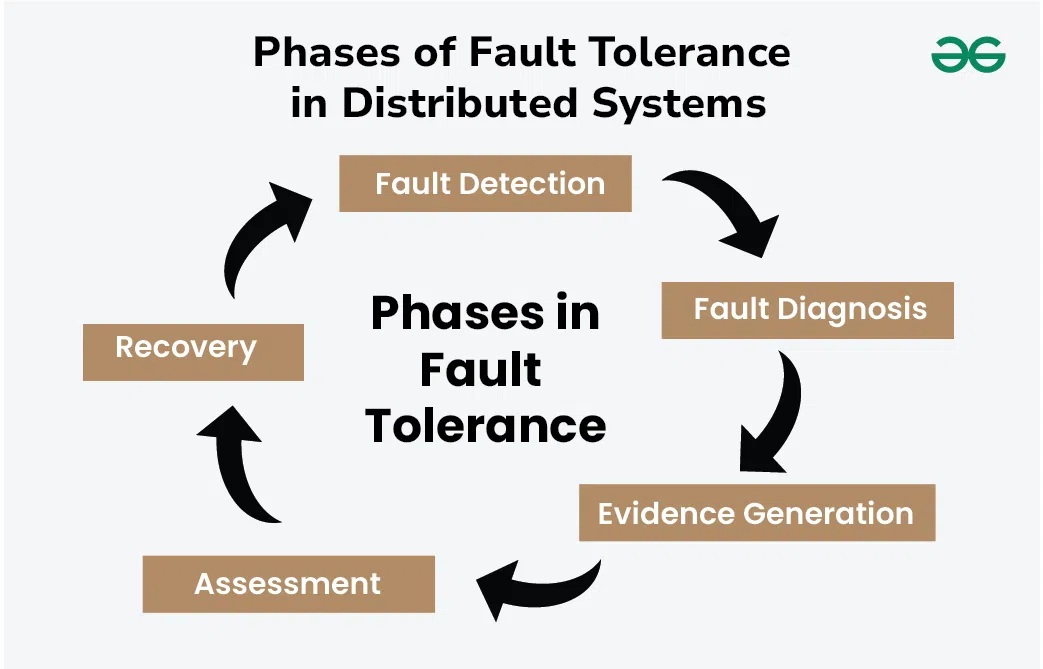
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
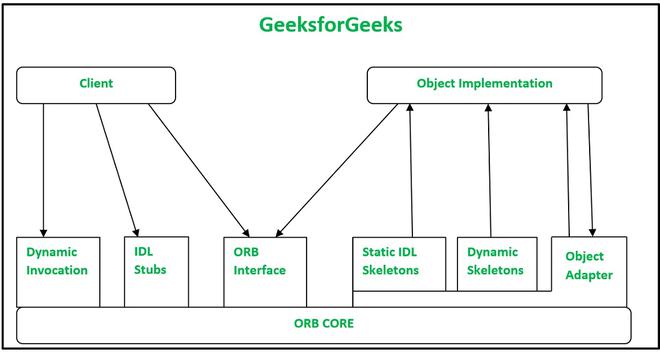
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
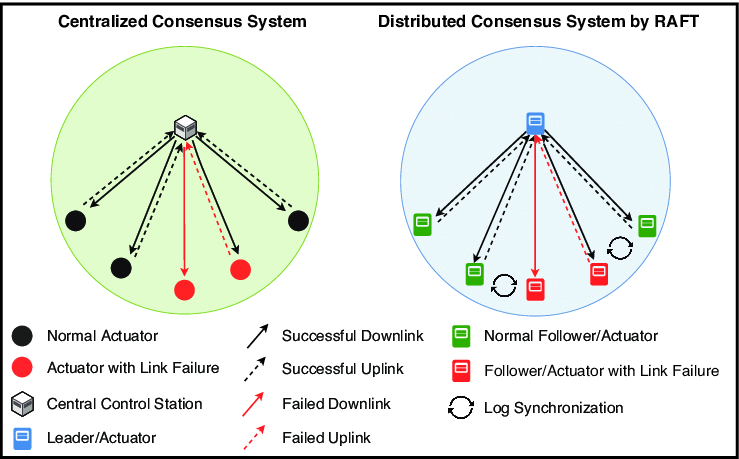
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
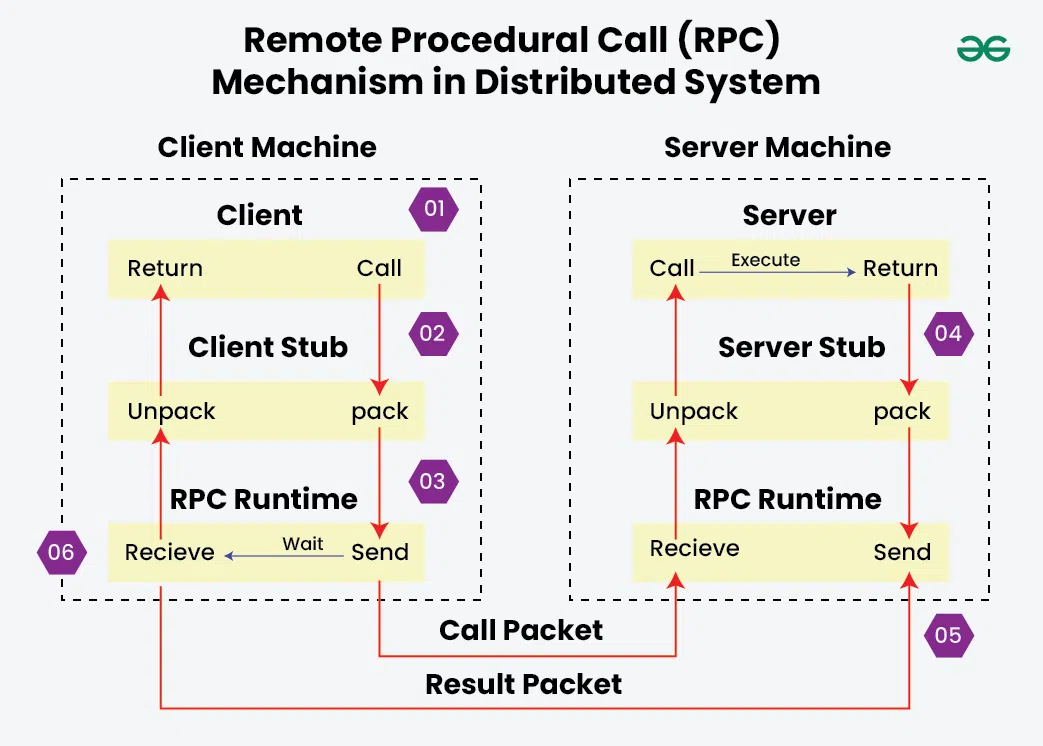
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes

Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
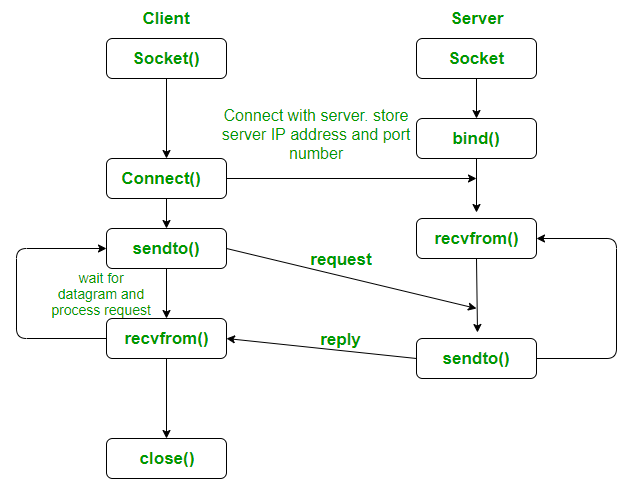
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
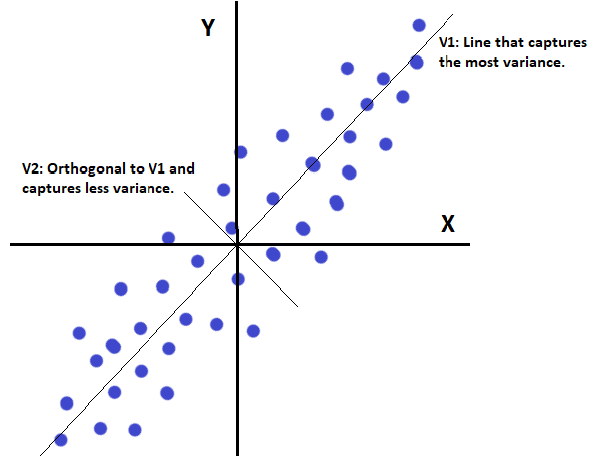
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
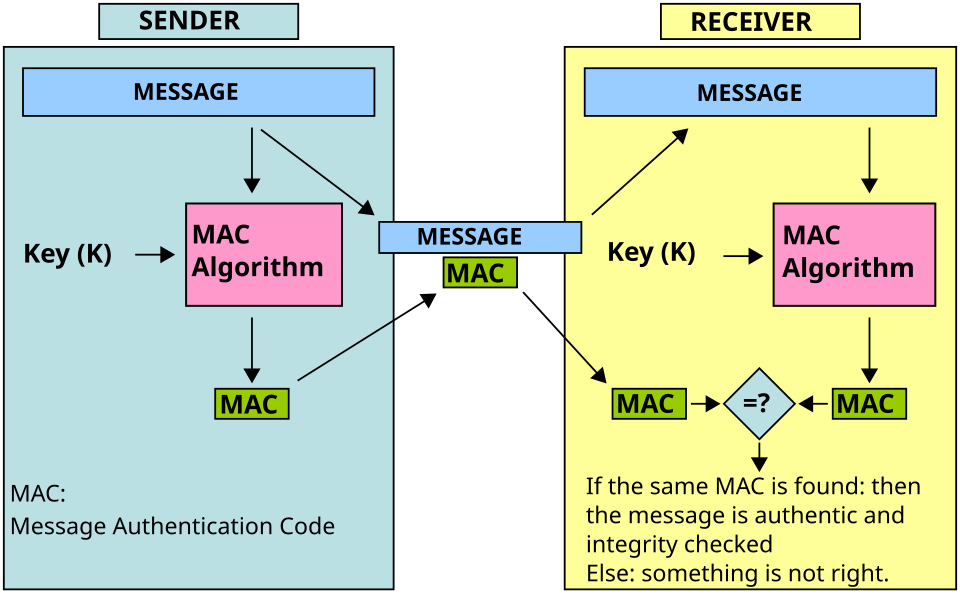
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
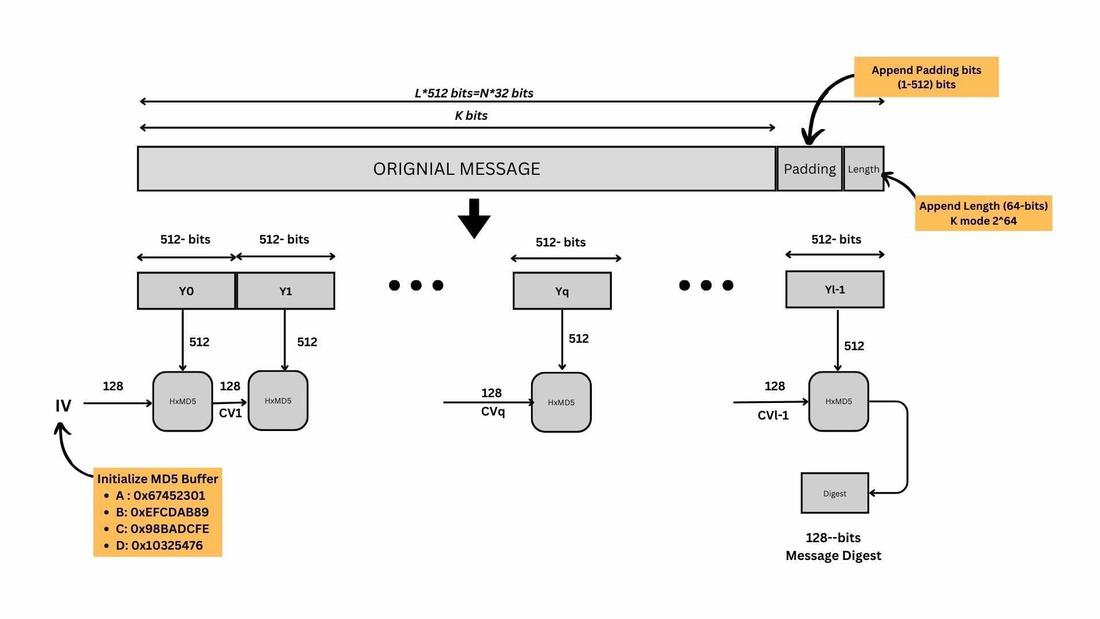
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
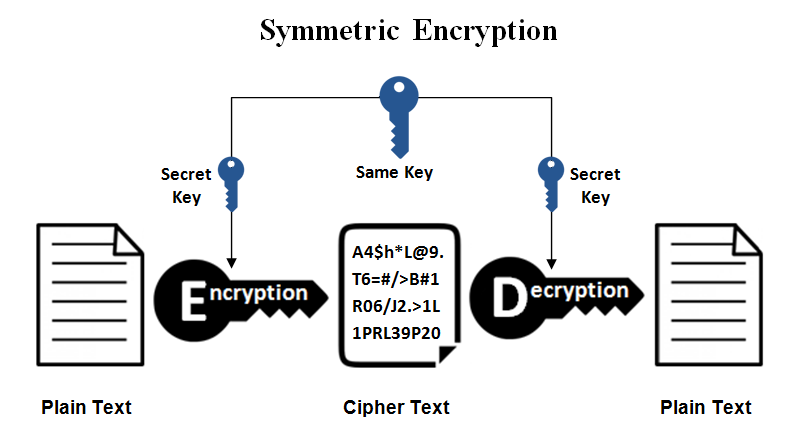
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
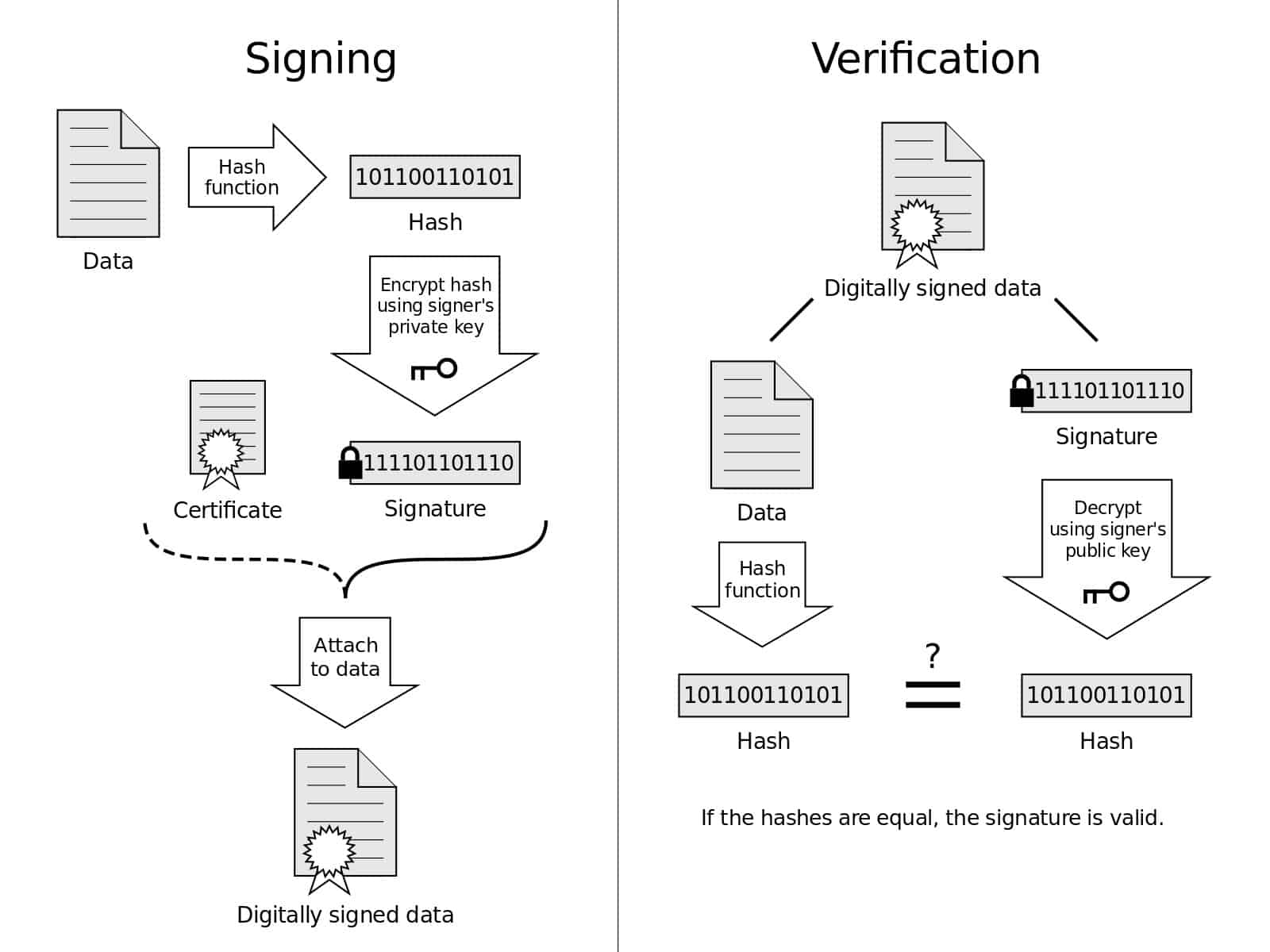
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
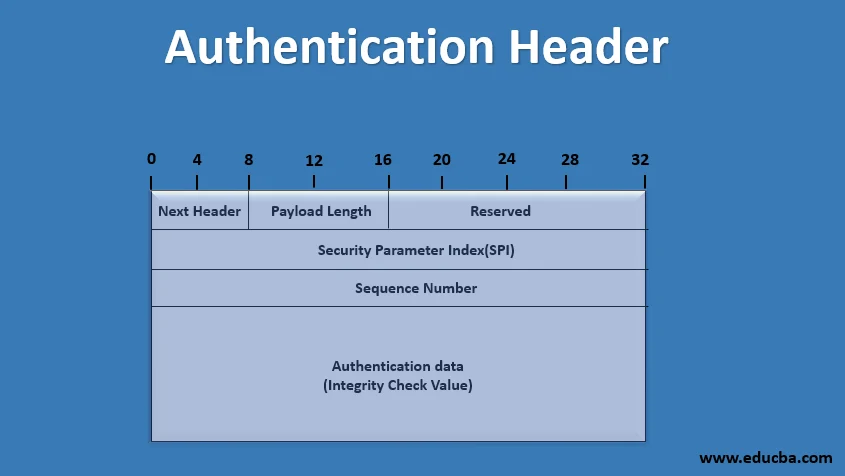
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes