
LeNet Architecture - The Original CNN
Convolution vs. Subsampling
- Subsampling changes spatial dimension, NOT feature space depth.
- Convolution can change both.
- Example: 6@28x28 (subsampling) -> 6@14x14.
- Spatial dimension decreases.
- Some depth increases.
Depth vs Spatial Dimension
- Increasing channel depth decreases depth of spatial dimension.
- Example: 16@14x14 -> 16@10x10. Convolution.
- IP channel depth = 6, there are 6 kernels.
- M-output = f(conv + bias)
Benefits of Convolution vs. FC
- Fewer parameters.
N_p = P(C²+1)+MN_p = (28x28+1) + 12.8 (FC)16x kernel = (7x7+1)=28 -> 30,100kN_p = 5x(5+1) = 6 kernelsP=(K²+1)xM 15x kernel size
- Translational invariance: FC needs to be trained on all translations of an image because pixel detection is fixed.
When to Use Convolution vs FC
- Convolution: Feature Extraction.
- FC: Classification.
- Note: At the end of LeNet, use FC because the output is a human-readable integer, not spatial like a CNN output.
AlexNet Architecture
- 5 convolutions, 3 FCs.
- 11x11 -> 7x7 -> 5x5.
5 Differences between Convolution/FC
- Fewer parameters:
(C_i * (K²+1) * M) - Translational invariance: maintains similar pixels.
- Dimensionality Reduction: pooling.
- FC training: needs to be trained on all translations because pixel detection is fixed.
- Hierarchies: CNN's first layer recognizes hierarchies, while MLPs do not; they are fixed at each layer equally.
LeNet vs. AlexNet
- Datasets: LeNet used MNIST, AlexNet used ImageNet. ImageNet was advanced with better images.
- Hardware: GPU parallelization became much better.
- Algorithmic Differences:
- ReLU activation: converges quicker, allowing for larger NNs.
- Local Response Normalization
- Overlapping Pools:
Z < S(kernel < Stride). This reduced overfitting. - Data Augmentation:
- Transforms dataset images to increase quantity.
- Cropping and extracting patches, horizontal rotation.
- Increases data by 2048.
- Adds random noise (RGB) using a scale factor.
- Dropout Method:
- At each epoch, some weights are "tossed out" to force the network to learn a slightly different structure each epoch.
- Increases robustness and doubles training time.
- All of Ensemble Method: Run all weights and average each epoch. Always a benefit.
Computer Vision
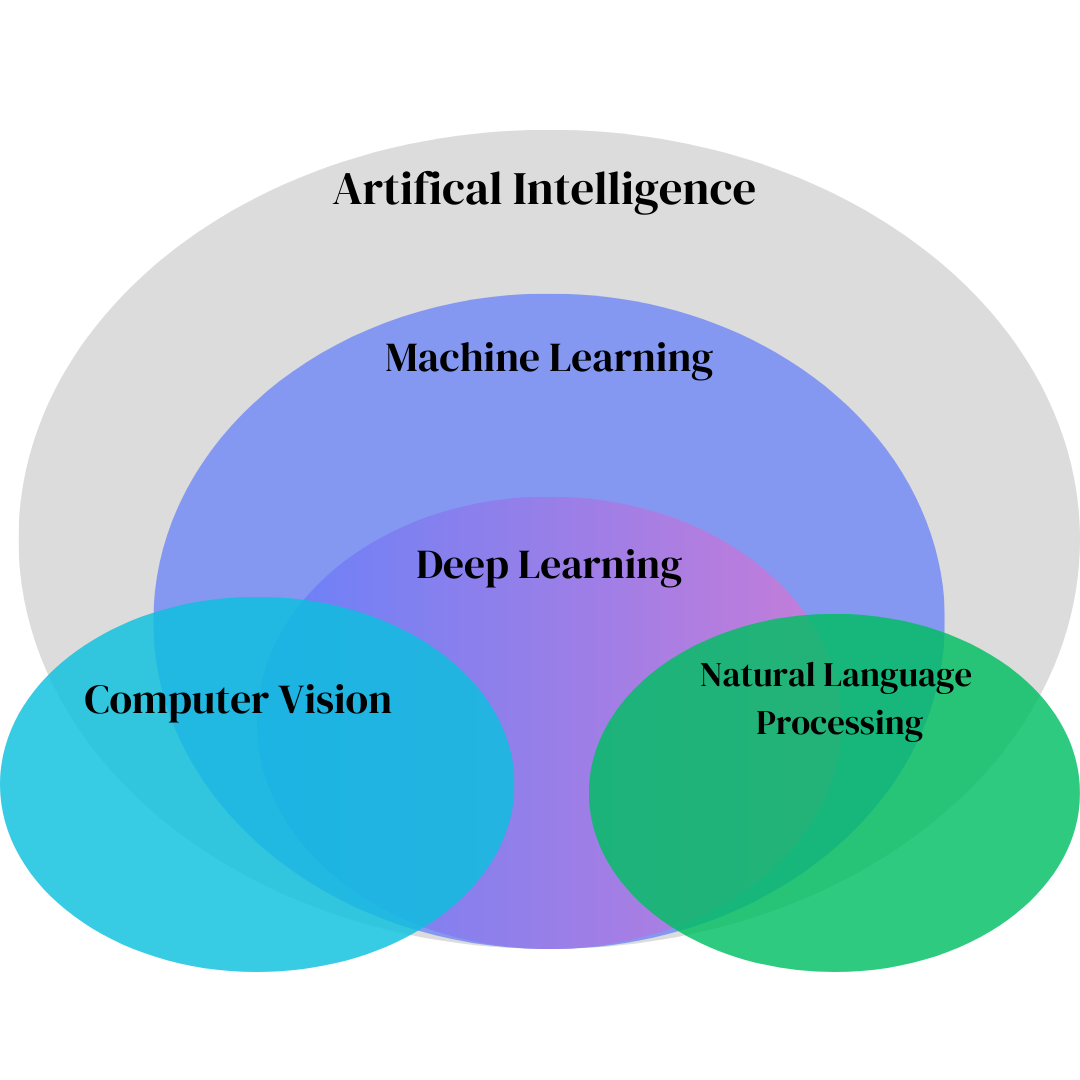
Overview of Computer Vision
Core concepts in computer vision and machine learning
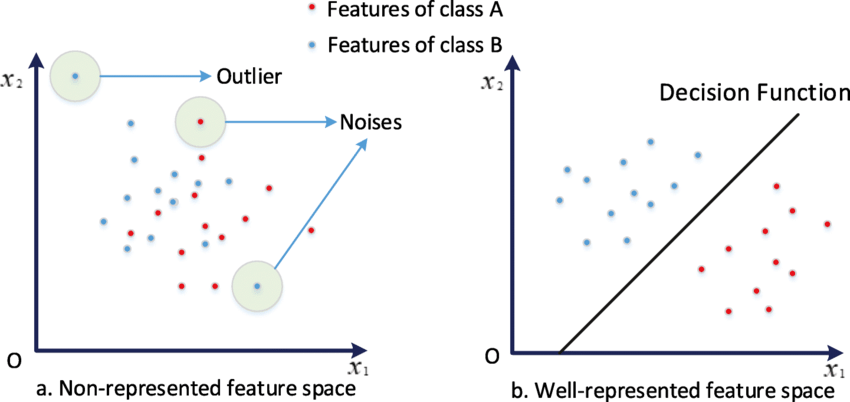
History of Computer Vision
How computer vision evolved through feature spaces
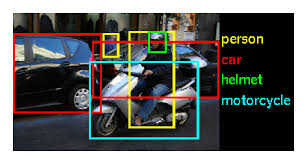
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
ImageNet's impact on modern computer vision

Region-CNNs
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
Distributed Systems
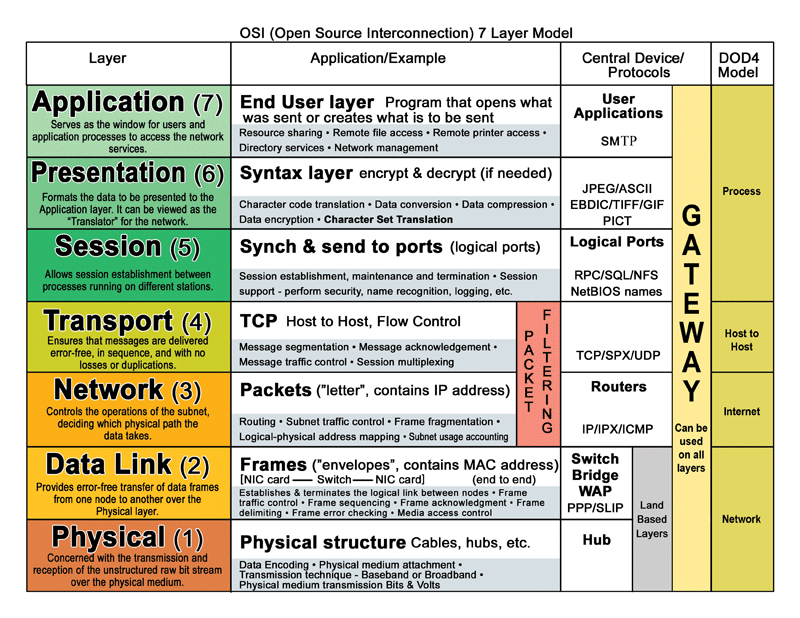
Overview of Distributed Systems
Fundamentals of distributed systems and the OSI model
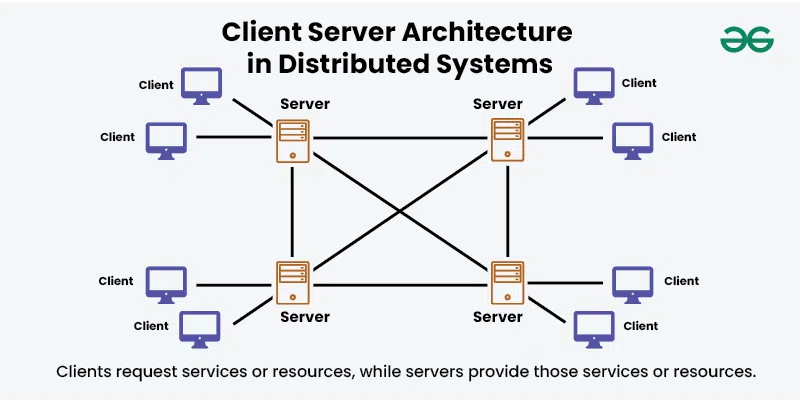
Distributed Systems Architectures
Common design patterns for distributed systems
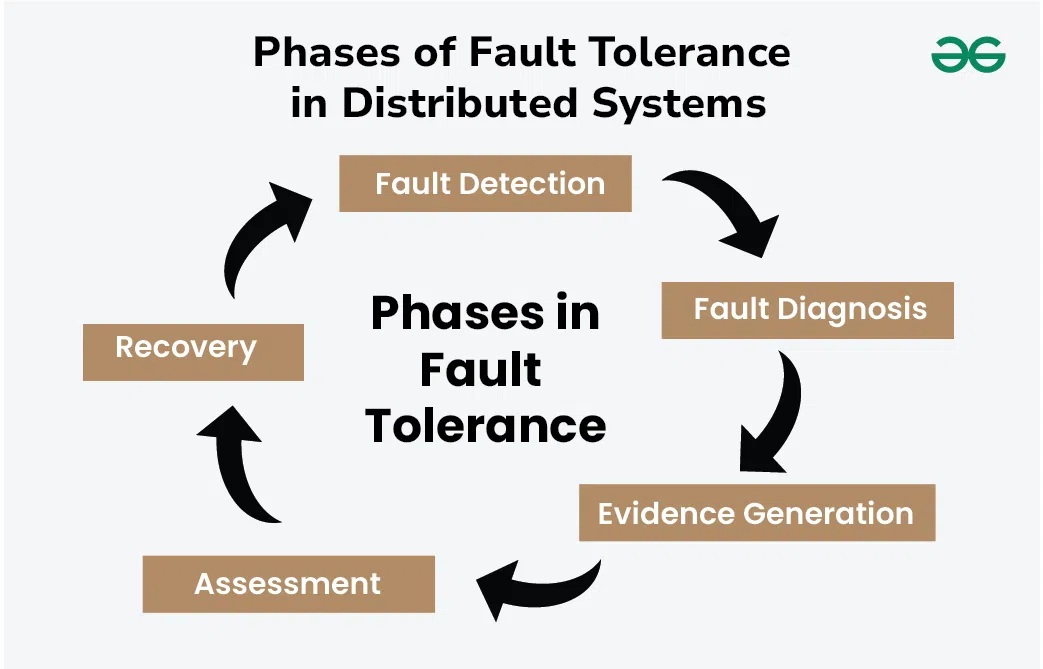
Dependability & Relevant Concepts
Reliability and fault tolerance in distributed systems
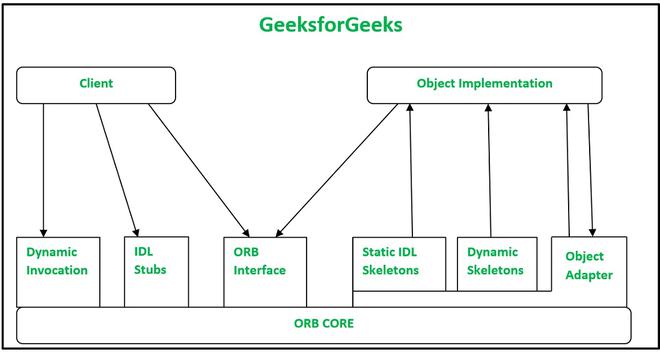
Marshalling
How data gets serialized for network communication
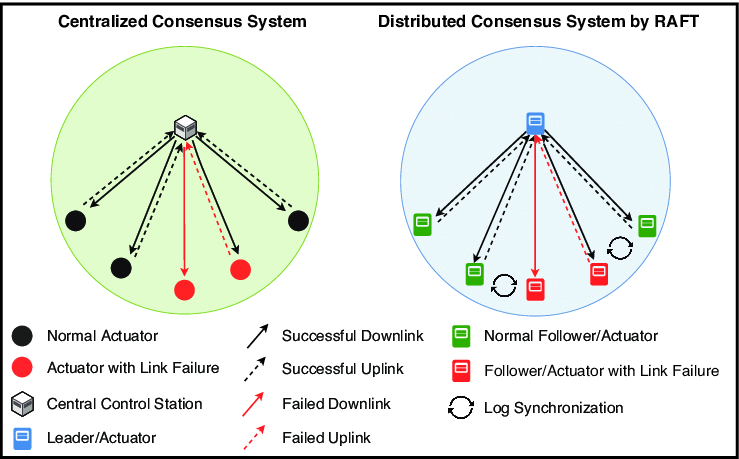
RAFT
Understanding the RAFT consensus algorithm
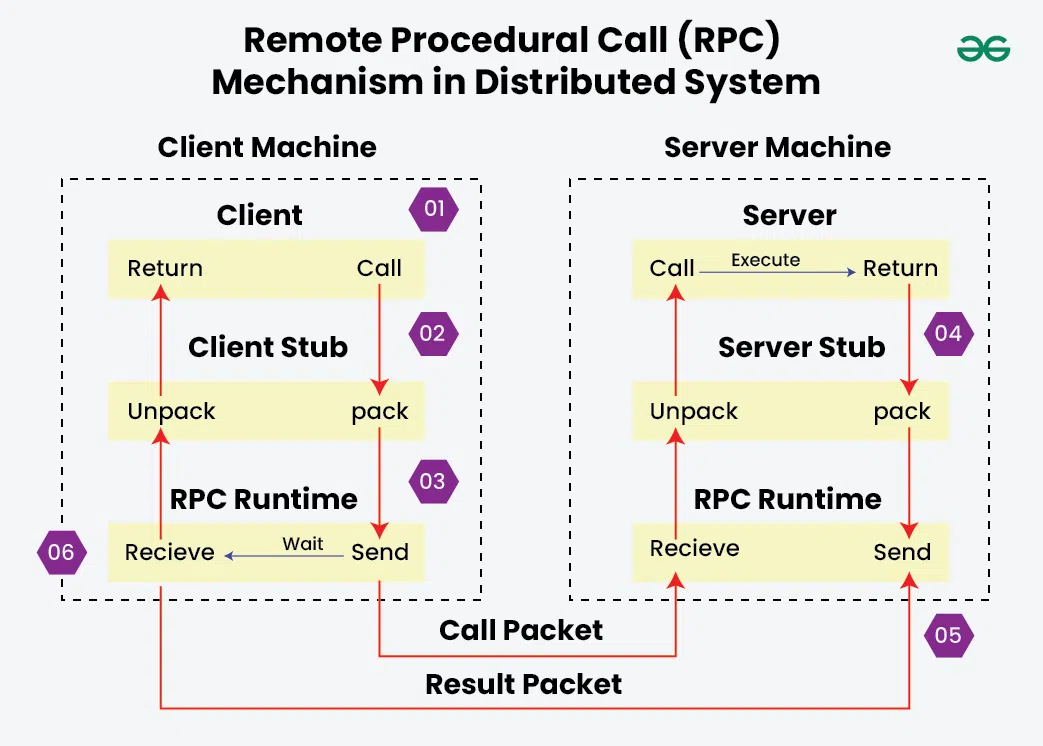
Remote Procedural Calls
How RPC enables communication between processes
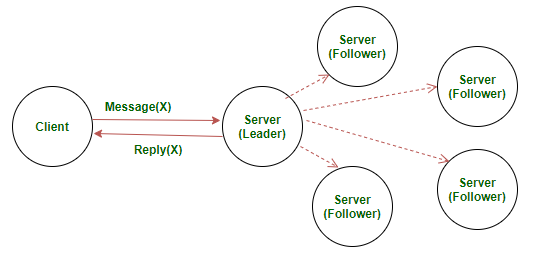
Servers
Server design and RAFT implementation
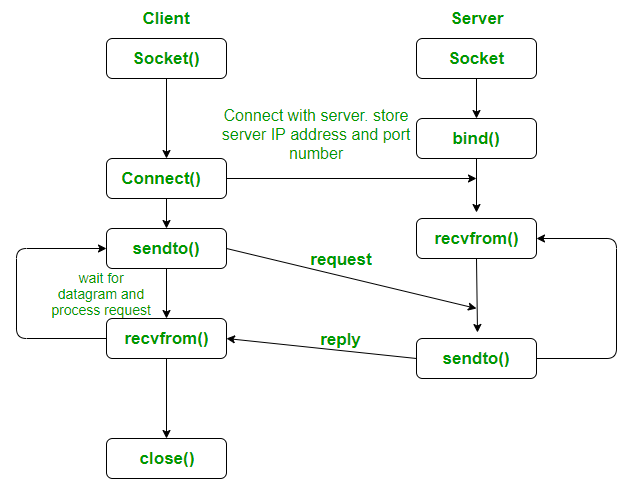
Sockets
Network programming with UDP sockets
Machine Learning (Generally Neural Networks)

Anatomy of Neural Networks
Traditional ML vs modern computer vision approaches
LeNet Architecture
The LeNet neural network
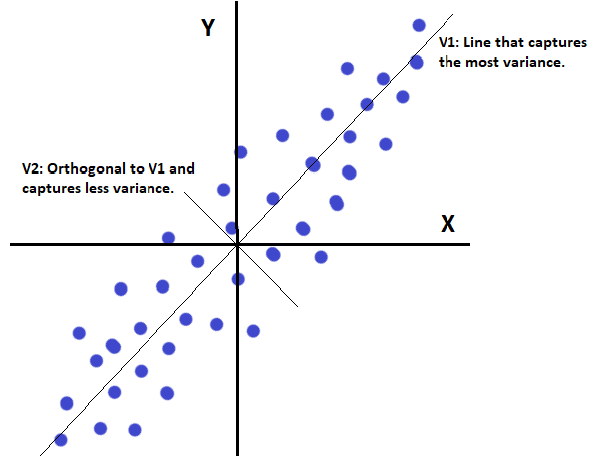
Principal Component Analysis
Explaining PCA from classical and ANN perspectives
Cryptography & Secure Digital Systems
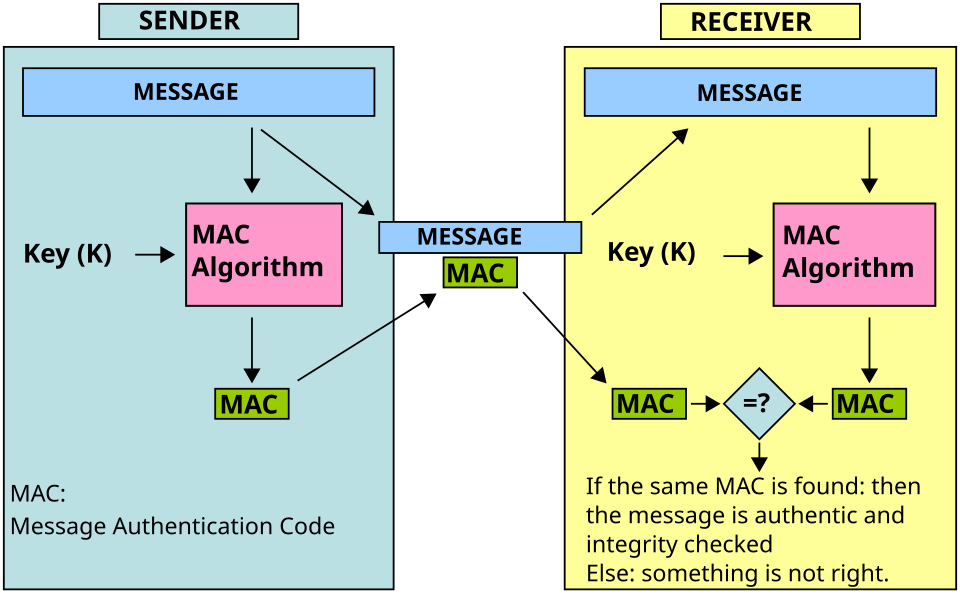
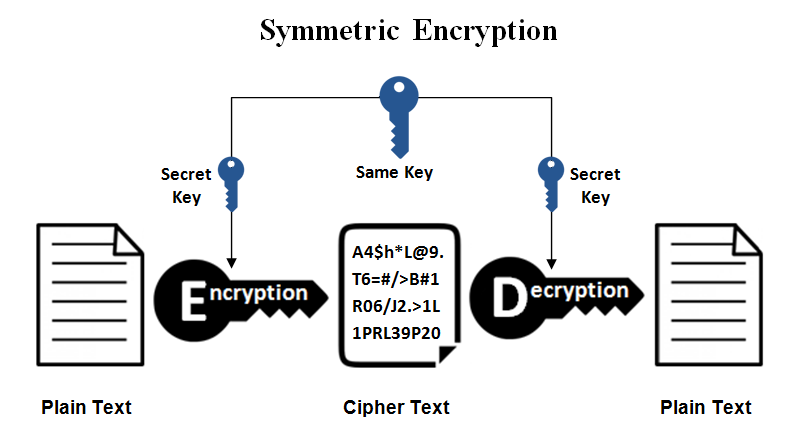
Symmetric Cryptography
covers MAC, secret key systems, and symmetric ciphers
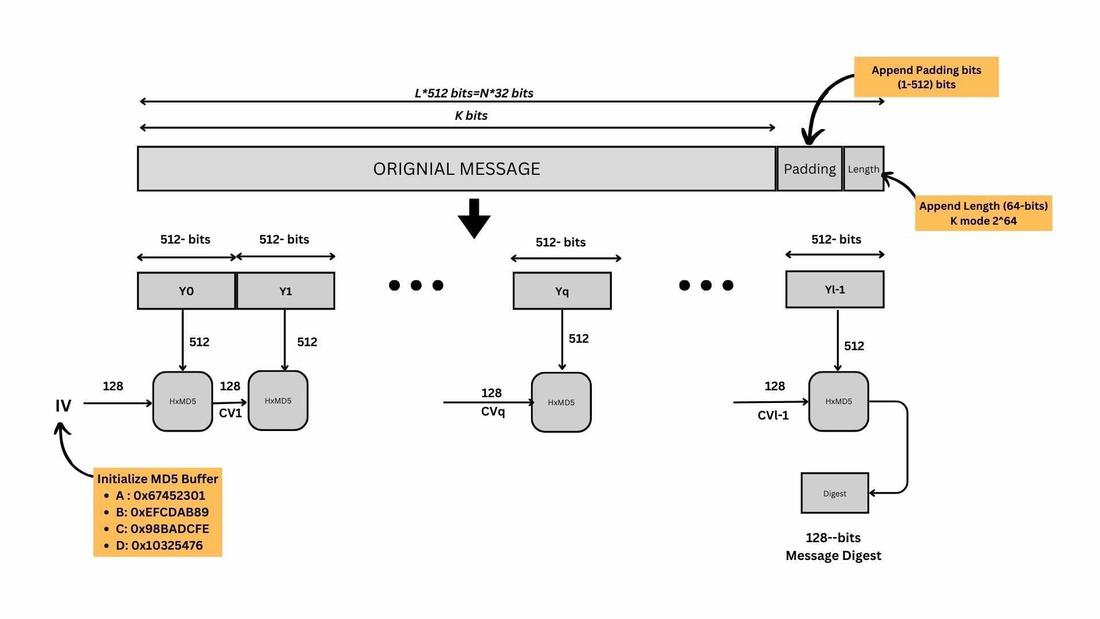
Hash Functions
Hash function uses in cryptographic schemes (no keys)
Public-Key Encryption
RSA, ECC, and ElGamal encryption schemes
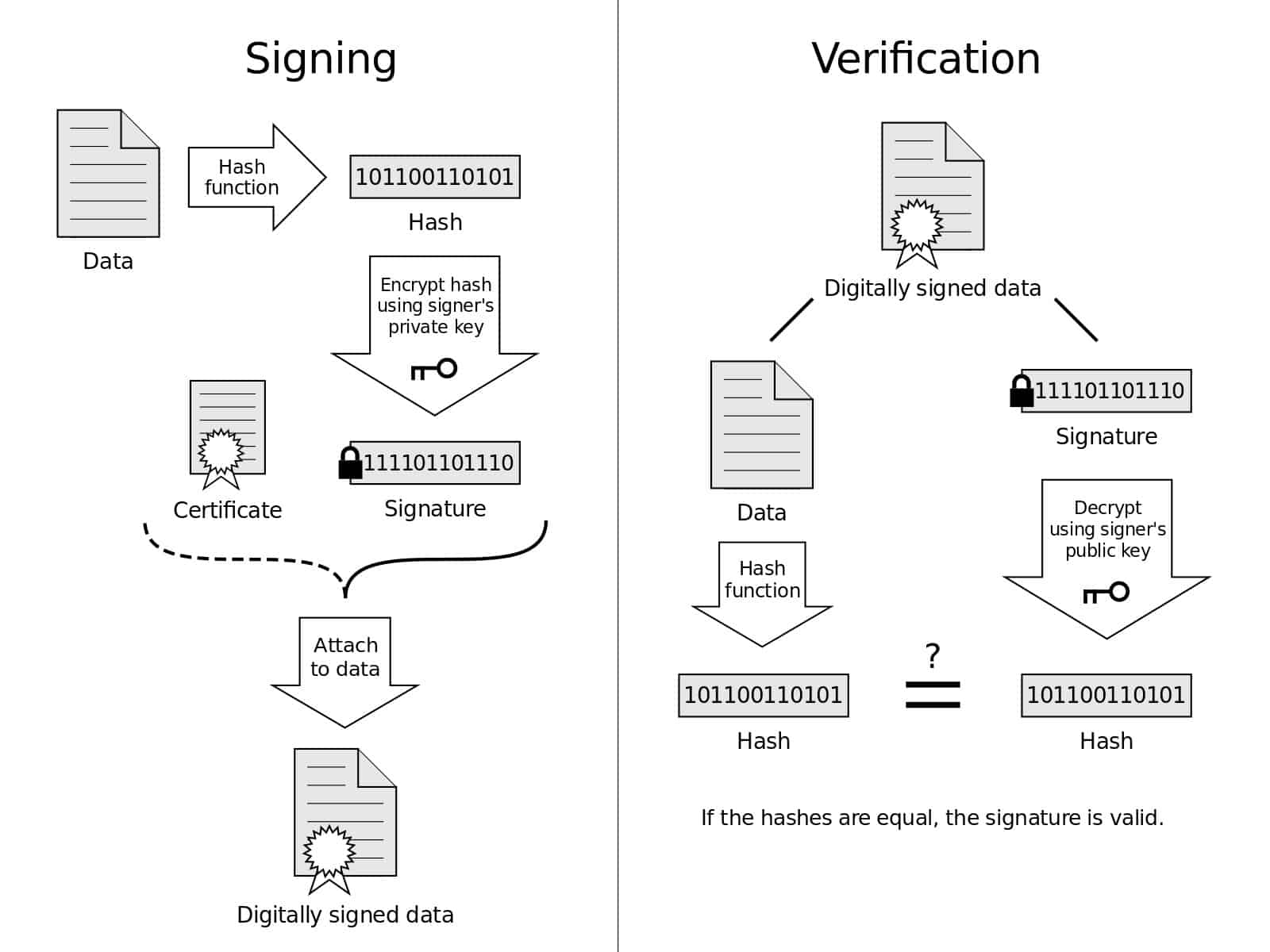
Digital Signatures & Authentication
Public-key authentication protocols, RSA signatures, and mutual authentication

Number Theory
Number theory in cypto - Euclidean algorithm, number factorization, modulo operations
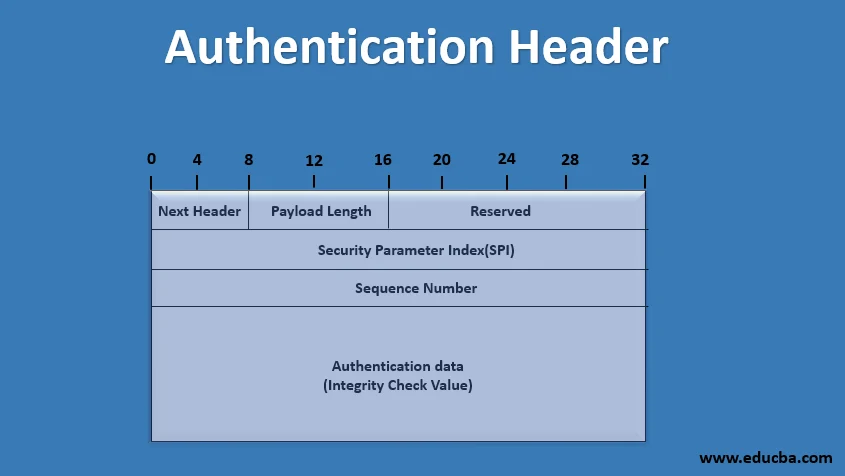
IPSec Types & Properties
Authentication Header (AH), ESP, Transport vs Tunnel modes